Restoration of Sagittal Balance in Spinal Deformity Surgery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Spine Service, Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons, New York, NY, USA.
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Spine Center, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea. hyunsj@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2408017
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2017.0404.013
Abstract
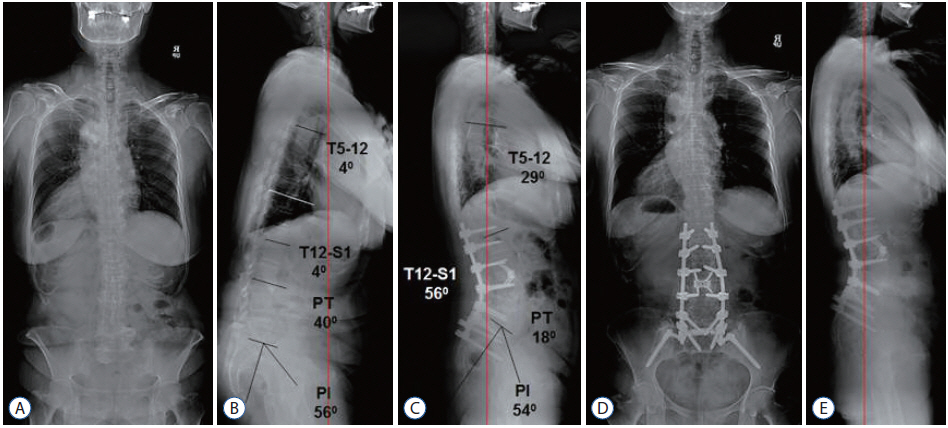
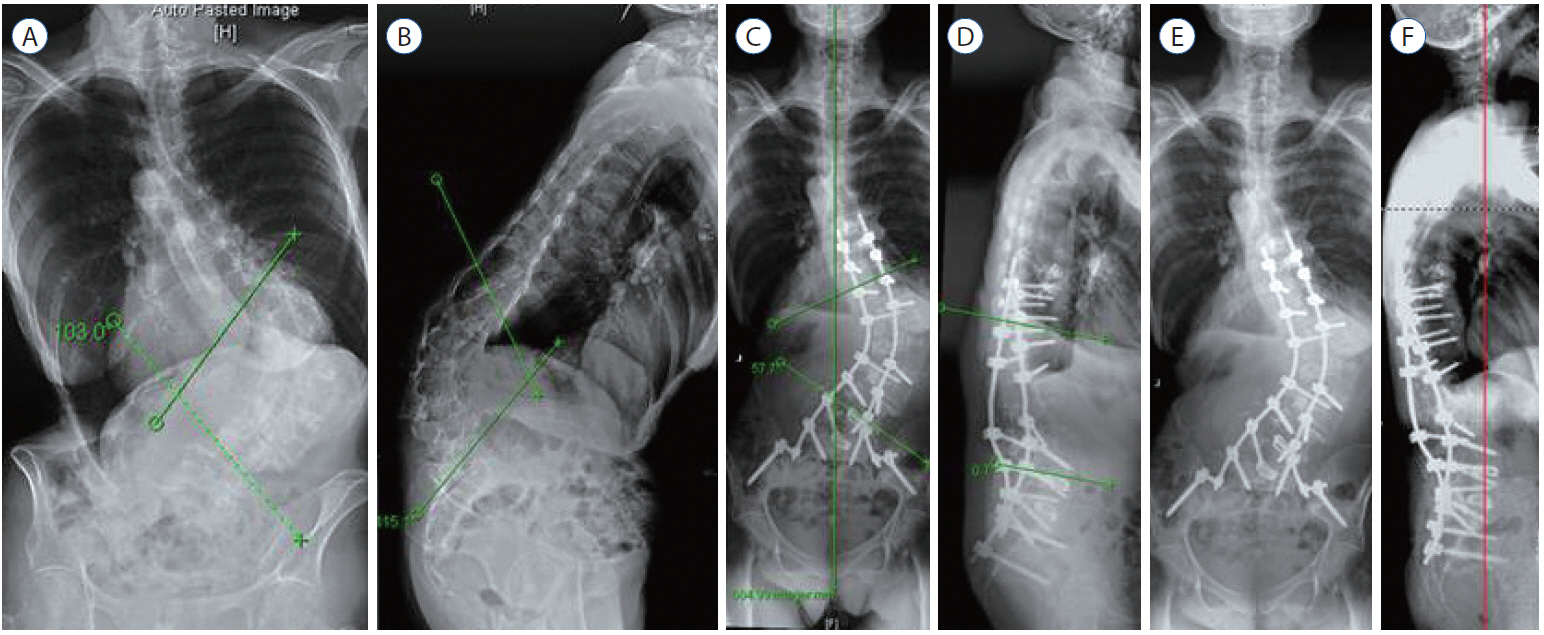
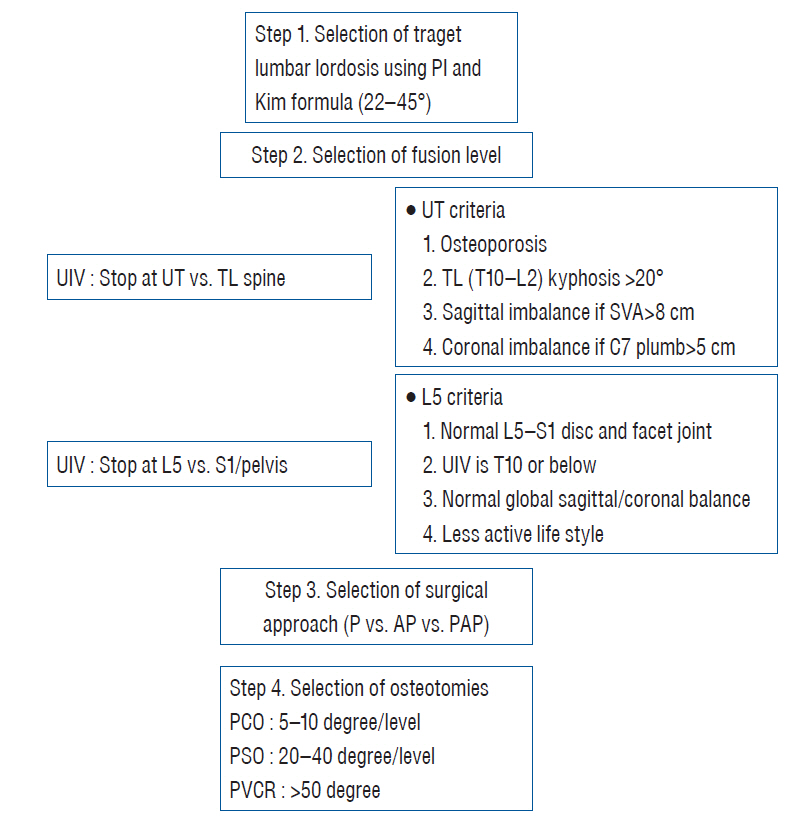
- The prevalence of patients with adult spinal deformity (ASD) has been reported as high as 68%. ASD often leads to significant pain and disability. Recent emphasis has been placed on sagittal plane balance and restoring normal sagittal alignment with regards to the three dimensional deformity of ASD. Optimal sagittal alignment has been known to increase spinal biomechanical efficiency, reduce energy expenditure by maintaining a stable posture with improved load absorption, influence better bony union, and help to decelerate adjacent segment deterioration. Increasingly positive sagittal imbalance has been shown to correlate with poor functional outcome and poor self-image along with poor psychological function. Compensatory mechanisms attempt to maintain sagittal balance through pelvic rotation, alterations in lumbar lordosis as well as knee and ankle flexion at the cost of increased energy expenditure. Restoring normal spinopelvic alignment is paramount to the treatment of complex spinal deformity with sagittal imbalance. Posterior osteotomies including posterior column osteotomies, pedicle subtraction osteotomies, and posterior vertebral column resection, as well anterior column support are well known to improve sagittal alignment. Understanding of whole spinal alignment and dynamics of spinopelvic alignment is essential to restore sagittal balance while minimizing the risk of developing sagittal decompensation after surgical intervention.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 6 articles
