Cancer Res Treat.
2017 Jan;49(1):219-229. 10.4143/crt.2016.190.
Anti-cancer Effects of a Novel Quinoline Derivative 83b1 on Human Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma through Down-Regulation of COX-2 mRNA and PGEâ‚‚
- Affiliations
-
- 1State Key Laboratory of Chirosciences, Lo Ka Chung Centre for Natural Anti-cancer Drug Development, Department of Applied Biology and Chemical Technology, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong, China. dr-johnny.tang@polyu.edu.hk
- 2Department of Surgery, Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China.
- 3Department of Pathology, Griffith Medical School and Griffith Health Institute, Griffith University, Gold Coast, Queensland, Australia.
- 4Clinical Division, School of Chinese Medicine, Hong Kong Baptist University, Hong Kong, China.
- 5Sun Yat Sen University, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Guangzhou, China.
- KMID: 2367520
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2016.190
Abstract
- PURPOSE
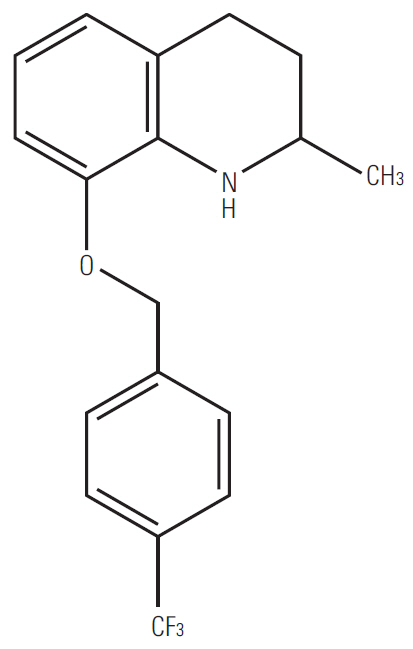
83b1 is a novel quinoline derivative that has been shown to inhibit cancer growth in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). This study was conducted to comprehensively evaluate the cytotoxic effects of 83b1 on a series of ESCC cell lines and investigate the mechanisms by which 83b1 suppresses cancer