Cancer Res Treat.
2017 Jan;49(1):150-160. 10.4143/crt.2015.462.
Gastric Carcinogenesis in the miR-222/221 Transgenic Mouse Model
- Affiliations
-
- 1Cancer Research Institute, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hkyang@snu.ac.kr
- 2Division of Genetics, Cancer Research Institute, Kanazawa University, Kanazawa, Japan.
- 3Center for RNA Research, Institute for Basic Science, Korea School of Biological Sciences, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Biochemistry, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea.
- 5Department of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Cell and Matrix Research Institute, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 6Department of Experimental Animal Research, Biomedical Research Institute, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 7Department of Pathology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 8Department of Veterinary Pathology, College of Veterinary Medicine, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- 9Department of Surgery, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2367512
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2015.462
Abstract
- PURPOSE
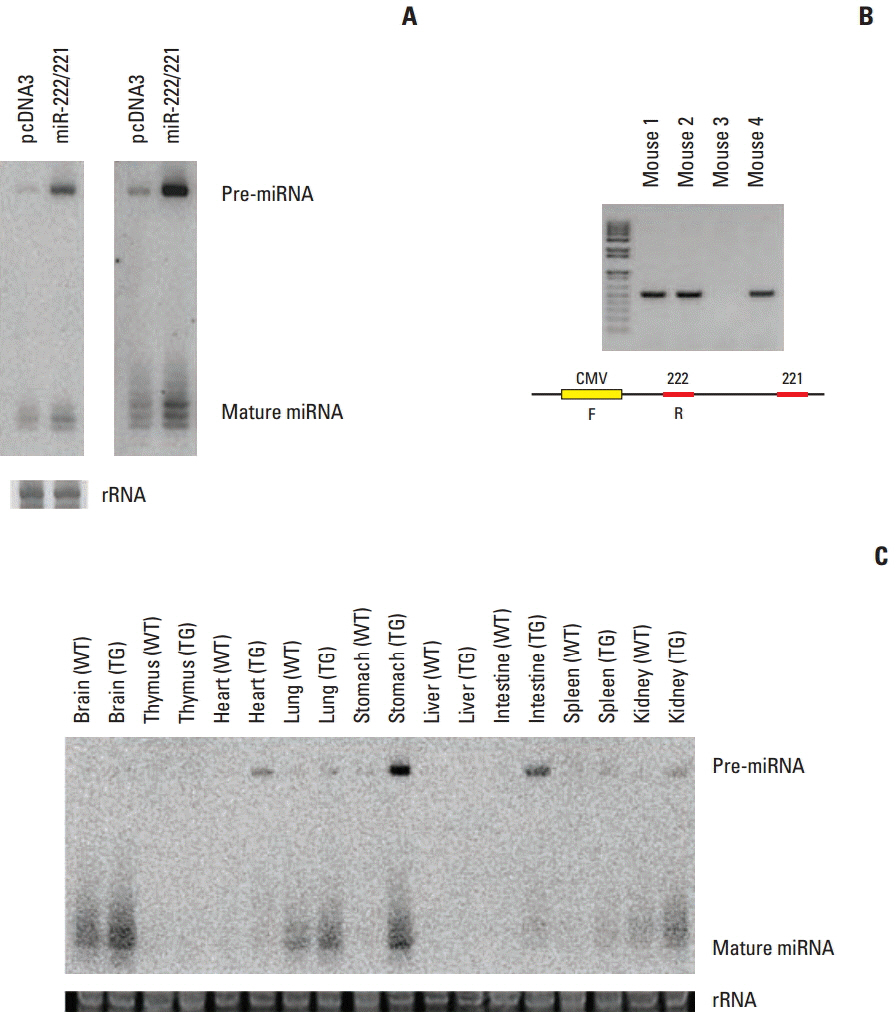