-
Total Deformity Angular Ratio as a Risk Factor for Complications after Posterior Vertebral Column Resection Surgery
Byoung Hun Lee, Seung-Jae Hyun, Sanghyun Han, Se-Il Jeon, Ki-Jeong Kim, Tae-Ahn Jahng, Hyun-Jib Kim
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2018;61(6):723-730. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2018.0125.Spinal Deformity Surgery : It Becomes an Essential Part of Neurosurgery
Seung-Jae Hyun, Jong-myung Jung
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2018;61(6):661-668. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2018.0150.Radiographic and Clinical Outcomes Following Pedicle Subtraction Osteotomy : Minimum 2-Year Follow-Up Data
Ho Yong Choi, Seung-Jae Hyun, Ki-Jeong Kim, Tae-Ahn Jahng, Hyun-Jib Kim
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2020;63(1):99-107. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2018.0170.Surgical Outcomes and Complications Following All Posterior Approach for Spinal Deformity Associated with Neurofibromatosis Type-1
Byoung-Joo Park, Seung-Jae Hyun, Seong-Hyun Wui, Jong-Myung Jung, Ki-Jeong Kim, Tae-Ahn Jahng
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2020;63(6):738-746. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2019.0218.Systematic Review of Reciprocal Changes after Spinal Reconstruction Surgery : Do Not Miss the Forest for the Trees
Chang-Wook Kim, Seung-Jae Hyun, Ki-Jeong Kim
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2021;64(6):843-852. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2020.0234.Publication Trends in the Pelvic Parameter Related Literature between 1992 and 2022 : A Bibliometric Review
Serdar Yüksel, Emre Özmen, Alican Barış, Esra Circi, Ozan Beytemür
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2024;67(1):50-59. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2023.0047.
Reference
-
References
1. Ames CP, Blondel B, Scheer JK, Schwab FJ, Le Huec JC, Massicotte EM, et al. Cervical radiographical alignment: comprehensive assessment techniques and potential importance in cervical myelopathy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 38(22 Suppl 1):S149–S160. 2013.2. Barrey C, Jund J, Noseda O, Roussouly P. Sagittal balance of the pelvis-spine complex and lumbar degenerative diseases. A comparative study about 85 cases. Eur Spine J. 16:1459–1467. 2007.
Article3. Bernhardt M, Bridwell KH. Segmental analysis of the sagittal plane alignment of the normal thoracic and lumbar spines and thoracolumbar junction. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 14:717–721. 1989.
Article4. Blondel B, Schwab F, Bess S, Ames C, Mummaneni PV, Hart R, et al. Posterior global malalignment after osteotomy for sagittal plane deformity: it happens and here is why. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 38:E394–E401. 2013.5. Bridwell KH. Causes of sagittal spinal imbalance and assessment of the extent of needed correction. Instr Course Lect. 55:567–575. 2006.6. Bridwell KH. Decision making regarding Smith-Petersen vs. pedicle subtraction osteotomy vs vertebral column resection for spinal deformity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 31(19 Suppl):S171–178. 2006.
Article7. Bridwell KH, Lewis SJ, Edwards C, Lenke LG, Iffrig TM, Berra A, et al. Complications and outcomes of pedicle subtraction osteotomies for fixed sagittal imbalance. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 28:2093–2101. 2003.
Article8. Burkett B, Ricart-Hoffiz PA, Schwab F, Ialenti M, Farcy JP, Lonner BS, et al. Comparative analysis of surgical approaches and osteotomies for the correction of sagittal plane spinal deformity in adults. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 38:188–194. 2013.
