Nat Prod Sci.
2016 Dec;22(4):293-298. 10.20307/nps.2016.22.4.293.
Effects of Triterpenoids from Luvunga scandens on Cytotoxic, Cell Cycle Arrest and Gene Expressions in MCF-7 Cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pharmaceutical Technology, Faculty of Pharmacy, International Islamic University Malaysia, 25200, Kuantan, Pahang, Malaysia. mtaher@iium.edu.my
- 2Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, International Islamic University Malaysia, 25200, Kuantan, Pahang, Malaysia.
- 3Department of Basic Medical Sciences, Faculty of Dentistry, International Islamic University Malaysia, 25200, Kuantan, Pahang, Malaysia.
- 4SIRIM Berhad, National Metrology Laboratory, Selangor, Malaysia.
- KMID: 2366699
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.20307/nps.2016.22.4.293
Abstract
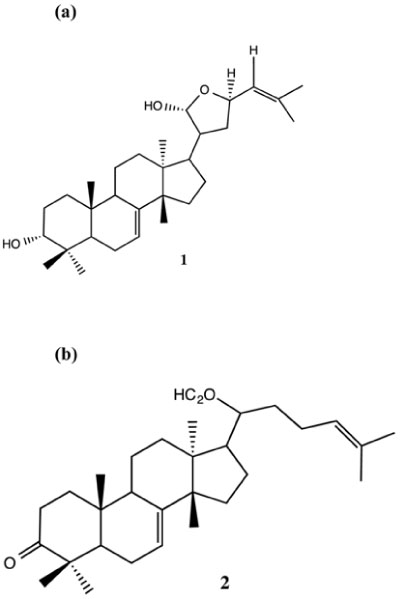
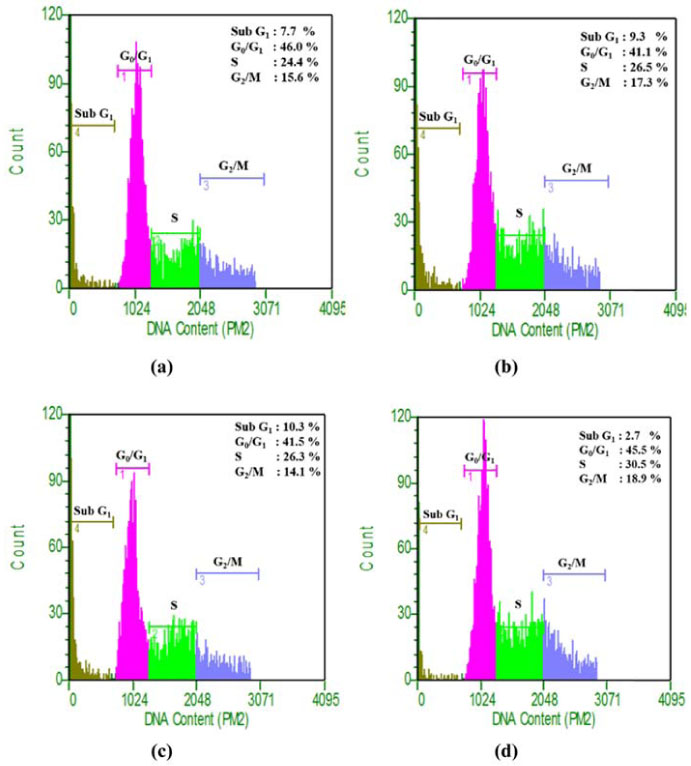
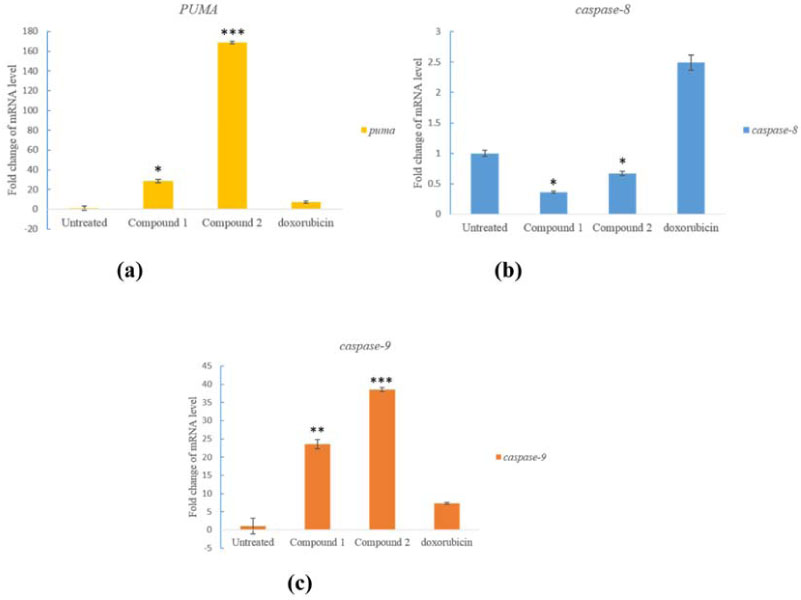
- Plant-derived triterpenoids commonly possesses biological properties such as anti-inflammatory, anti-microbial, anti-viral and anti-cancer. Luvunga scandens is one of the plant that produced triterpenoids. The aims of the study was to analyze cell cycle profile and to determine the expression of p53 unregulated modulator of apoptosis (PUMA), caspase-8 and caspase-9 genes at mRNA level in MCF-7 cell line treated with two triterpenoids, flindissol (1) and 3-oxotirucalla-7,24-dien-21-oic-acid (2) isolated from L. scandens. The compounds were tested for cell cycle analysis using flow cytometer and mRNA expression level using quantitative RT-PCR. The number of MCF-7 cells population which distributed in Sub G1 phase after treated with compound 1 and 2 were 7.7 and 9.3% respectively. The evaluation of the expression of genes showed that both compounds exhibited high level of expression of PUMA, caspase-8 and caspase-9 as normalized to β-actin via activation of those genes. In summary, the isolated compounds of L. scandens plant showed promising anticancer properties in MCF-7 cell lines.