J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2004 Dec;11(4):194-201.
The Effect of Pulsed Electromagnetic Field in Human Intervertebral Disc Cell
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hwanlee@yumc.yonsei.ac.kr
Abstract
- STUDY DESIGN: An in vitro experiment.
OBJECTIVES
To assess the effect of pulsed sinusoidal EMF on human intervertebral disc (IVD) cells. LITERATURE REVIEW SUMMARY: Electromagnetic field (EMF) is known to modify some relevant physiological parameters of cells cultured in vitro, such as proliferation, synthesis, secretion of growth factors and transcription. EMF induces bone formation in delayed, non union and spinal fusion models. Also, the exposure of EMF has been shown to protect against the hazardous effect of smoking in the rabbit IVD.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
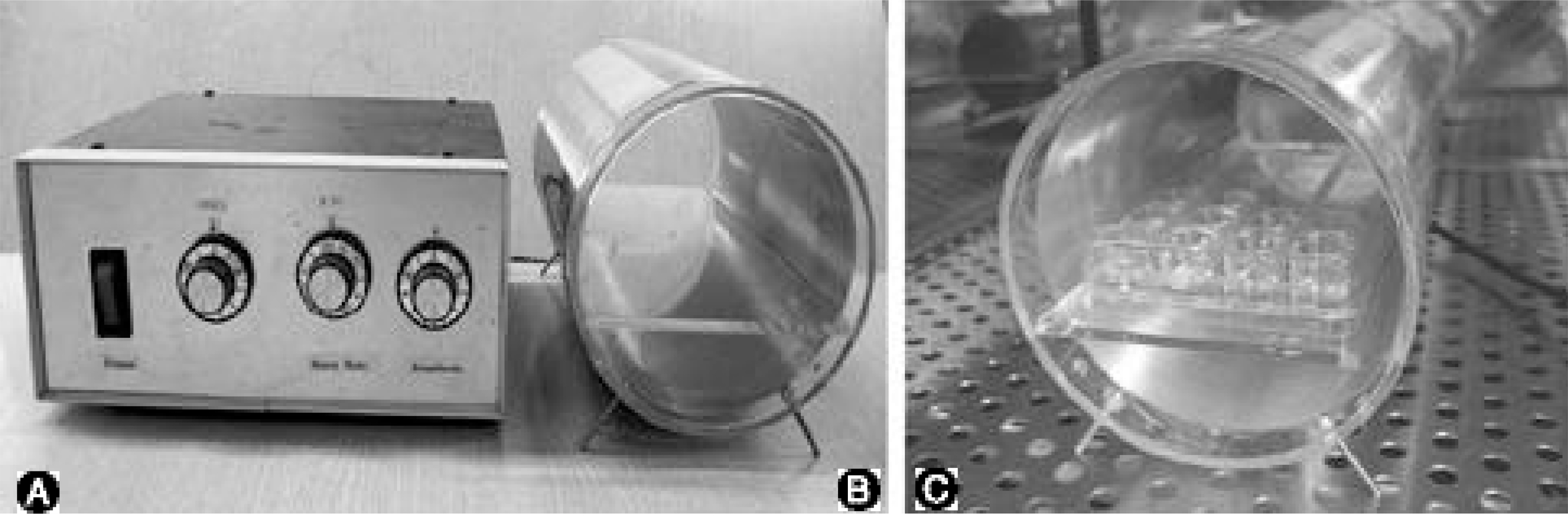
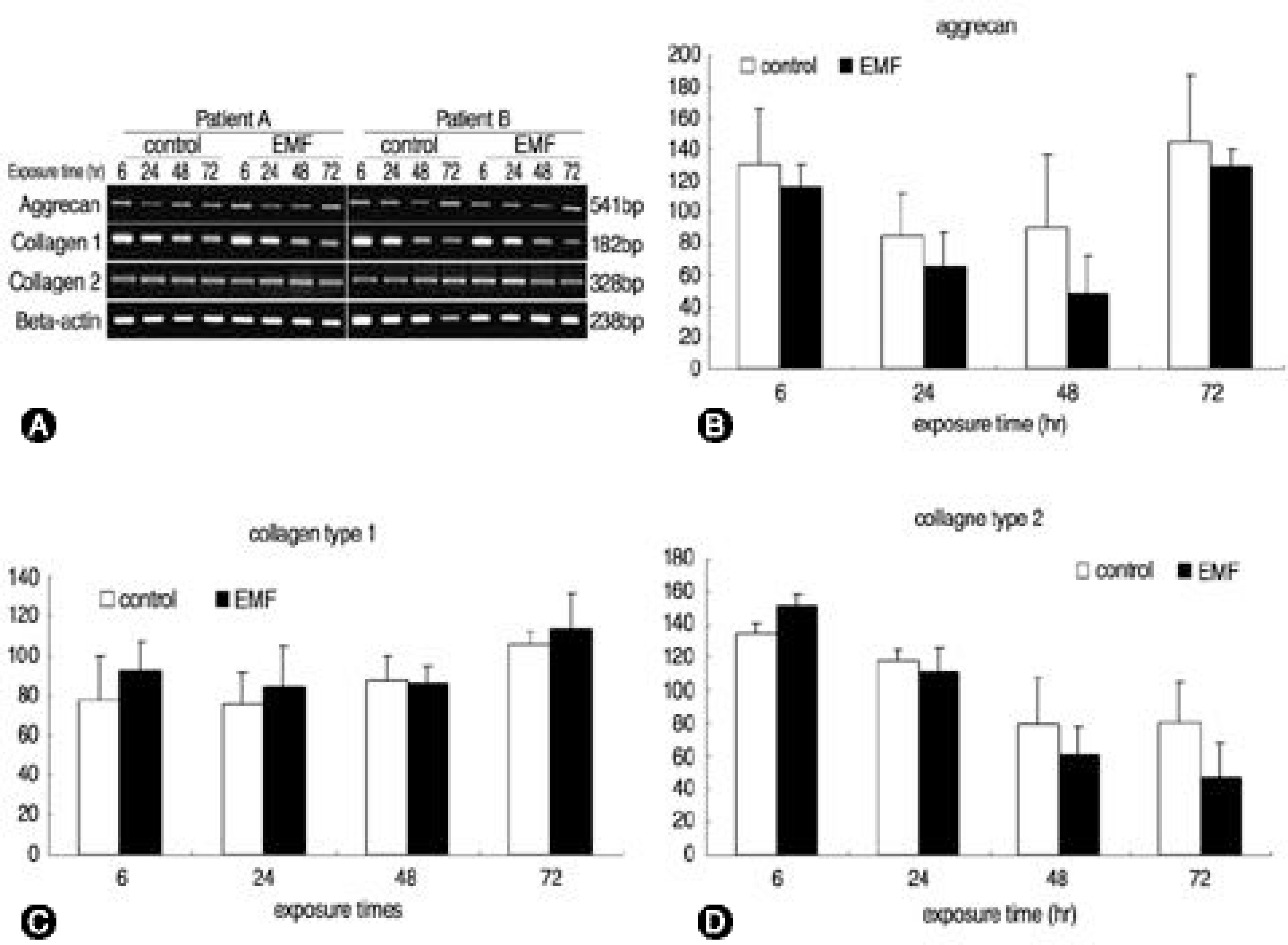
Human IVD cells were three-dimensionally cultured in alginate beads and exposed to a 650 omega, 1.8millitesla magnetic flux density, 60Hz sinusoidal wave of EMF. The cultures were divided into the control and EMF groups, with various exposure times. The cytotoxicity, and DNA and proteoglycan syntheses were measured by the MTT assay, and [3H]-thymidine and [35S]-sulfate incorporation, respectively. RT-PCRs were performed for aggrecan, and collagen types I and II mRNA expressions.