growth based on molecular docking analysis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A series of ESCC and nontumor immortalized cell lines were exposed to 83b1 and cisplatin (CDDP) in a dose-dependent manner, and the cytotoxicity was examined by a MTS assay kit. Prediction of the molecular targets of 83b1 was conducted by molecular docking analysis. Expression of cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2) mRNA and COX-2-derived prostaglandin Eâ‚‚ (PGEâ‚‚) were measured by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction and enzymelinked immuno-sorbent assay, respectively. In vivo anti-tumor effect was determined using a nude mice xenografted model transplanted with an ESCC cell line, KYSE-450.
RESULTS
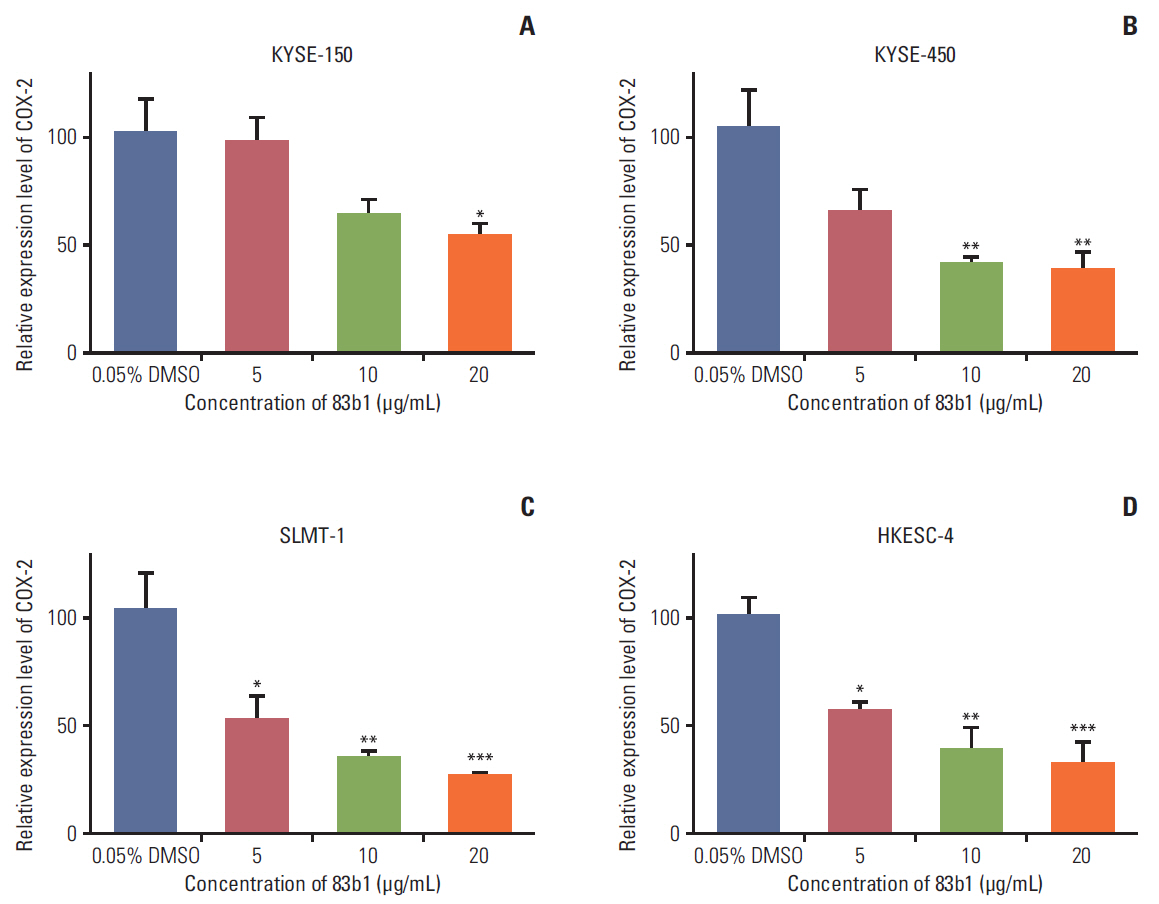
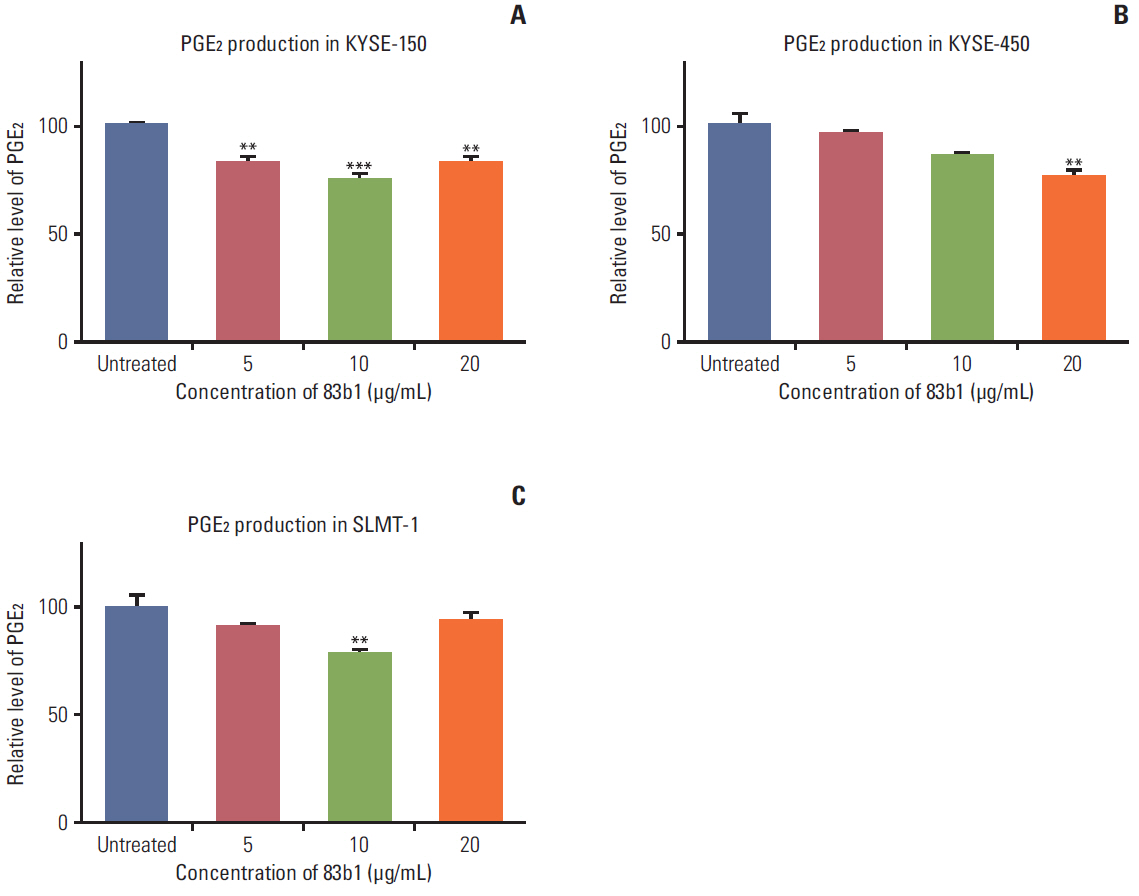
83b1 showed the significant anti-cancer effects on all ESCC cell lines compared to CDDP; however, 83b1 revealed much lower toxic effects on non-tumor cell lines than CDDP. The predicted molecular target of 83b1 is peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta (PPARδ), which is a widely known oncoprotein. Additionally the expression of COX-2 mRNA and COX-2-derived PGE2 were down-regulated by 83b1 in a dose-dependent manner in ESCC cell lines. Furthermore, 83b1 was shown to significantly reduce the tumor size in nude mice xenograft.
CONCLUSION
The results of this study suggest that the potential anti-cancer effects of 83b1 on human esophageal cancers occur through the possible oncotarget, PPARδ, and down-regulation of the cancer related genes and molecules.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Carcinoma, Squamous Cell*
Cell Line
Cisplatin
Cyclooxygenase 2
Dinoprostone
Down-Regulation*
Epithelial Cells*
Esophageal Neoplasms
Heterografts
Humans*
Mice
Mice, Nude
Molecular Docking Simulation
PPAR delta
Quinolines
Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
RNA, Messenger*
Cisplatin
Cyclooxygenase 2
Dinoprostone
PPAR delta
Quinolines
RNA, Messenger
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011; 61:69–90.
Article2. Qiu H, Mao Y, Gu Y, Zhu J, Wang Y, Zeng J, et al. The potential of photodynamic therapy to treat esophageal candidiasis coexisting with esophageal cancer. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2014; 130:305–9.
Article3. Sakaeda T, Yamamori M, Kuwahara A, Nishiguchi K. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacogenomics in esophageal cancer chemoradiotherapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2009; 61:388–401.
Article4. Souza RF, Shewmake K, Beer DG, Cryer B, Spechler SJ. Selective inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 suppresses growth and induces apoptosis in human esophageal adenocarcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 2000; 60:5767–72.5. Chan SH, Chui CH, Chan SW, Kok SHL, D. C, Tsoi MYT, et al. Synthesis of 8-hydroxyquinoline derivatives as novel antitumor agents. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2013; 4:170–4.
Article6. Michael JP. Quinoline, quinazoline and acridone alkaloids. Nat Prod Rep. 1998; 15:595–606.
Article7. Kumar S, Bawa S, Gupta H. Biological activities of quinoline derivatives. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2009; 9:1648–54.
Article8. Tharayil N, Bhowmik P, Alpert P, Walker E, Amarasiriwardena D, Xing B. Dual purpose secondary compounds: phytotoxin of Centaurea diffusa also facilitates nutrient uptake. New Phytol. 2009; 181:424–34.9. Jeon JH, Lee CH, Lee HS. Antimicrobial activities of 2-methyl-8-hydroxyquinoline and its derivatives against human intestinal bacteria. J Korean Soc Appl Biol Chem. 2009; 52:202–5.
Article10. Lam KH, Gambari R, Lee KK, Chen YX, Kok SH, Wong RS, et al. Preparation of 8-hydroxyquinoline derivatives as potential antibiotics against Staphylococcus aureus. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2014; 24:367–70.
Article11. Takayama O, Yamamoto H, Damdinsuren B, Sugita Y, Ngan CY, Xu X, et al. Expression of PPARdelta in multistage carcinogenesis of the colorectum: implications of malignant cancer morphology. Br J Cancer. 2006; 95:889–95.12. Xu L, Han C, Wu T. A novel positive feedback loop between peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-δ and prostaglandin E2 signaling pathways for human cholangiocarcinoma cell growth. J Biol Chem. 2006; 281:33982–96.
Article13. Fournier T, Tsatsaris V, Handschuh K, Evain-Brion D. PPARs and the placenta. Placenta. 2007; 28:65–76.
