Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 Increases the Expression of Inflammatory Biomarkers and Sebum Production in Cultured Sebocytes
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Busan Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 2Department of Dermatology, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. weonju@knu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2368023
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2017.29.1.20
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Acne vulgaris has been linked to the Western diet. Hyperglycemic diet increases insulin and insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-1. Deeper insights into IGF-1-mediated signal pathway are critical importance to understand the impact of Western diet.
OBJECTIVE
We investigated the effect of IGF-1 on the expression of inflammatory biomarkers and sebum production in cultured sebocytes.
METHODS
Polymerase chain reaction and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay were performed to measure changes in the expression of inflammatory biomarkers including interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, IL-8, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB), IGF1R, IGFBP2, sterol response element-binding protein (SREBP), and phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase, catalytic subunit alpha (PI3KCA) after the treatment of cultured sebocytes with 10â»â· M or 10â»âµ M IGF-1. Sebum production was evaluated after the treatment of cultured sebocytes with 10â»â· M or 10â»âµ M IGF-1 using lipid analysis.
RESULTS
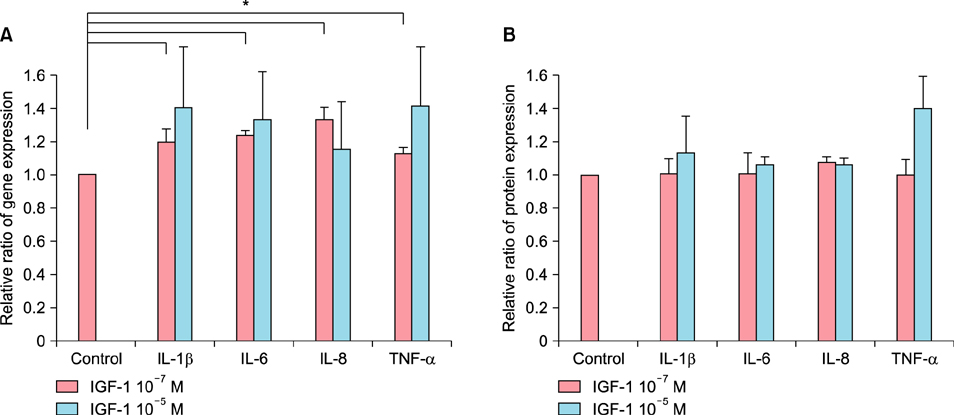
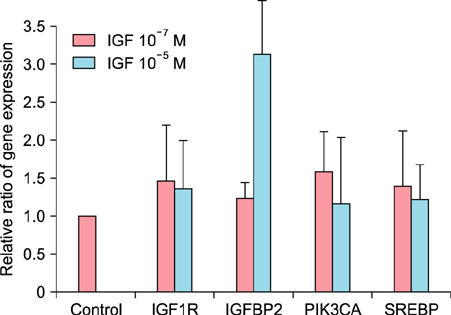
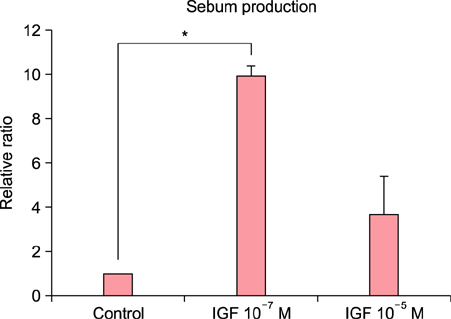
The expression levels of IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-α in cultured sebocytes after treatment with 10â»â· M or 10â»âµ M IGF-1 were increased. Increased gene expression levels of NF-κB in cultured sebocytes were also shown after 10â»â· M or 10â»âµ M IGF-1 treatments. Gene expression of these inflammatory biomarkers was decreased after 10â»â· M or 10â»âµ M IGF-1 treatment in the presence of 100 nM NF-κB inhibitor. Treatment with 10â»â· M or 10â»âµ M IGF-1 increased the gene expression levels of IGF1R, IGFBP2, SREBP and PI3KCA in cultured sebocytes. Sebum production from cultured sebocytes treated with 10â»â· M or 10â»âµ M IGF-1 was also increased.
CONCLUSION
It is suggestive that IGF-1 might be involved in the pathogenesis of acne by increasing both expression of inflammatory biomarkers and also sebum production in sebocytes.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Acne Vulgaris
B-Lymphocytes
Biomarkers*
Catalytic Domain
Diet
Diet, Western
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Gene Expression
Insulin
Insulin-Like Growth Factor I
Interleukin-6
Interleukin-8
Interleukins
Polymerase Chain Reaction
Sebum*
Signal Transduction
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
Biomarkers
Insulin
Insulin-Like Growth Factor I
Interleukin-6
Interleukin-8
Interleukins
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Epidermal Growth Factor Attenuated the Expression of Inflammatory Cytokines in Human Epidermal Keratinocyte Exposed to Propionibacterium acnes
Ji Min Kim, Jung Eun Choo, Heun Joo Lee, Ki Nam Kim, Sung Eun Chang
Ann Dermatol. 2018;30(1):54-63. doi: 10.5021/ad.2018.30.1.54.Inhibition of Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1–Induced Sebum Production by Bilobetin in Cultured Human Sebocytes
Cong Wang, Yul-Lye Hwang, Xue Mei Li, Soo Jung Kim, Ming Ji Zhu, Jeung-Hoon Lee, Ri-Hua Jiang, Chang Deok Kim
Ann Dermatol. 2019;31(3):294-299. doi: 10.5021/ad.2019.31.3.294.Isoginkgetin Inhibits Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1-Induced Sebum Production in Cultured Human Sebocytes
Yul-Lye Hwang, Min-Ho Lee, Hyun-In Oh, Hyung-Jin Kim, Cho-Ah Lim, Jeung-Hoon Lee, Chang Deok Kim
Ann Dermatol. 2018;30(3):394-396. doi: 10.5021/ad.2018.30.3.394.
Reference
-
1. Winston MH, Shalita AR. Acne vulgaris. Pathogenesis and treatment. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1991; 38:889–903.
Article2. Zouboulis CC. Acne and sebaceous gland function. Clin Dermatol. 2004; 22:360–366.
Article3. Zouboulis CC, Adjaye J, Akamatsu H, Moe-Behrens G, Niemann C. Human skin stem cells and the ageing process. Exp Gerontol. 2008; 43:986–997.
Article4. Kurokawa I, Danby FW, Ju Q, Wang X, Xiang LF, Xia L, et al. New developments in our understanding of acne pathogenesis and treatment. Exp Dermatol. 2009; 18:821–832.
Article5. Melnik BC. Diet in acne: further evidence for the role of nutrient signalling in acne pathogenesis. Acta Derm Venereol. 2012; 92:228–231.
Article6. Kwon HH, Yoon JY, Hong JS, Jung JY, Park MS, Suh DH. Clinical and histological effect of a low glycaemic load diet in treatment of acne vulgaris in Korean patients: a randomized, controlled trial. Acta Derm Venereol. 2012; 92:241–246.
Article7. Smith TM, Gilliland K, Clawson GA, Thiboutot D. IGF-1 induces SREBP-1 expression and lipogenesis in SEB-1 sebocytes via activation of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway. J Invest Dermatol. 2008; 128:1286–1293.
Article8. Renier G, Clément I, Desfaits AC, Lambert A. Direct stimulatory effect of insulin-like growth factor-I on monocyte and macrophage tumor necrosis factor-alpha production. Endocrinology. 1996; 137:4611–4618.
Article9. Kooijman R, Coppens A, Hooghe-Peters E. IGF-I stimulates IL-8 production in the promyelocytic cell line HL-60 through activation of extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase. Cell Signal. 2003; 15:1091–1098.
Article10. Tu W, Cheung PT, Lau YL. IGF-I increases interferon-gamma and IL-6 mRNA expression and protein production in neonatal mononuclear cells. Pediatr Res. 1999; 46:748–754.
Article11. Im M, Kim SY, Sohn KC, Choi DK, Lee Y, Seo YJ, et al. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate suppresses IGF-I-induced lipogenesis and cytokine expression in SZ95 sebocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 2012; 132:2700–2708.
Article12. Cappel M, Mauger D, Thiboutot D. Correlation between serum levels of insulin-like growth factor 1, dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate, and dihydrotestosterone and acne lesion counts in adult women. Arch Dermatol. 2005; 141:333–338.
Article13. Zouboulis CC. Is acne vulgaris a genuine inflammatory disease? Dermatology. 2001; 203:277–279.
Article14. Zouboulis CC, Eady A, Philpott M, Goldsmith LA, Orfanos C, Cunliffe WC, et al. What is the pathogenesis of acne? Exp Dermatol. 2005; 14:143–152.
Article15. Webster GF. Inflammation in acne vulgaris. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1995; 33:247–253.
Article16. Kang S, Cho S, Chung JH, Hammerberg C, Fisher GJ, Voorhees JJ. Inflammation and extracellular matrix degradation mediated by activated transcription factors nuclear factor-kappaB and activator protein-1 in inflammatory acne lesions in vivo. Am J Pathol. 2005; 166:1691–1699.
Article17. Rasmussen JE. Diet and acne. Int J Dermatol. 1977; 16:488–492.
Article18. Pappas A. The relationship of diet and acne: a review. Dermatoendocrinol. 2009; 1:262–267.19. Liakou AI, Theodorakis MJ, Melnik BC, Pappas A, Zouboulis CC. Nutritional clinical studies in dermatology. J Drugs Dermatol. 2013; 12:1104–1109.
Article20. Smith R, Mann N, Mäkeläinen H, Roper J, Braue A, Varigos G. A pilot study to determine the short-term effects of a low glycemic load diet on hormonal markers of acne: a nonrandomized, parallel, controlled feeding trial. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2008; 52:718–726.
Article21. Clarke SB, Nelson AM, George RE, Thiboutot DM. Pharmacologic modulation of sebaceous gland activity: mechanisms and clinical applications. Dermatol Clin. 2007; 25:137–146.
Article22. Alestas T, Ganceviciene R, Fimmel S, Müller-Decker K, Zouboulis CC. Enzymes involved in the biosynthesis of leukotriene B4 and prostaglandin E2 are active in sebaceous glands. J Mol Med (Berl). 2006; 84:75–87.
Article23. Lee WJ, Jung HD, Lee HJ, Kim BS, Lee SJ, Kim DW. Influence of substance-P on cultured sebocytes. Arch Dermatol Res. 2008; 300:311–316.
Article24. Lee WJ, Jung HD, Chi SG, Kim BS, Lee SJ, Kim DW, et al. Effect of dihydrotestosterone on the upregulation of inflammatory cytokines in cultured sebocytes. Arch Dermatol Res. 2010; 302:429–433.
Article25. Lee WJ, Chae SY, Ryu HS, Jang YH, Lee SJ, Kim DW. Inflammatory cytokine expression and sebum production after exposure of cultured human sebocytes to ultraviolet a radiation and light at wavelengths of 650 nm and 830 nm. Ann Dermatol. 2015; 27:163–170.
Article26. Mirdamadi Y, Thielitz A, Wiede A, Goihl A, Papakonstantinou E, Hartig R, et al. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor-1 can modulate the phosphoinositide-3-kinase/Akt/FoxO1 pathway in SZ95 sebocytes in vitro. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2015; 415:32–44.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Inflammatory Cytokine Expression and Sebum Production after Exposure of Cultured Human Sebocytes to Ultraviolet A Radiation and Light at Wavelengths of 650 nm and 830 nm
- Dieckol Inhibits the Effects of Particulate Matter 10 on Sebocytes, Outer Root Sheath Cells, and Cutibacterium Acnes−Pretreated Mice
- Inhibition of Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1–Induced Sebum Production by Bilobetin in Cultured Human Sebocytes
- Effects of Black Ginseng Water Extract under the Inflammatory Conditions of Cultured Sebocytes and Outer Root Sheath Cells
- Isoginkgetin Inhibits Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1-Induced Sebum Production in Cultured Human Sebocytes