Investig Clin Urol.
2016 Jan;57(1):63-72. 10.4111/icu.2016.57.1.63.
Upregulated expression of BCL2, MCM7, and CCNE1 indicate cisplatin-resistance in the set of two human bladder cancer cell lines: T24 cisplatin sensitive and T24R2 cisplatin resistant bladder cancer cell lines
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, National Cancer Center, Goyang, Korea.
- 2Biomedical Research Institute, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 3Department of Urology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea. ssbyun@snubh.org
- 4Department of Urology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2363126
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4111/icu.2016.57.1.63
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The mechanism of resistance to cisplatin during treatment of bladder cancer (BC) has been a subject of intense investigation in clinical research. This study aims to identify candidate genes associated with resistance to cisplatin, in order to understand the resistance mechanism of BC cells to the drug, by combining the use of microarray profiling, quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), and Western blot analyses.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
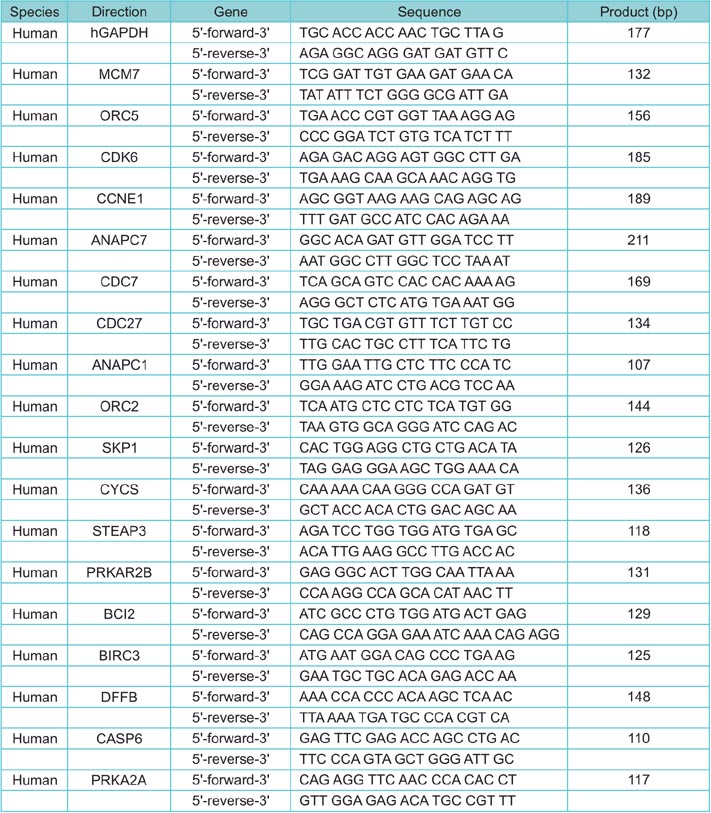
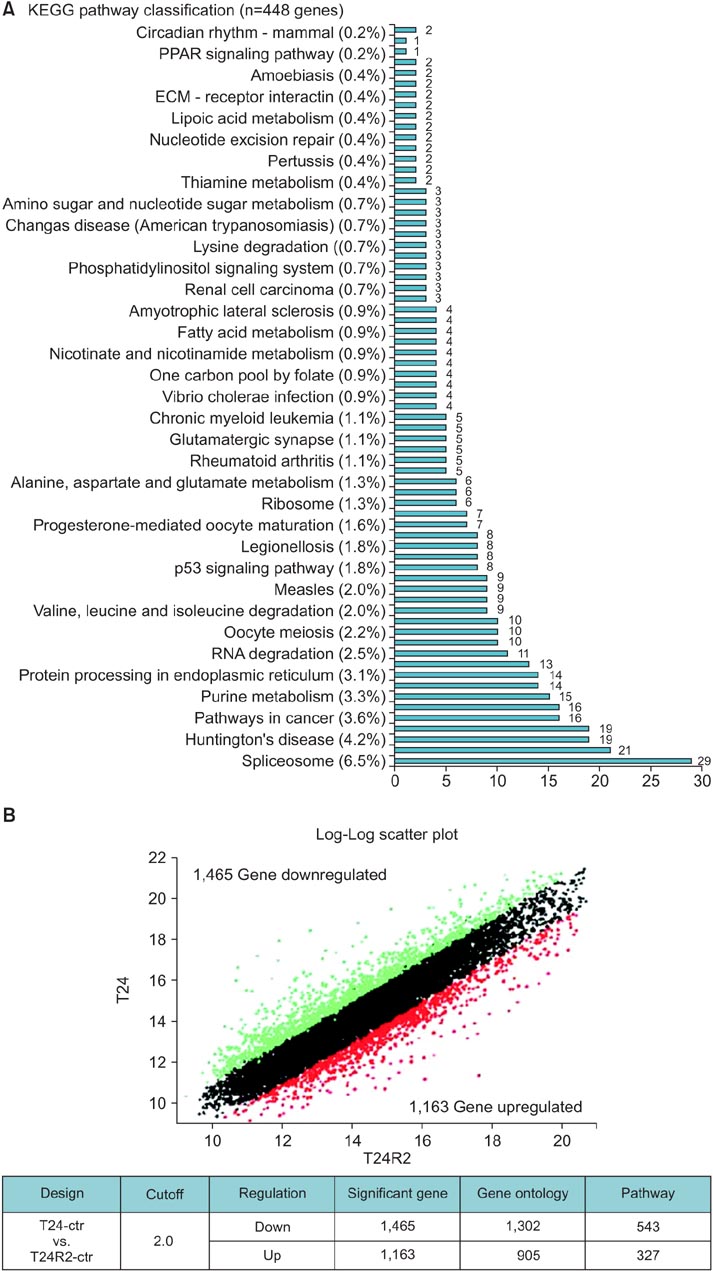
The cisplatin sensitive human BC cell line (T24) and the cisplatin resistant BC cell line, T24R2, were used for microarray analysis to determine the differential expression of genes that are significant in cisplatin resistance. Candidate upregulated genes belonging to three well-known cancer-related KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) pathways (p53 tumor suppressor, apoptosis, and cell cycle) were selected from the microarray data. These candidate genes, differentially expressed in T24 and T24R2, were then confirmed by quantitative RT-PCR and western blot. A fold change > or =2 with a p-value <0.05 was considered significant.
RESULTS
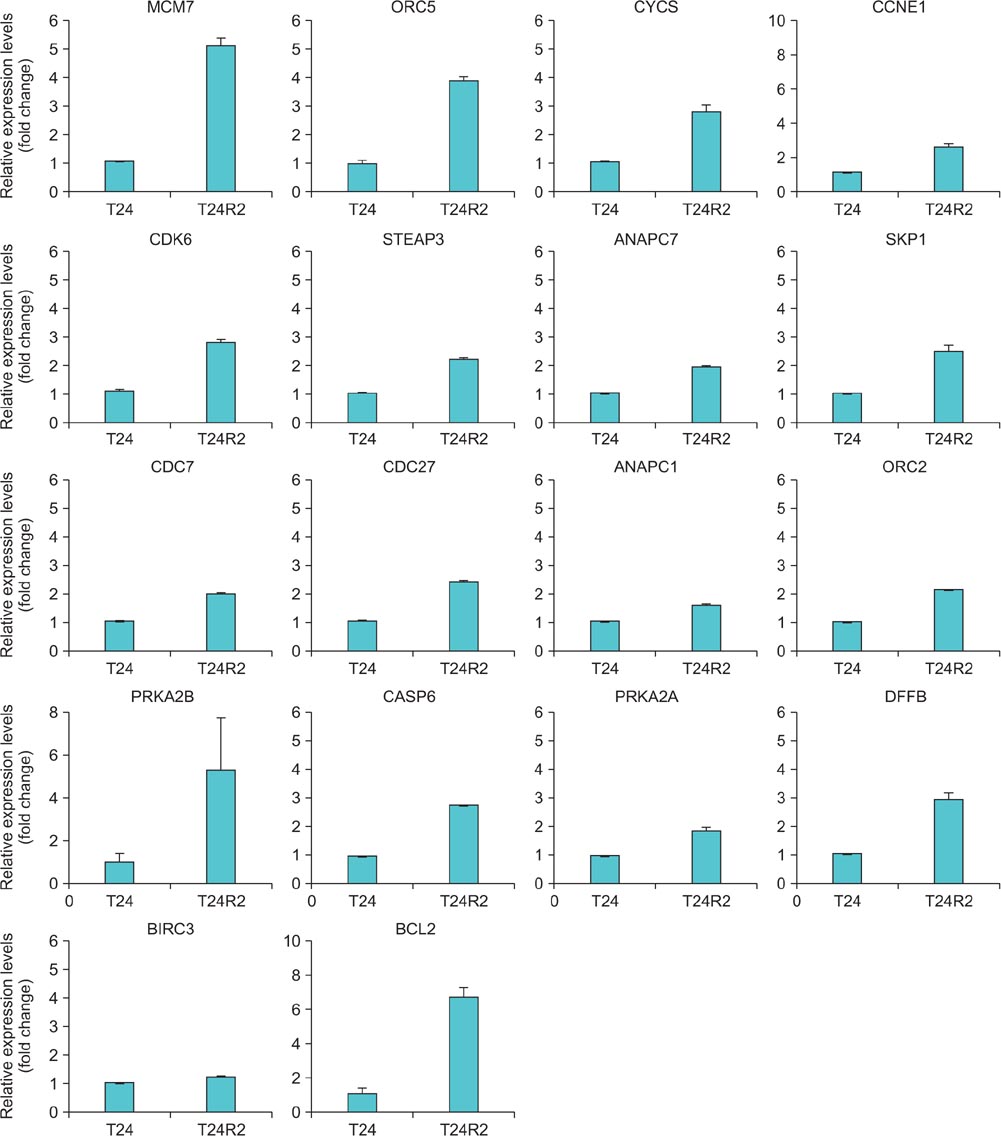
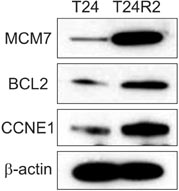
A total of 18 significantly upregulated genes were detected in the three selected cancer-related pathways in both microarray and RT-PCR analyses. These genes were PRKAR2A, PRKAR2B, CYCS, BCL2, BIRC3, DFFB, CASP6, CDK6, CCNE1, STEAP3, MCM7, ORC2, ORC5, ANAPC1, and ANAPC7, CDC7, CDC27, and SKP1 . Western blot analyses also confirmed the upregulation of BCL2, MCM7, and CCNE1 at the protein level, indicating their crucial association with cisplatin resistance.
CONCLUSIONS
The BCL2, MCM7, and CCNE1 genes might play distinctive roles in cisplatin resistance in BC.
MeSH Terms
-
Antineoplastic Agents/*pharmacology
Cell Line, Tumor
Cisplatin/*pharmacology
Cyclin E/*biosynthesis/genetics
Drug Resistance, Neoplasm/genetics
Gene Expression Regulation, Neoplastic
Genes, Neoplasm
Humans
Minichromosome Maintenance Complex Component 7/*biosynthesis/genetics
Oncogene Proteins/*biosynthesis/genetics
Protein Array Analysis/methods
Proto-Oncogene Proteins c-bcl-2/*biosynthesis/genetics
Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction/methods
Up-Regulation
Urinary Bladder Neoplasms/*drug therapy/genetics/metabolism
Antineoplastic Agents
Cisplatin
Cyclin E
Minichromosome Maintenance Complex Component 7
Oncogene Proteins
Proto-Oncogene Proteins c-bcl-2
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bamias A, Dafni U, Karadimou A, Timotheadou E, Aravantinos G, Psyrri A, et al. Prospective, open-label, randomized, phase III study of two dose-dense regimens MVAC versus gemcitabine/cisplatin in patients with inoperable, metastatic or relapsed urothelial cancer: a Hellenic Cooperative Oncology Group study (HE 16/03). Ann Oncol. 2013; 24:1011–1017.2. Gloeckler Ries LA, Reichman ME, Lewis DR, Hankey BF, Edwards BK. Cancer survival and incidence from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) program. Oncologist. 2003; 8:541–552.3. Gorin MA, Ayyathurai R, Soloway MS. Diagnosis and treatment of bladder cancer: how can we improve? Postgrad Med. 2012; 124:28–36.4. Konstantakou EG, Voutsinas GE, Karkoulis PK, Aravantinos G, Margaritis LH, Stravopodis DJ. Human bladder cancer cells undergo cisplatin-induced apoptosis that is associated with p53-dependent and p53-independent responses. Int J Oncol. 2009; 35:401–416.5. Galluzzi L, Senovilla L, Vitale I, Michels J, Martins I, Kepp O, et al. Molecular mechanisms of cisplatin resistance. Oncogene. 2012; 31:1869–1883.6. Lee S, Yoon CY, Byun SS, Lee E, Lee SE. The role of c-FLIP in cisplatin resistance of human bladder cancer cells. J Urol. 2013; 189:2327–2334.7. Choi MK, Kim DD. Platinum transporters and drug resistance. Arch Pharm Res. 2006; 29:1067–1073.8. Miyake H, Hanada N, Nakamura H, Kagawa S, Fujiwara T, Hara I, et al. Overexpression of Bcl-2 in bladder cancer cells inhibits apoptosis induced by cisplatin and adenoviral-mediated p53 gene transfer. Oncogene. 1998; 16:933–943.9. Cho HJ, Kim JK, Kim KD, Yoon HK, Cho MY, Park YP, et al. Upregulation of Bcl-2 is associated with cisplatin-resistance via inhibition of Bax translocation in human bladder cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2006; 237:56–66.10. Byun SS, Kim SW, Choi H, Lee C, Lee E. Augmentation of cisplatin sensitivity in cisplatin-resistant human bladder cancer cells by modulating glutathione concentrations and glutathione-related enzyme activities. BJU Int. 2005; 95:1086–1090.11. Lee E, Min KJ, Kim SW, Lee HW, Cho KS, Kim KM, et al. Change of chemosensitivity and cellular characteristics of cisplatinum resistant human bladder cancer cells induced by long-term cisplatinum treatment. Korean J Urol. 1998; 39:305–310.12. Kim JK, Kim KD, Lee E, Lim JS, Cho HJ, Yoon HK, et al. Upregulation of Bfl-1/A1 via NF-kappaB activation in cisplatin-resistant human bladder cancer cell line. Cancer Lett. 2004; 212:61–70.13. Tamayo P, Slonim D, Mesirov J, Zhu Q, Kitareewan S, Dmitrovsky E, et al. Interpreting patterns of gene expression with self-organizing maps: methods and application to hematopoietic differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999; 96:2907–2912.14. Talaat S, Somji S, Toni C, Garrett SH, Zhou XD, Sens MA, et al. Kindlin-2 expression in arsenite- and cadmium-transformed bladder cancer cell lines and in archival specimens of human bladder cancer. Urology. 