RESULTS
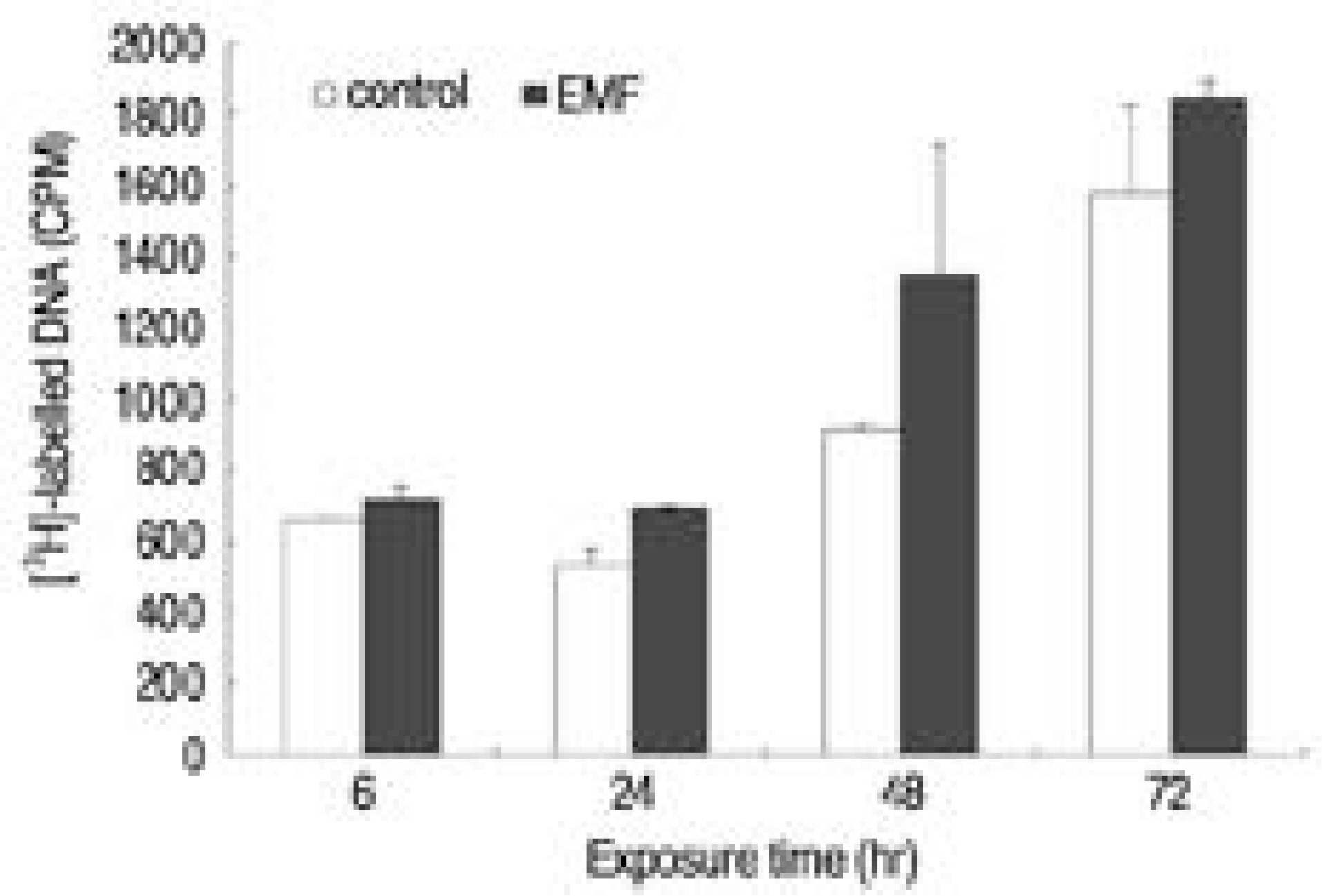
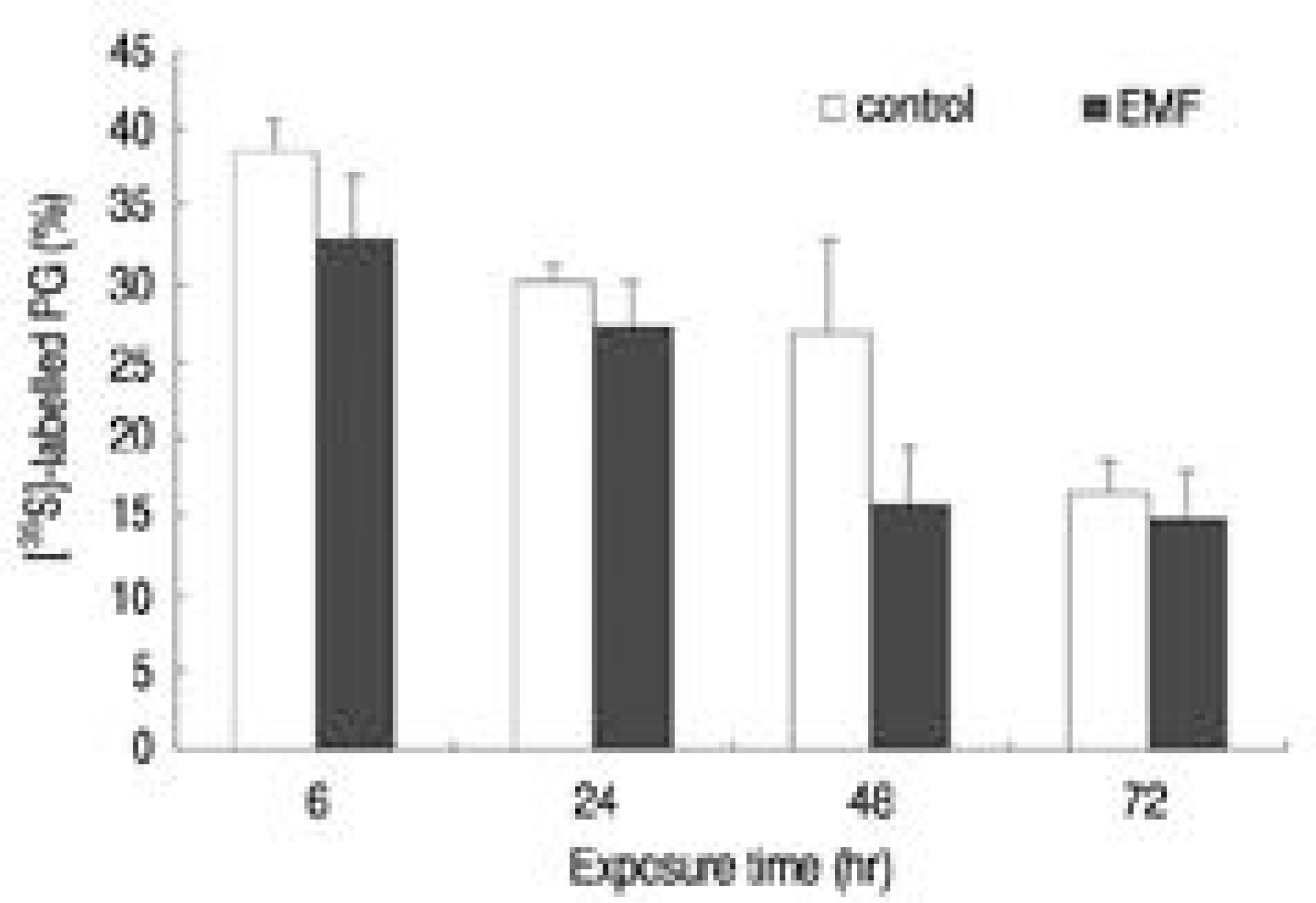
There was no recognizable cytotoxicity in the EMF group, but cellular proliferation was stimulated (p<0.05). Newly synthesized proteoglycan, normalized by DNA synthesis, was decreased in the EMF group (p<0.05) as were the expressions of aggrecan (48hour exposure) and type II collagen (72 hours exposure) mRNA compared to the control group.