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) regulate various cellular functions, including development, cell proliferation, apoptosis, and tumorigenesis. Different signatures associated with various tissue types, diagnosis, progression, prognosis, staging, and treatment response have been identified by miRNA expression profiling of human tumors. miRNAs function as oncogenes or as tumor suppressors. The relationship between gastric cancer and miRNA garnered attention due to the high incidence of gastric cancer in Asian countries. miR-222/221 expression increases in gastric tumor tissues. The oncogenic effect of miR-222/221 was previously determined in functional studies and xenograft models. In this study, transgenic mice over-expressing miR-222/221 were generated to confirm the effect of miR-222/221 on gastric carcinogenesis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
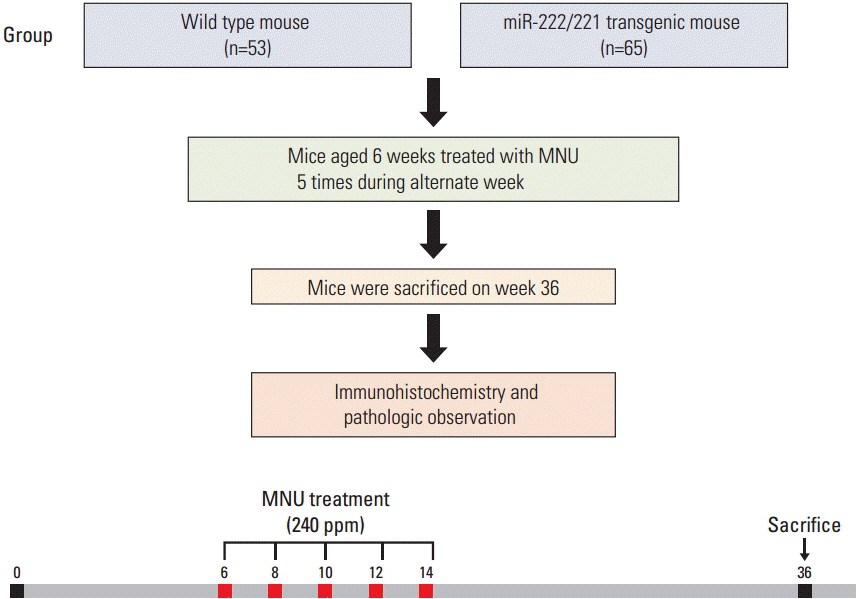
At 6 weeks of age, 65 transgenic mice and 53 wild-type mice were given drinking water containing N-nitroso-N-methylurea (MNU) for 5 alternating weeks to induce gastric cancer. The mice were euthanized at 36 weeks of age and histologic analysis was performed.
RESULTS
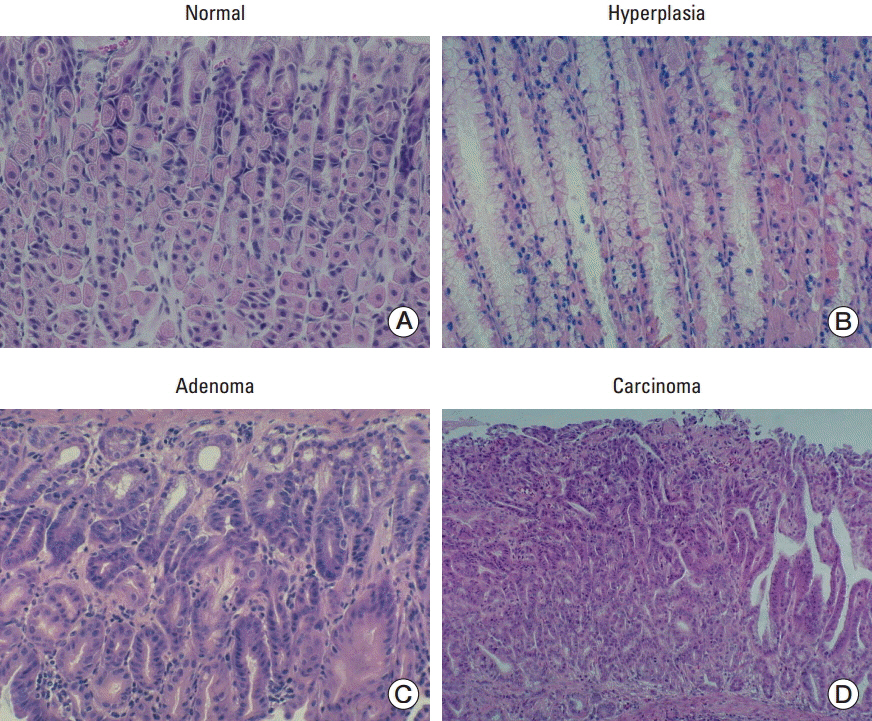
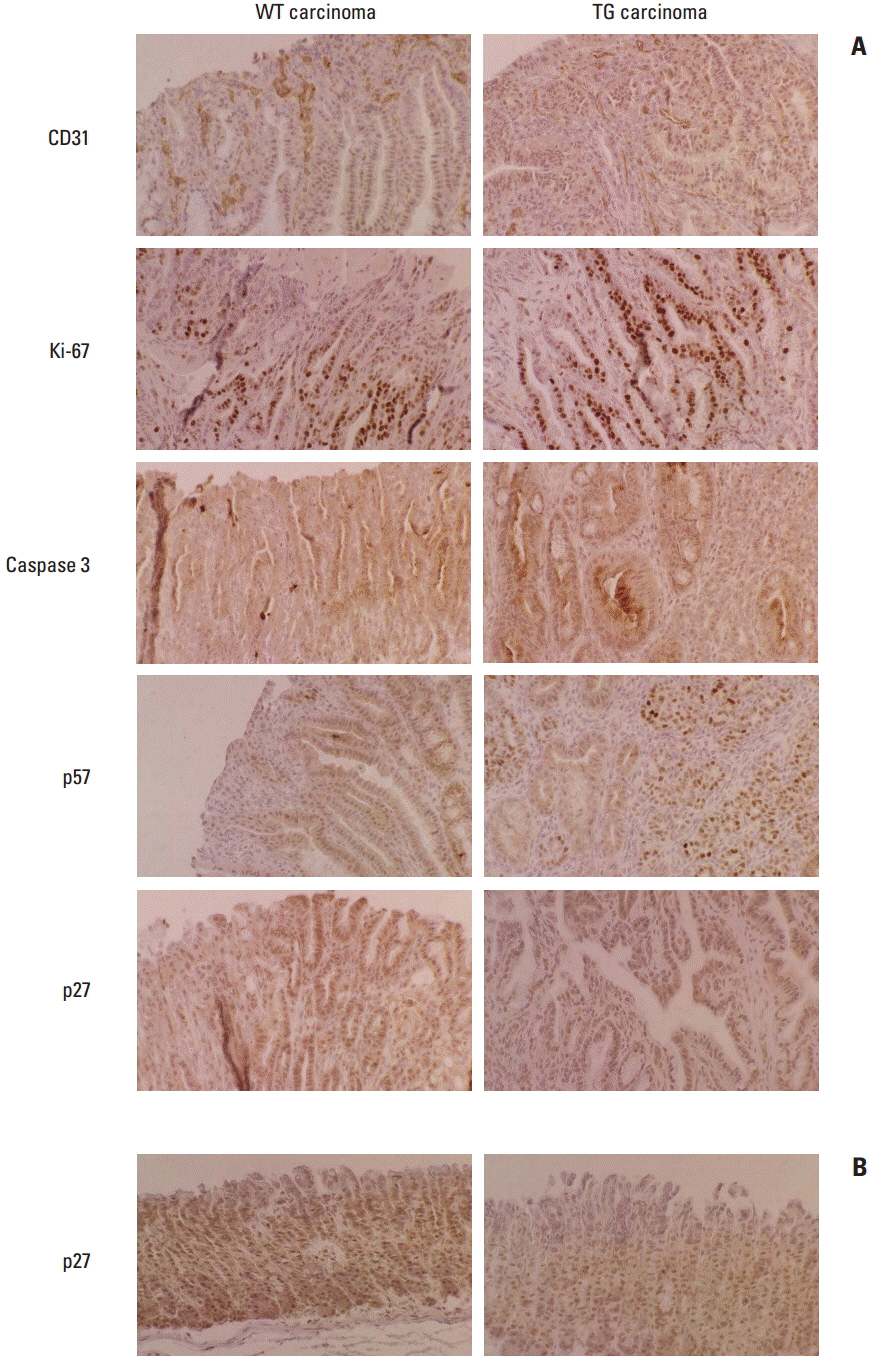
Hyperplasia was observed in 3.77% of the wild-type mice and in 18.46% of the transgenic mice (p=0.020). Adenoma was observed in 20.75% of the wild-type mice and 26.15% of the transgenic mice (p=0.522). Carcinoma was observed in 32.08% of the wild-type mice and 41.54% of the transgenic mice (p=0.341). The frequency of hyperplasia, adenoma, and carcinoma was higher in transgenic mice, but the difference was statistically significant only in hyperplasia.