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. DeSantis CE, Fedewa SA, Goding Sauer A, Kramer JL, Smith RA, Jemal A. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016; 66:31–42.2. Hortobagyi GN, de la Garza Salazar J, Pritchard K, Amadori D, Haidinger R, Hudis CA, Khaled H, Liu MC, Martin M, Namer M, O'Shaughnessy JA, Shen ZZ, Albain KS. ABREAST Investigators. Clin Breast Cancer. 2005; 6:391–401.3. O'Donovan N, Crown J, Stunell H, Hill AD, McDermott E, O'Higgins N, Duffy MJ. Clin Cancer Res. 2003; 9:738–742.4. Simstein R, Burow M, Parker A, Weldon C, Beckman B. Exp Biol Med. 2003; 228:995–1003.5. Al-Zikri PNH, Taher M, Susanti D, Rezali MF, Read RW, Sohrab MH, Hasan CM, Ahmad F. Rev Bras Farmacogn. 2014; 24:561–564.6. Yu J, Zhang L. Oncogene. 2009; 27:S71–S83.7. Yu J, Yue W, Wu B, Zhang L. Clin Cancer Res. 2006; 12:2928–2936.8. Yu J, Zhang L, Hwang PM, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B. Mol Cell. 2001; 7:673–682.9. Jänicke RU. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2009; 117:219–221.10. Chaabane W, User SD, El-Gazzah M, Jaksik R, Sajjadi E, Rzeszowska-Wolny J, Łos MJ. Arch Immunol Ther Exp. 2013; 61:43–58.11. Crighton D, Wilkinson S, O'Prey J, Syed N, Smith P, Harrison PR, Gasco M, Garrone O, Crook T, Ryan KM. Cell. 2006; 126:121–134.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Changes of Cell Cycle Phase Fractions and Expression of p53 by the Treatment of Staurosporine in MCF-7 Cell Line
- Anti-Cancer Effect of 3-(4-dimethylamino phenyl)-N-hydroxy-2-propenamide in MCF-7 Human Breast Cancer
- Inductoin of Radioresistance by Overexpression of Glutathione S-Transferase K1 (hGSTK1) in MCF-7 Cells
- Cytotoxic Triterpenoids from the Fruits of Ligustrum japonicum
- Effects of HMGB-1 Overexpression on Cell-Cycle Progression in MCF-7 Cells