CONCLUSIONS
EMF seems to be hazardous in the synthesis of the chondrogenic matrix, while marginally beneficial in the cellular proliferation of human IVD cells.
MeSH Terms
-
Aggrecans
Cell Proliferation
Collagen
Collagen Type II
DNA
Electromagnetic Fields*
Humans*
Intercellular Signaling Peptides and Proteins
Intervertebral Disc*
Magnets*
Osteogenesis
Proteoglycans
RNA, Messenger
Smoke
Smoking
Spinal Fusion
Aggrecans
Collagen
Collagen Type II
DNA
Intercellular Signaling Peptides and Proteins
Proteoglycans
RNA, Messenger
Smoke
Figure
Reference
-
1). Fontanesi G, Dal Monte A, Rinaldi E, et al. The effect of low frequency pulsing of an electromagnetic field for the treatment of congenital and acquired pseudoarthrosis. J Bioelectricity. 1984; 3:155–175.2). Traina GC, Fontanesi G, Costa P, et al. Effects of electromagnetic stimulation on patients suffering from non-union. A retrospective study with a control group. J Bioelectricity. 1991; 10:101–117.3). Brighton CT. Advanced clinical applications of electromagnetic field effects: bone and cartilage. Brighton CT, Pollack SR, editors. Electromagnetics in biology and medicine. San Francisco Press;San Francisco: p. 293–308. 1991.4). Guizzardi S, Di Silvestre M, Govoni P, Scandroglio R. Pulsed electromagnetic field stimulation on posterior spinal fusions: a histological study in rats. J Spinal Disord. 1994; 7:36–40.5). Goodman EM, Greenebaum B, Marron MT. Effects of electromagnetic fields on molecules and cells. International Rev Cytol 1. 1995; 58:279–338.
Article6). Hinsenkamp MG, Rooze MA. Morphological effect of electromagnetic stimulation on the skeleton of fetal or newborn mice. Acta Orthop Scand(suppl). 1982; 196:39–50.
Article7). Smith RL, Nagel DA. Effects of pulsing electromagnetic fields on bone growth and articular cartilage. Clin Orthop. 1983; 181:277–282.
Article8). Diniz P, Soejima K, Ito G. Nitric oxide mediates the e.ffects of pulsed electromagnetic field stimulation on the osteoblast proliferation and differentiation. Nitric Oxide. 2002; 7:18–23.
Article9). Chang K, Chang WHS. Pulsed electromagnetic fields prevent osteoporosis in an ovariectomized female rat model: A prostaglandin E2-associated process. Bioelectromagnetics. 2003; 24:189–198.
Article10). Libo AR, Williams TJ, Strong DM, Wistar RJ. Time varying magnetic fields: Effect on the DNA synthesis, Sci -ence. 1984; 223:818–819.11). Shomura K. Effects of pulsing electromagnetic field on the proliferation and calcification of osteoblast-like cell line, MC3T3-E1, J. Jpn. Orthod. Soc. 1997; 56:211–223.12). Hambly MF, Mooney V. Effect of smoking and pulsed electromagnetic fields on intradiscal pH in rabbits. Spine. 1992; 17(Suppl):S83–85.
Article13). McLeod KJ, Donahue HJ, Levin PE, Fontaine MA, Rubin CT. Electric fields modulate bone cell function in a density-dependent manner. J Bone Miner Res. 1983; 8:977–984.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The effects of static magnetic field and pulsed electromagnetic field on alkaline phosphatase and dna synthetic activity of ME3t3-E1 cells
- Biological Effect of TGF - B 1 on Human Intervertebral Disc by Cell Culture System
- The effect of pulsed electromagnetic field on the cultured calvarial cells of rat
- Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Stimulates Cellular Proliferation in Human Intervertebral Disc Cells
- An experimental study on the effect of half sine-wave pulsed electromagnetic field in orthodontic tooth movement