CONCLUSION
These results suggest that hyperplasia, a gastric pre-cancerous lesion, is associated with miR-222/221 expression but miR-222/221 expression does not affect tumorigenesis itself.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 1993; 75:843–54.
Article2. Filipowicz W, Bhattacharyya SN, Sonenberg N. Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by microRNAs: are the answers in sight? Nat Rev Genet. 2008; 9:102–14.
Article3. Meng F, Hackenberg M, Li Z, Yan J, Chen T. Discovery of novel microRNAs in rat kidney using next generation sequencing and microarray validation. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e34394.
Article4. Friedman RC, Farh KK, Burge CB, Bartel DP. Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res. 2009; 19:92–105.
Article5. Alvarez-Garcia I, Miska EA. MicroRNA functions in animal development and human disease. Development. 2005; 132:4653–62.
Article6. Fornari F, Gramantieri L, Ferracin M, Veronese A, Sabbioni S, Calin GA, et al. MiR-221 controls CDKN1C/p57 and CDKN1B/p27 expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene. 2008; 27:5651–61.
Article7. Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005; 55:74–108.
Article8. Leung WK, Wu MS, Kakugawa Y, Kim JJ, Yeoh KG, Goh KL, et al. Screening for gastric cancer in Asia: current evidence and practice. Lancet Oncol. 2008; 9:279–87.