Article14. Hla T, Neilson K. Human cyclooxygenase-2 cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992; 89:7384–8.
Article15. Dimberg J, Hugander A, Sirsjo A, Soderkvist P. Enhanced expression of cyclooxygenase-2 and nuclear beta-catenin are related to mutations in the APC gene in human colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res. 2001; 21:911–5.16. Zimmermann KC, Sarbia M, Weber AA, Borchard F, Gabbert HE, Schror K. Cyclooxygenase-2 expression in human esophageal carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1999; 59:198–204.17. Sun WH, Sun YL, Fang RN, Shao Y, Xu HC, Xue QP, et al. Expression of cyclooxygenase-2 and matrix metalloproteinase-9 in gastric carcinoma and its correlation with angiogenesis. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2005; 35:707–13.
Article18. Sun WH, Zhu F, Chen GS, Su H, Luo C, Zhao QS, et al. Blockade of cholecystokinin-2 receptor and cyclooxygenase-2 synergistically induces cell apoptosis, and inhibits the proliferation of human gastric cancer cells in vitro. Cancer Lett. 2008; 263:302–11.
Article19. Greenhough A, Smartt HJ, Moore AE, Roberts HR, Williams AC, Paraskeva C, et al. The COX-2/PGE2 pathway: key roles in the hallmarks of cancer and adaptation to the tumour microenvironment. Carcinogenesis. 2009; 30:377–86.
Article20. Lam KH, Xu L, Feng L, Fan QH, Lam FL, Lo WH, et al. Highly enantioselective iridium-catalyzed hydrogenation of quinoline derivatives using chiral phosphinite H8-BINAPO. Adv Synth Catal. 2005; 347:1755–8.
Article21. Tang JC, Wan TS, Wong N, Pang E, Lam KY, Law SY, et al. Establishment and characterization of a new xenograft-derived human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell line SLMT-1 of Chinese origin. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2001; 124:36–41.
Article22. Shimada Y, Imamura M, Wagata T, Yamaguchi N, Tobe T. Characterization of 21 newly established esophageal cancer cell lines. Cancer. 1992; 69:277–84.
Article23. Deng W, Tsao SW, Guan XY, Lucas JN, Si HX, Leung CS, et al. Distinct profiles of critically short telomeres are a key determinant of different chromosome aberrations in immortalized human cells: whole-genome evidence from multiple cell lines. Oncogene. 2004; 23:9090–101.
Article24. Zhang H, Jin Y, Chen X, Jin C, Law S, Tsao SW, et al. Cytogenetic aberrations in immortalization of esophageal epithelial cells. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2006; 165:25–35.
Article25. Tang WK, Chui CH, Fatima S, Kok SH, Pak KC, Ou TM, et al. Inhibitory effects of Gleditsia sinensis fruit extract on telomerase activity and oncogenic expression in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Mol Med. 2007; 19:953–60.
Article26. Kim MO, Hong ES, Chai JY, Leem JM, You IY, Kim WD, et al. Concurrent FP (5-fluorouracil, cisplatin) chemoradiotherapy for patients with esophageal cancer. Cancer Res Treat. 2003; 35:330–4.
Article27. Keiser MJ, Roth BL, Armbruster BN, Ernsberger P, Irwin JJ, Shoichet BK. Relating protein pharmacology by ligand chemistry. Nat Biotechnol. 2007; 25:197–206.
Article28. Bikadi Z, Hazai E. Application of the PM6 semi-empirical method to modeling proteins enhances docking accuracy of AutoDock. J Cheminform. 2009; 1:15.
Article29. Zhang D, Wood CE. Neuronal prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase 2 responses to oxygen and glucose deprivation are mediated by mitogen-activated protein kinase ERK1/2. Brain Res. 2005; 1060:100–7.
Article30. Jin M, Li L, Xu C, Wen Y, Zhao M. Estrogenic activities of two synthetic pyrethroids and their metabolites. J Environ Sci (China). 2010; 22:290–6.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Cutaneous Metastasis of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Mimicking Benign Soft Tissue Tumor
- Immunotherapy for Advanced/Metastatic Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- Diagnosis and Clinical Management of Esophageal Squamous Dysplasia
- Change of the Invasiveness with Selective Cox-2 Inhibition in an Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cell Line, KB; Preliminary in Vitro Study
- Expression of Cyclooxygenase 1 and 2 in Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma