Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2017 Mar;10(1):77-84. https://doi.org/10.21053/ceo.2016.00045.
Effect of High Glucose on MUC5B Expression in Human Airway Epithelial Cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Gyeongsan, Korea. ydkim@med.yu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Physiology, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Gyeongsan, Korea.
- 3Regional Center for Respiratory Diseases, Yeungnam University Medical Center, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 2376412
- DOI: http://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.21053/ceo.2016.00045
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
Excessive production of mucus results in plugging of the airway tract, which can increase morbidity and mortality in affected patients. In patients with diabetes, inflammatory airway disease appears with more frequent relapse and longer duration of symptoms. However, the effects of high glucose (HG) on the secretion of mucin in inflammatory respiratory diseases are not clear. Therefore, this study was conducted in order to investigate the effect and the brief signaling pathway of HG on MUC5B expression in human airway epithelial cells.
METHODS
The effect and signaling pathway of HG on MUC5B expression were investigated using reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), real-time PCR, enzyme immunoassay, and immunoblot analysis with specific inhibitors and small interfering RNA.
RESULTS
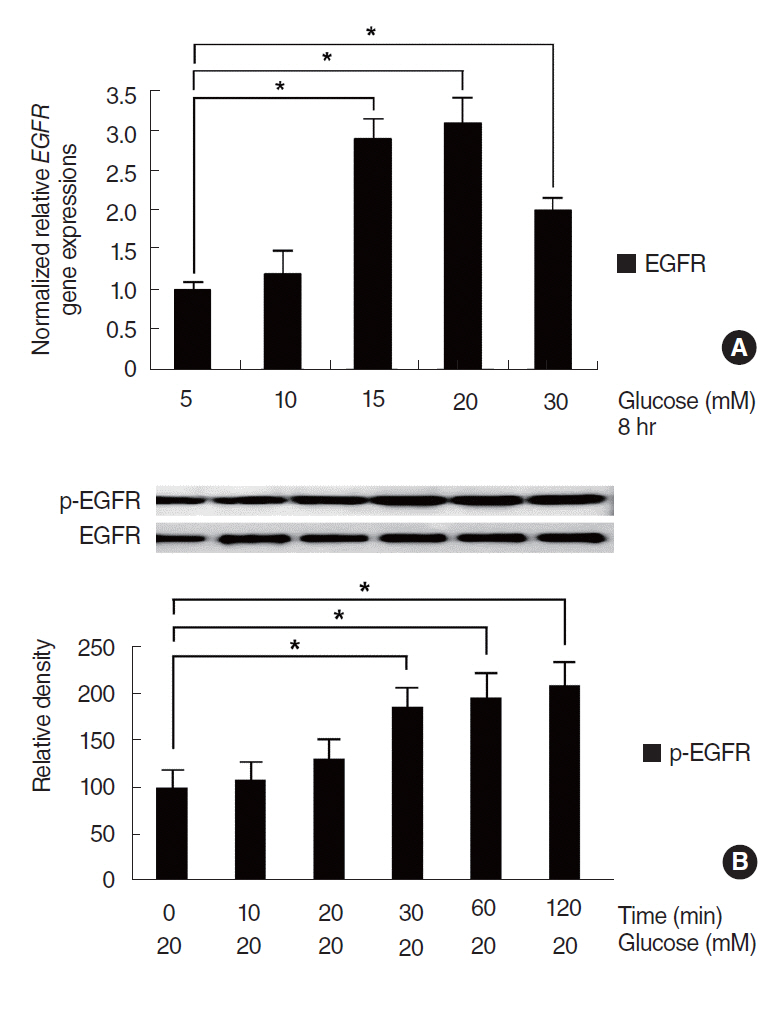
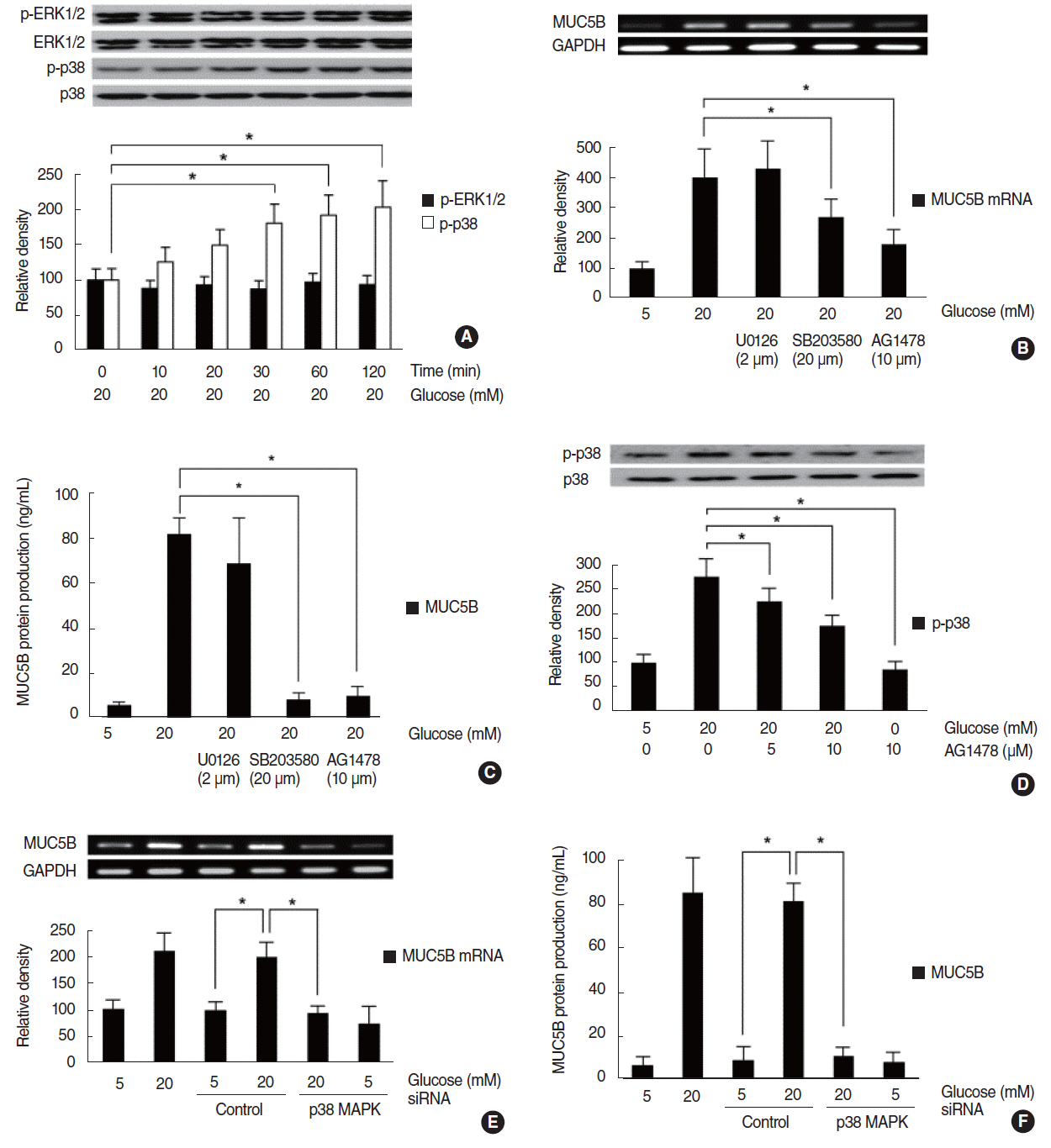
HG increased MUC5B expression and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) expression, and activated the phosphorylation of EGFR and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK). Pretreatment with EGFR inhibitor significantly attenuated the HG-induced phosphorylation of p38 MAPK, and pretreatments with p38 inhibitor or EGFR inhibitor significantly attenuated HG-induced MUC5B expression. In addition, knockdown of p38 MAPK by p38 MAPK siRNA significantly blocked HG-induced MUC5B expression.