Article9. Tsukamoto Y, Nakada C, Noguchi T, Tanigawa M, Nguyen LT, Uchida T, et al. MicroRNA-375 is downregulated in gastric carcinomas and regulates cell survival by targeting PDK1 and 14-3-3zeta. Cancer Res. 2010; 70:2339–49.10. Guo J, Miao Y, Xiao B, Huan R, Jiang Z, Meng D, et al. Differential expression of microRNA species in human gastric cancer versus non-tumorous tissues. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009; 24:652–7.
Article11. Petrocca F, Visone R, Onelli MR, Shah MH, Nicoloso MS, de Martino I, et al. E2F1-regulated microRNAs impair TGFbeta-dependent cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis in gastric cancer. Cancer Cell. 2008; 13:272–86.12. Xia L, Zhang D, Du R, Pan Y, Zhao L, Sun S, et al. miR-15b and miR-16 modulate multidrug resistance by targeting BCL2 in human gastric cancer cells. Int J Cancer. 2008; 123:372–9.
Article13. Kim YK, Yu J, Han TS, Park SY, Namkoong B, Kim DH, et al. Functional links between clustered microRNAs: suppression of cell-cycle inhibitors by microRNA clusters in gastric cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009; 37:1672–81.
Article14. Yoshizawa N, Yamaguchi H, Yamamoto M, Shimizu N, Furihata C, Tatematsu M, et al. Gastric carcinogenesis by N-Methyl-N-nitrosourea is enhanced in db/db diabetic mice. Cancer Sci. 2009; 100:1180–5.15. Tomita H, Yamada Y, Oyama T, Hata K, Hirose Y, Hara A, et al. Development of gastric tumors in Apc (Min/+) mice by the activation of the beta-catenin/Tcf signaling pathway. Cancer Res. 2007; 67:4079–87.16. Yamachika T, Nakanishi H, Inada K, Tsukamoto T, Shimizu N, Kobayashi K, et al. N-methyl-N-nitrosourea concentration-dependent, rather than total intake-dependent, induction of adenocarcinomas in the glandular stomach of BALB/c mice. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1998; 89:385–91.
Article17. Jiang J, Xu N, Wu C, Deng H, Lu M, Li M, et al. Treatment of advanced gastric cancer by chemotherapy combined with autologous cytokine-induced killer cells. Anticancer Res. 2006; 26:2237–42.18. Hahm KB, Song YJ, Oh TY, Lee JS, Surh YJ, Kim YB, et al. Chemoprevention of Helicobacter pylori-associated gastric carcinogenesis in a mouse model: is it possible? J Biochem Mol Biol. 2003; 36:82–94.
Article19. Lu J, Imamura K, Nomura S, Mafune K, Nakajima A, Kadowaki T, et al. Chemopreventive effect of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma on gastric carcinogenesis in mice. Cancer Res. 2005; 65:4769–74.20. Nam KT, Hahm KB, Oh SY, Yeo M, Han SU, Ahn B, et al. The selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor nimesulide prevents Helicobacter pylori-associated gastric cancer development in a mouse model. Clin Cancer Res. 2004; 10:8105–13.
Article21. Han SU, Kim YB, Joo HJ, Hahm KB, Lee WH, Cho YK, et al. Helicobacter pylori infection promotes gastric carcinogenesis in a mice model. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2002; 17:253–61.
Article22. le Sage C, Nagel R, Egan DA, Schrier M, Mesman E, Mangiola A, et al. Regulation of the p27(Kip1) tumor suppressor by miR-221 and miR-222 promotes cancer cell proliferation. EMBO J. 2007; 26:3699–708.
Article23. Galardi S, Mercatelli N, Giorda E, Massalini S, Frajese GV, Ciafre SA, et al. miR-221 and miR-222 expression affects the proliferation potential of human prostate carcinoma cell lines by targeting p27Kip1. J Biol Chem. 2007; 282:23716–24.
Article24. Visone R, Russo L, Pallante P, De Martino I, Ferraro A, Leone V, et al. MicroRNAs (miR)-221 and miR-222, both overexpressed in human thyroid papillary carcinomas, regulate p27Kip1 protein levels and cell cycle. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2007; 14:791–8.
Article25. Callegari E, Elamin BK, Giannone F, Milazzo M, Altavilla G, Fornari F, et al. Liver tumorigenicity promoted by microRNA-221 in a mouse transgenic model. Hepatology. 2012; 56:1025–33.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Genistein Improves the Major Depression through Suppressing the Expression of miR-221/222 by Targeting Connexin 43
- Mouse Models of Gastric Carcinogenesis
- Combined Detection of Serum MiR-221-3p and MiR-122-5p Expression in Diagnosis and Prognosis of Gastric Cancer
- Expression of miR-221 and miR-18a in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and its clinical significance
- MicroRNA-222 Expression as a Predictive Marker for Tumor Progression in Hormone Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer