J Vet Sci.
2017 Dec;18(4):449-456. 10.4142/jvs.2017.18.4.449.
Mechanisms of quinolone resistance in Escherichia coli isolated from companion animals, pet-owners, and non-pet-owners
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Veterinary Microbiology, College of Veterinary Medicine, BK21 Plus Program for Veterinary Science and Research Institute for Veterinary Science, Seoul National University, Seoul 08826, Korea. magic007@snu.ac.kr
- 2Animal and Plant Quarantine Agency, Gimcheon 39660, Korea.
- 3Department of Animal Science and Technology, College of Biotechnology and Natural Resource, Chung-Ang University, Anseong 06974, Korea.
- KMID: 2398503
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2017.18.4.449
Abstract
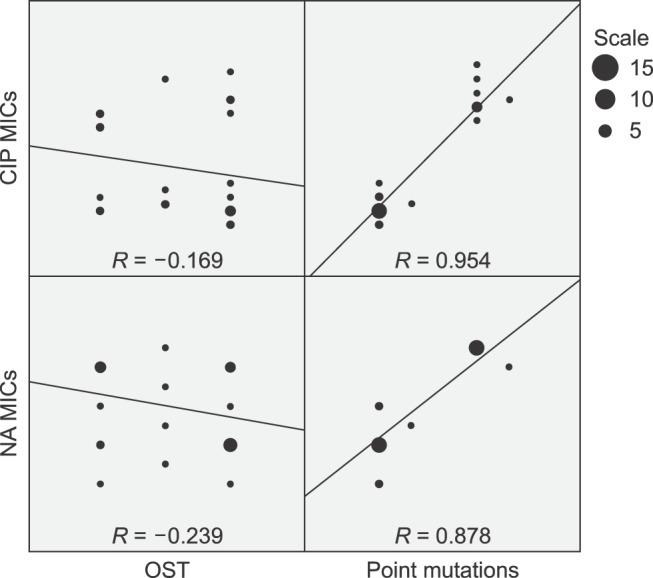
- The present study investigated the prevalence and mechanisms of fluoroquinolone (FQ)/quinolone (Q) resistance in Escherichia (E.) coli isolates from companion animals, pet-owners, and non-pet-owners. A total of 63 E. coli isolates were collected from 104 anal swab samples, and 27 nalidixic acid (NA)-resistant isolates were identified. Of those, 10 showed ciprofloxacin (CIP) resistance. A plasmid-mediated Q resistance gene was detected in one isolate. Increased efflux pump activity, as measured by organic solvent tolerance assay, was detected in 18 NA-resistant isolates (66.7%), but was not correlated with an increase in minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC). Target gene mutations in Q resistance-determining regions (QRDRs) were the main cause of (FQ)Q resistance in E. coli. Point mutations in QRDRs were detected in all NA-resistant isolates, and the number of mutations was strongly correlated with increased MIC (R = 0.878 for NA and 0.954 for CIP). All CIP-resistant isolates (n = 10) had double mutations in the gyrA gene, with additional mutations in parC and parE. Interestingly, (FQ)Q resistance mechanisms in isolates from companion animals were the same as those in humans. Therefore, prudent use of (FQ)Q in veterinary medicine is warranted to prevent the dissemination of (FQ)Q-resistant bacteria from animals to humans.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Aathithan S, French GL. Organic solvent tolerance and fluoroquinolone resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae clinical isolates. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2009; 64:870–871. PMID: 19679596.2. Bai H, Du Jf, Hu M, Qi J, Cai YN, Niu WW, Liu YQ. Analysis of mechanisms of resistance and tolerance of Escherichia coli to enrofloxacin. Ann Microbiol. 2012; 62:293–298.3. Bennett PM. Plasmid encoded antibiotic resistance: acquisition and transfer of antibiotic resistance genes in bacteria. Br J Pharmacol. 2008; 153(Suppl 1):S347–S357. PMID: 18193080.
Article4. Breines DM, Ouabdesselam S, NG EY, Tankovic J, Shah S, Soussy CJ, Hooper DC. Quinolone resistance locus nfxD of Escherichia coli is a mutant allele of the parE gene encoding a subunit of topoisomerase IV. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1997; 41:175–179. PMID: 8980775.5. Cattoir V, Poirel L, Rotimi V, Soussy CJ, Nordmann P. Multiplex PCR for detection of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance qnr genes in ESBL-producing enterobacterial isolates. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2007; 60:394–397. PMID: 17561500.
Article6. Chung YS, Song JW, Kim DH, Shin S, Park YK, Yang SJ, Lim SK, Park KT, Park YH. Isolation and characterization of antimicrobial-resistant E. coli from national horse racetracks and private horse-riding courses in Korea. J Vet Sci. 2016; 17:199–206. PMID: 26645344.7. CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing; Nineteenth Informational Supplement. CLSI document M100-S19. Wayne: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2009.8. Corcoran D, Quinn T, Cotter L, Fanning S. Relative contribution of target gene mutation and efflux to varying quinolone resistance in Irish Campylobacter isolates. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2005; 253:39–46. PMID: 16213669.9. Doyle MP, Ruoff KL, Pierson M, Weinberg W, Soule B, Michaels BS. Reducing transmission of infectious agents in the home-part I: sources of infection. Dairy Food Environ Sanit. 2000; 20:330–337.10. Fendukly F, Karlsson I, Hanson HS, Kronvall G, Dornbusch K. Patterns of mutations in target genes in septicemia isolates of Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae with resistance or reduced susceptibility to ciprofloxacin. APMIS. 2003; 111:857–866. PMID: 14510643.11. Frank T, Mbecko JR, Misatou P, Monchy D. Emergence of quinolone resistance among extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae in the Central African Republic: genetic characterization. BMC Res Notes. 2011; 4:309. PMID: 21867486.
Article12. Gandolfi-Decristophoris P, De Benedetti A, Petignat C, Attinger M, Guillaume J, Fiebig L, Hattendorf J, Cernela N, Regula G, Petrini O, Zinsstag J, Schelling E. Evaluation of pet contact as a risk factor for carriage of multidrug-resistant staphylococci in nursing home residents. Am J Infect Control. 2012; 40:128–133. PMID: 21824684.13. Guillard T, de Jong A, Limelette A, Lebreil AL, Madoux J, de Champs C. The ComPath Study Group. Characterization of quinolone resistance mechanisms in Enterobacteriaceae recovered from diseased companion animals in Europe. Vet Microbiol. 2016; 194:23–29. PMID: 26701806.14. Gustavsson L, Westin J, Andersson LM, Lindh M. Rectal swabs can be used for diagnosis of viral gastroenteritis with a multiple real-time PCR assay. J Clin Virol. 2011; 51:279–282. PMID: 21683649.
Article15. Heisig P, Tschorny R. Characterization of fluoroquinolone-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli selected in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1994; 38:1284–1291. PMID: 8092826.16. Hopkins KL, Davies RH, Threlfall EJ. Mechanisms of quinolone resistance in Escherichia coli and Salmonella: recent developments. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2005; 25:358–373. PMID: 15848289.17. Jacoby GA. Mechanisms of resistance to quinolones. Clin Infect Dis. 2005; 41(Suppl 2):S120–S126. PMID: 15942878.
Article18. Jiang Y, Zhou Z, Qian Y, Wei Z, Yu Y, Hu S, Li L. Plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance determinants qnr and aac(6′)-Ib-cr in extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae in China. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2008; 61:1003–1006. PMID: 18299311.19. Karczmarczyk M, Martins M, Quinn T, Leonard N, Fanning S. Mechanisms of fluoroquinolone resistance in Escherichia coli isolates from food-producing animals. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011; 77:7113–7120. PMID: 21856834.20. Khodursky AB, Zechiedrich EL, Cozzarelli NR. Topoisomerase IV is a target of quinolones in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995; 92:11801–11805. PMID: 8524852.21. Kos VN, Desjardins CA, Griggs A, Cerqueira G, Van Tonder A, Holden MT, Godfrey P, Palmer KL, Bodi K, Mongodin EF. Comparative genomics of vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains and their positions within the clade most commonly associated with methicillin-resistant S. aureus hospital-acquired infection in the United States. MBio. 2012; 3:e00112-12. PMID: 22617140.
Article22. Liebana E, Batchelor M, Hopkins K, Clifton-Hadley F, Teale C, Foster A, Barker L, Threlfall E, Davies R. Longitudinal farm study of extended-spectrum β-lactamase-mediated resistance. J Clin Microbiol. 2006; 44:1630–1634. PMID: 16672386.
Article23. Ma J, Zeng Z, Chen Z, Xu X, Wang X, Deng Y, Lü D, Huang L, Zhang Y, Liu J. High prevalence of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance determinants qnr, aac(6′)-Ib-cr, and qepA among ceftiofur-resistant Enterobacteriaceae isolates from companion and food-producing animals. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009; 53:519–524. PMID: 18936192.24. Morgan-Linnell SK, Boyd LB, Steffen D, Zechiedrich L. Mechanisms accounting for fluoroquinolone resistance in Escherichia coli clinical isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009; 53:235–241. PMID: 18838592.25. Nam YS, Cho SY, Yang HY, Park KS, Jang JH, Kim YT, Jeong JW, Suh JT, Lee HJ. Investigation of mutation distribution in DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV genes in ciprofloxacin-non-susceptible Enterobacteriaceae isolated from blood cultures in a tertiary care university hospital in South Korea, 2005–2010. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2013; 41:126–129. PMID: 23265914.26. Park CH, Robicsek A, Jacoby GA, Sahm D, Hooper DC. Prevalence in the United States of aac(6′)-Ib-cr encoding a ciprofloxacin-modifying enzyme. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006; 50:3953–3955. PMID: 16954321.27. Redgrave LS, Sutton SB, Webber MA, Piddock LJ. Fluoroquinolone resistance: mechanisms, impact on bacteria, and role in evolutionary success. Trends Microbiol. 2014; 22:438–445. PMID: 24842194.
Article28. Sato T, Yokota Si, Okubo T, Ishihara K, Ueno H, Muramatsu Y, Fujii N, Tamura Y. Contribution of the AcrAB-TolC efflux pump to high-level fluoroquinolone resistance in Escherichia coli isolated from dogs and humans. J Vet Med Sci. 2013; 75:407–414. PMID: 23149545.29. Schneiders T, Amyes S, Levy S. Role of AcrR and RamA in fluoroquinolone resistance in clinical Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates from Singapore. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003; 47:2831–2837. PMID: 12936981.30. So JH, Kim J, Bae IK, Jeong SH, Kim SH, Lim SK, Park YH, Lee K. Dissemination of multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli in Korean veterinary hospitals. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2012; 73:195–199. PMID: 22516765.31. Strand L, Jenkins A, Henriksen IH, Allum AG, Grude N, Kristiansen BE. High levels of multiresistance in quinolone resistant urinary tract isolates of Escherichia coli from Norway; a non clonal phenomen? BMC Res Notes. 2014; 7:376. PMID: 24941949.
Article32. Vila J, Ruiz J, Goñi P, De Anta M. Detection of mutations in parC in quinolone-resistant clinical isolates of Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1996; 40:491–493. PMID: 8834907.33. von Salviati C, Laube H, Guerra B, Roesler U, Friese A. Emission of ESBL/AmpC-producing Escherichia coli from pig fattening farms to surrounding areas. Vet Microbiol. 2015; 175:77–84. PMID: 25465658.34. Wang H, Dzink-Fox JL, Chen M, Levy SB. Genetic characterization of highly fluoroquinolone-resistant clinical Escherichia coli strains from China: role of acrR mutations. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2001; 45:1515–1521. PMID: 11302820.35. White DG, Goldman JD, Demple B, Levy SB. Role of the acrAB locus in organic solvent tolerance mediated by expression of marA, soxS, or robA in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1997; 179:6122–6126. PMID: 9324261.36. Yamane K, Wachino Ji, Suzuki S, Arakawa Y. Plasmid-mediated qepA gene among Escherichia coli clinical isolates from Japan. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008; 52:1564–1566. PMID: 18285488.37. Yang H, Duan G, Zhu J, Zhang W, Xi Y, Fan Q. Prevalence and characterisation of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance and mutations in the gyrase and topoisomerase IV genes among Shigella isolates from Henan, China, between 2001 and 2008. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2013; 42:173–177. PMID: 23796894.38. Yoshida H, Bogaki M, Nakamura M, Nakamura S. Quinolone resistance-determining region in the DNA gyrase gyrA gene of Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990; 34:1271–1272. PMID: 2168148.39. Yue L, Jiang HX, Liao XP, Liu JH, Li SJ, Chen XY, Chen CX, Lü DH, Liu YH. Prevalence of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance qnr genes in poultry and swine clinical isolates of Escherichia coli. Vet Microbiol. 2008; 132:414–420. PMID: 18573620.40. Zurfluh K, Abgottspon H, Hächler H, Nüesch-Inderbinen M, Stephan R. Quinolone resistance mechanisms among extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL) producing Escherichia coli isolated from rivers and lakes in Switzerland. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e95864. PMID: 24755830.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Dog and Cat Allergies and Allergen Avoidance Measures in Korean Adult Pet Owners Who Participated in a Pet Exhibition
- Parasitic Zoonosis Transmitted by Pet Animals
- Whole genome sequencing analysis of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli from human and companion animals in Korea
- Quinolone susceptibility and genetic characterization of Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica isolated from pet turtles
- Antimicrobial resistance of Escherichia coli isolated from healthy animals during 2010-2012