CONCLUSION
These findings suggest that HG induces MUC5B expression via the sequential activations of the EGFR/p38 MAPK signaling pathway in human airway epithelial cells.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Epithelial Cells*
Glucose*
Humans*
Immunoenzyme Techniques
Mortality
Mucins
Mucus
p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases
Phosphorylation
Protein Kinases
Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
Receptor, Epidermal Growth Factor
Recurrence
RNA, Small Interfering
Glucose
Mucins
Protein Kinases
RNA, Small Interfering
Receptor, Epidermal Growth Factor
p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases
Figure
Reference
-
1. Brownlee M. The pathobiology of diabetic complications: a unifying mechanism. Diabetes. 2005; Jun. 54(6):1615–25.2. Baker EH, Wood DM, Brennan AL, Clark N, Baines DL, Philips BJ. Hyperglycaemia and pulmonary infection. Proc Nutr Soc. 2006; Aug. 65(3):227–35.
Article3. Baker EH, Bell D. Blood glucose: of emerging importance in COPD exacerbations. Thorax. 2009; Oct. 64(10):830–2.
Article4. Roy S, Trudeau K, Roy S, Tien T, Barrette KF. Mitochondrial dysfunction and endoplasmic reticulum stress in diabetic retinopathy: mechanistic insights into high glucose-induced retinal cell death. Curr Clin Pharmacol. 2013; Nov. 8(4):278–84.
Article5. Wu D, Peng F, Zhang B, Ingram AJ, Kelly DJ, Gilbert RE, et al. EGFR-PLCgamma1 signaling mediates high glucose-induced PKCbeta1-Akt activation and collagen I upregulation in mesangial cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2009; Sep. 297(3):F822–34.6. Singh R, Kishore L, Kaur N. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy: current perspective and future directions. Pharmacol Res. 2014; Feb. 80:21–35.
Article7. Lan CC, Wu CS, Huang SM, Wu IH, Chen GS. High-glucose environment enhanced oxidative stress and increased interleukin-8 secretion from keratinocytes: new insights into impaired diabetic wound healing. Diabetes. 2013; Jul. 62(7):2530–8.8. Han L, Ma Q, Li J, Liu H, Li W, Ma G, et al. High glucose promotes pancreatic cancer cell proliferation via the induction of EGF expression and transactivation of EGFR. PLoS One. 2011. 6(11):e27074.
Article9. Tiengo A, Fadini GP, Avogaro A. The metabolic syndrome, diabetes and lung dysfunction. Diabetes Metab. 2008; Nov. 34(5):447–54.
Article10. Forgiarini LA Jr, Kretzmann NA, Porawski M, Dias AS, Marroni NA. Experimental diabetes mellitus: oxidative stress and changes in lung structure. J Bras Pneumol. 2009; Aug. 35(8):788–91.11. Baker EH, Janaway CH, Philips BJ, Brennan AL, Baines DL, Wood DM, et al. Hyperglycaemia is associated with poor outcomes in patients admitted to hospital with acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Thorax. 2006; Apr. 61(4):284–9.
Article12. Yu H, Yang J, Xiao Q, Lu Y, Zhou X, Xia L, et al. Regulation of high glucose-mediated mucin expression by matrix metalloproteinase-9 in human airway epithelial cells. Exp Cell Res. 2015; Apr. 333(1):127–35.
Article13. Bae CH, Choi YS, Song SY, Kim YD. Effect of thymic stromal lymphopoietin on MUC5B expression in human airway epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014; May. 448(2):231–5.