2011; 77:1507.e1–1507.e7.15. Borst P, Rottenberg S, Jonkers J. How do real tumors become resistant to cisplatin? Cell Cycle. 2008; 7:1353–1359.16. Kaufmann SH, Hengartner MO. Programmed cell death: alive and well in the new millennium. Trends Cell Biol. 2001; 11:526–534.17. Thornberry NA, Lazebnik Y. Caspases: enemies within. Science. 1998; 281:1312–1316.18. Benchimol S. p53-dependent pathways of apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2001; 8:1049–1051.19. Saleem A, Ibrahim N, Patel M, Li XG, Gupta E, Mendoza J, et al. Mechanisms of resistance in a human cell line exposed to sequential topoisomerase poisoning. Cancer Res. 1997; 57:5100–5106.20. Sasada T, Iwata S, Sato N, Kitaoka Y, Hirota K, Nakamura K, et al. Redox control of resistance to cis-diamminedichloroplatinum (II) (CDDP): protective effect of human thioredoxin against CDDP-induced cytotoxicity. J Clin Invest. 1996; 97:2268–2276.21. Cheng Q, Lee HH, Li Y, Parks TP, Cheng G. Upregulation of Bcl-x and Bfl-1 as a potential mechanism of chemoresistance, which can be overcome by NF-kappaB inhibition. Oncogene. 2000; 19:4936–4940.22. Golka K, Selinski S, Lehmann ML, Blaszkewicz M, Marchan R, Ickstadt K, et al. Genetic variants in urinary bladder cancer: collective power of the "wimp SNPs". Arch Toxicol. 2011; 85:539–554.23. Fu YP, Kohaar I, Moore LE, Lenz P, Figueroa JD, Tang W, et al. The 19q12 bladder cancer GWAS signal: association with cyclin E function and aggressive disease. Cancer Res. 2014; 74:5808–5818.24. Santamaria D, Ortega S. Cyclins and CDKS in development and cancer: lessons from genetically modified mice. Front Biosci. 2006; 11:1164–1188.25. Lei M. The MCM complex: its role in DNA replication and implications for cancer therapy. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2005; 5:365–380.26. Ma T, Van Tine BA, Wei Y, Garrett MD, Nelson D, Adams PD, et al. Cell cycle-regulated phosphorylation of p220(NPAT) by cyclin E/Cdk2 in Cajal bodies promotes histone gene transcription. Genes Dev. 2000; 14:2298–2313.27. Juric V, Chen CC, Lau LF. TNFα-induced apoptosis enabled by CCN1/CYR61: pathways of reactive oxygen species generation and cytochrome c release. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e31303.28. Cramer Borde E, Ouzegdouh Y, Ledgerwood EC, Morison IM. Congenital thrombocytopenia and cytochrome C mutation: a matter of birth and death. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2011; 37:664–672.29. Remus D, Beuron F, Tolun G, Griffith JD, Morris EP, Diffley JF. Concerted loading of Mcm2-7 double hexamers around DNA during DNA replication origin licensing. Cell. 2009; 139:719–730.30. Frohling S, Nakabayashi K, Scherer SW, Dohner H, Dohner K. Mutation analysis of the origin recognition complex subunit 5 (ORC5L) gene in adult patients with myeloid leukemias exhibiting deletions of chromosome band 7q22. Hum Genet. 2001; 108:304–309.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Expression of Bcl-2 and Bax in cis-Diamminedichloroplatinum (II)-Resistant Bladder Cancer Cell Lines
- Morphological Change with the Induction of Cisplatin Resistance from the Bladder Cell Lines
- Change of MDR Gene Expression and Glutathione Metabolism during Long Standing Low-dose Cisplatin Exposure in Bladder Carcinoma Cell Line
- Expression of p53, p16, PTEN, and c-myc Gene with Cisplatin Treatment in Cisplatin Resistant Ovarian Cancer Cell Line
- Change of Chemosensitivity and Cellular Characteristics of Cisplatinum Resistant Human Bladder Cancer Cells Induced by Long-term Cisplatinum Treatment