Article9. Cho KJ, Suk SI, Park SR, Kim JH, Jung JH. Selection of proximal fusion level for adult degenerative lumbar scoliosis. Eur Spine J. 22:394–401. 2013.
Article10. Choi HY, Hyun SJ, Kim KJ, Jahng TA, Kim HJ. Surgical and radiographic outcomes after pedicle subtraction osteotomy according to surgeon’s experience. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 24:E795–E801. 2016.
Article11. Deukmedjian AR, Le TV, Baaj AA, Dakwar E, Smith DA, Uribe JS. Anterior longitudinal ligament release using the minimally invasive lateral retroperitoneal transpsoas approach: a cadaveric feasibility study and report of 4 clinical cases. J Neurosurg Spine. 17:530–539. 2012.
Article12. Gill JB, Levin A, Burd T, Longley M. Corrective osteotomies in spine surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 90:2509–2520. 2008.
Article13. Glassman SD, Bridwell K, Dimar JR, Horton W, Berven S, Schwab F. The impact of positive sagittal balance in adult spinal deformity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 30:2024–2029. 2005.
Article14. Gomez JA, Makhni MC, Vitale MG. Recurrent spinal deformity after scoliosis surgery in children. Instr Course Lect. 63:345–351. 2014.15. Han S, Hyun SJ, Kim KJ, Jahng TA, Lee S, Rhim SC. Rod stiffness as a risk factor of proximal junctional kyphosis after adult spinal deformity surgery: comparative study between cobalt chrome multiple-rod constructs and titanium alloy two-rod constructs. Spine J. 17:962–968. 2017.
Article16. Hanson DS, Bridwell KH, Rhee JM, Lenke LG. Correlation of pelvic incidence with low- and high-grade isthmic spondylolisthesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 27:2026–2029. 2002.
Article17. Hardacker JW, Shuford RF, Capicotto PN, Pryor PW. Radiographic standing cervical segmental alignment in adult volunteers without neck symptoms. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 22:1472–1480. discussion 1480. 1997.
Article18. Harimaya K, Lenke LG, Mishiro T, Bridwell KH, Koester LA, Sides BA. Increasing lumbar lordosis of adult spinal deformity patients via intraoperative prone positioning. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 34:2406–2412. 2009.
Article19. Harroud A, Labelle H, Joncas J, Mac-Thiong JM. Global sagittal alignment and health-related quality of life in lumbosacral spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J. 22:849–856. 2013.
Article20. Hwang JH, Modi HN, Suh SW, Hong JY, Park YH, Park JH, et al. Reliability of lumbar lordosis measurement in patients with spondylolisthesis: a case-control study comparing the Cobb, centroid, and posterior tangent methods. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 35:1691–1700. 2010.
Article21. Hyun SJ, Kim KJ, Jahng TA, Kim HJ. Relationship between T1 slope and cervical alignment following multilevel posterior cervical fusion surgery: impact of T1 slope minus cervical lordosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 41:E396–E402. 2016.22. Hyun SJ, Kim YJ, Rhim SC. Patients with proximal junctional kyphosis after stopping at thoracolumbar junction have lower muscularity, fatty degeneration at the thoracolumbar area. Spine J. 16:1095–1101. 2016.
Article23. Hyun SJ, Lee BH, Park JH, Kim KJ, Jahng TA, Kim HJ. Proximal junctional kyphosis and proximal junctional failure following adult spinal deformity surgery. Korean J Spine. 14:126–132. 2017.
Article24. Hyun SJ, Lenke LG, Kim YC, Koester LA, Blanke KM. Comparison of standard 2-rod constructs to multiple-rod constructs for fixation across 3-column spinal osteotomies. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 39:1899–1904. 2014.
Article25. Hyun SJ, Rhim SC. Clinical outcomes and complications after pedicle subtraction osteotomy for fixed sagittal imbalance patients : a long-term follow-up data. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 47:95–101. 2010.