Article14. Kim YD, Kwon EJ, Park DW, Song SY, Yoon SK, Baek SH. Interleukin-1beta induces MUC2 and MUC5AC synthesis through cyclooxygenase-2 in NCI-H292 cells. Mol Pharmacol. 2002; Nov. 62(5):1112–8.15. Jorissen RN, Walker F, Pouliot N, Garrett TP, Ward CW, Burgess AW. Epidermal growth factor receptor: mechanisms of activation and signalling. Exp Cell Res. 2003; Mar. 284(1):31–53.
Article16. Burgel PR, Nadel JA. Epidermal growth factor receptor-mediated innate immune responses and their roles in airway diseases. Eur Respir J. 2008; Oct. 32(4):1068–81.
Article17. Hao Y, Kuang Z, Jing J, Miao J, Mei LY, Lee RJ, et al. Mycoplasma pneumoniae modulates STAT3-STAT6/EGFR-FOXA2 signaling to induce overexpression of airway mucins. Infect Immun. 2014; Dec. 82(12):5246–55.
Article18. Yuan-Chen Wu D, Wu R, Reddy SP, Lee YC, Chang MM. Distinctive epidermal growth factor receptor/extracellular regulated kinase-independent and -dependent signaling pathways in the induction of airway mucin 5B and mucin 5AC expression by phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate. Am J Pathol. 2007; Jan. 170(1):20–32.
Article19. Rada B, Gardina P, Myers TG, Leto TL. Reactive oxygen species mediate inflammatory cytokine release and EGFR-dependent mucin secretion in airway epithelial cells exposed to Pseudomonas pyocyanin. Mucosal Immunol. 2011; Mar. 4(2):158–71.
Article20. Burgel PR, Montani D, Danel C, Dusser DJ, Nadel JA. A morphometric study of mucins and small airway plugging in cystic fibrosis. Thorax. 2007; Feb. 62(2):153–61.
Article21. Puddicombe SM, Polosa R, Richter A, Krishna MT, Howarth PH, Holgate ST, et al. Involvement of the epidermal growth factor receptor in epithelial repair in asthma. FASEB J. 2000; Jul. 14(10):1362–74.
Article22. Williams OW, Sharafkhaneh A, Kim V, Dickey BF, Evans CM. Airway mucus: from production to secretion. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2006; May. 34(5):527–36.23. Rogers DF. Physiology of airway mucus secretion and pathophysiology of hypersecretion. Respir Care. 2007; Sep. 52(9):1134–46.24. Rose MC, Voynow JA. Respiratory tract mucin genes and mucin glycoproteins in health and disease. Physiol Rev. 2006; Jan. 86(1):245–78.
Article25. Turner J, Jones CE. Regulation of mucin expression in respiratory diseases. Biochem Soc Trans. 2009; Aug. 37(Pt 4):877–81.
Article26. Woo HJ, Yoo WJ, Bae CH, Song SY, Kim YW, Park SY, et al. Leptin up-regulates MUC5B expression in human airway epithelial cells via mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Exp Lung Res. 2010; Jun. 36(5):262–9.27. Ohtsu H, Dempsey PJ, Eguchi S. ADAMs as mediators of EGF receptor transactivation by G protein-coupled receptors. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2006; Jul. 291(1):C1–10.
Article28. Zwick E, Hackel PO, Prenzel N, Ullrich A. The EGF receptor as central transducer of heterologous signalling systems. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1999; Oct. 20(10):408–12.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of High-Insulin on MUC4, MUC5AC, and MUC5B Expression in Airway Epithelial Cells
- High Concentration of Glucose Induces MUC5B Expression via Reactive Oxygen Species in Human Airway Epithelial Cells
- Effect of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes on MUC5AC and MUC5B Expression in Airway Epithelial Cells
- Roxithromycin Suppresses MUC5B/8 Mucin Genes and Mucin Production in Airway Epithelial Cells
- Effect of Polyinosinic-Polycytidylic Acid on MUC5B Expression in Human Airway Epithelial Cells