Article26. Iyer S, Lenke LG, Nemani VM, Fu M, Shifflett GD, Albert TJ, et al. Variations in occipitocervical and cervicothoracic alignment parameters based on age: a prospective study of asymptomatic volunteers using full-body radiographs. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 41:1837–1844. 2016.
Article27. Kim HJ, Boachie-Adjei O, Shaffrey CI, Schwab F, Lafage V, Bess S, et al. Upper thoracic versus lower thoracic upper instrumented vertebrae endpoints have similar outcomes and complications in adult scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 39:E795–E799. 2014.
Article28. Kim Y, Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, Boachie-Adjei O, Hamill CL, Cho S, et al. Sagittal decompensation following pedicle subtraction osteotomy for adult patients with sagittal imbalance: incidence, risk factors, and SRS outcomes score. Spine. 10(Suppl 3):130. 2009.29. Kim YJ, Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, Boachie-Adjei O, Hamill C, Kim YB. Sagittal spinopelvic alignment change after lumbar pedicle subtraction osteotomy: a multicenter analysis of 113 patients with a minimum 2 years follow-up. In : SRS 2008: Proceedings of the 43rd annual meeting of scoliosis research society; Salt Lake City. 2008.30. Kim Y, Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, Kim YB, Kim P. Comparative radiographic analysis of the sagittal spinopelvic alignment between 100 asymptomatic adults and 100 patients with sagittal imbalance: the best angular parameters to sagittal vertical axis. Spine. 10(Suppl 3):178–180. 2009.31. Kim YJ, Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, Cheh G, Baldus C. Results of lumbar pedicle subtraction osteotomies for fixed sagittal imbalance: a minimum 5-year follow-up study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 32:2189–2197. 2007.
Article32. Kim YJ, Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, Rhim S, Cheh G. An analysis of sagittal spinal alignment following long adult lumbar instrumentation and fusion to L5 or S1: can we predict ideal lumbar lordosis? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 31:2343–2352. 2006.
Article33. Kim YJ, Hyun SJ, Cheh G, Cho SK, Rhim SC. Decision making algorithm for adult spinal deformity surgery. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 59:327–333. 2016.
Article34. Knott PT, Mardjetko SM, Techy F. The use of the T1 sagittal angle in predicting overall sagittal balance of the spine. Spine J. 10:994–998. 2010.
Article35. Lafage V, Ames C, Schwab F, Klineberg E, Akbarnia B, Smith J, et al. Changes in thoracic kyphosis negatively impact sagittal alignment after lumbar pedicle subtraction osteotomy: a comprehensive radiographic analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 37:E180–E187. 2012.36. Lee CS, Chung SS, Kang KC, Park SJ, Shin SK. Normal patterns of sagittal alignment of the spine in young adults radiological analysis in a Korean population. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 36:E1648–E1654. 2011.
Article37. Lee SH, Kim KT, Seo EM, Suk KS, Kwack YH, Son ES. The influence of thoracic inlet alignment on the craniocervical sagittal balance in asymptomatic adults. J Spinal Disord Tech. 25:E41–E47. 2012.
Article38. Lee SH, Son ES, Seo EM, Suk KS, Kim KT. Factors determining cervical spine sagittal balance in asymptomatic adults: correlation with spinopelvic balance and thoracic inlet alignment. Spine J. 15:705–712. 2015.
Article39. Legaye J, Duval-Beaupère G, Hecquet J, Marty C. Pelvic incidence: a fundamental pelvic parameter for three-dimensional regulation of spinal sagittal curves. Eur Spine J. 7:99–103. 1998.
Article40. Mac-Thiong JM, Pinel-Giroux FM, de Guise JA, Labelle H. Comparison between constrained and non-constrained Cobb techniques for the assessment of thoracic kyphosis and lumbar lordosis. Eur Spine J. 16:1325–1331. 2007.
Article41. Nunez-Pereira S, Hitzl W, Bullmann V, Meier O, Koller H. Sagittal balance of the cervical spine: an analysis of occipitocervical and spinopelvic interdependence, with C-7 slope as a marker of cervical and spinopelvic alignment. J Neurosurg Spine. 23:16–23. 2015.
Article42. Park JH, Hyun SJ, Kim KJ, Jahng TA. Comparative study between pedicle subtraction osteotomy (PSO) and closing-opening wedge osteotomy (fish-mouth PSO) for sagittal plane deformity correction. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 24:E899–E905. 2016.
Article43. Potter BK, Lenke LG, Kuklo TR. Prevention and management of iatrogenic flatback deformity. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 86-A:1793–1808. 2004.
Article44. Qiao J, Zhu F, Xu L, Liu Z, Zhu Z, Qian B, et al. T1 pelvic angle: a new predictor for postoperative sagittal balance and clinical outcomes in adult scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 39:2103–2107. 2014.45. Rajnics P, Templier A, Skalli W, Lavaste F, Illés T. The association of sagittal spinal and pelvic parameters in asymptomatic persons and patients with isthmic spondylolisthesis. J Spinal Disord Tech. 15:24–30. 2002.
Article46. Rose PS, Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, Cronen GA, Mulconrey DS, Buchowski JM, et al. Role of pelvic incidence, thoracic kyphosis, and patient factors on sagittal plane correction following pedicle subtraction osteotomy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 34:785–791. 2009.
Article47. Roussouly P, Nnadi C. Sagittal plane deformity: an overview of interpretation and management. Eur Spine J. 19:1824–1836. 2010.
Article48. Ryan DJ, Protopsaltis TS, Ames CP, Hostin R, Klineberg E, Mundis GM, et al. T1 pelvic angle (TPA) effectively evaluates sagittal deformity and assesses radiographical surgical outcomes longitudinally. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 39:1203–1210. 2014.
Article49. Saville PA, Kadam AB, Smith HE, Arlet V. Anterior hyperlordotic cages: early experience and radiographic results. J Neurosurg Spine. 25:713–719. 2016.
Article50. Schwab F, Dubey A, Gamez L, El Fegoun AB, Hwang K, Pagala M, et al. Adult scoliosis: prevalence, SF-36, and nutritional parameters in an elderly volunteer population. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 30:1082–1085. 2005.
Article51. Schwab F, Lafage V, Patel A, Farcy JP. Sagittal plane considerations and the pelvis in the adult patient. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 34:1828–1833. 2009.
Article52. Schwab F, Patel A, Ungar B, Farcy JP, Lafage V. Adult spinal deformity-postoperative standing imbalance: how much can you tolerate? An overview of key parameters in assessing alignment and planning corrective surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 35:2224–2231. 2010.53. Suk SI, Kim JH, Kim WJ, Lee SM, Chung ER, Nah KH. Posterior vertebral column resection for severe spinal deformities. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 27:2374–2382. 2002.
Article54. Thomasen E. Vertebral osteotomy for correction of kyphosis in ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. (194):142–152. 1985.
Article55. Vialle R, Levassor N, Rillardon L, Templier A, Skalli W, Guigui P. Radiographic analysis of the sagittal alignment and balance of the spine in asymptomatic subjects. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 87:260–267. 2005.
Article56. Wang Y, Zhang Y, Zhang X, Wang Z, Mao K, Chen C, et al. Posterior-only multilevel modified vertebral column resection for extremely severe Pott’s kyphotic deformity. Eur Spine J. 18:1436–1441. 2009.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- From the Spinopelvic Parameters to Global Alignment and Proportion Scores in Adult Spinal Deformity
- Spino-Pelvic Parameters in Adult Spinal Deformities
- Radiologic Findings of Pelvic Parameters Related to Sagittal Balance
- The Important Role of Paraspinal Muscle Quality for Maintaining Sagittal Balance While Walking: Commentary on “Correlation of Paraspinal Muscle Mass With Decompensation of Sagittal Adult Spinal Deformity After Setting of Fatigue Post 10-Minute Walk”
- Cervical Sagittal Alignment: Literature Review and Future Directions