Tuberc Respir Dis.
2012 Oct;73(4):234-238.
A Case of Peritoneal Tuberculosis Developed after Infliximab Therapy for Refractory RA
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Hanyang University Guri Hospital, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Guri, Korea. drterry@hanyang.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Hanyang University Guri Hospital, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Guri, Korea.
Abstract
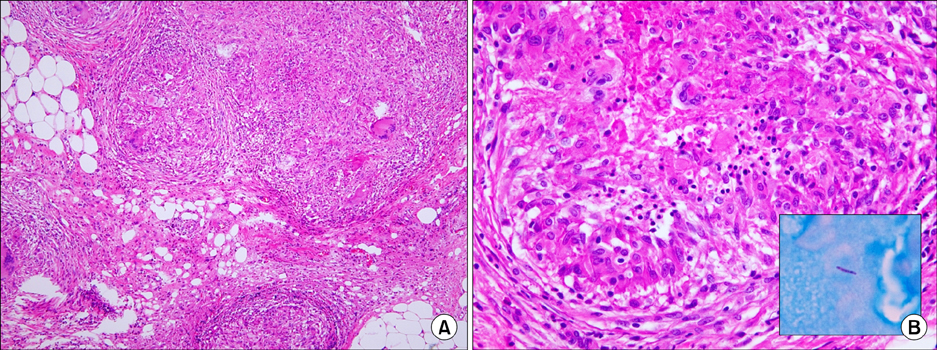
- Recently, interferon gamma releasing assay has been recommended to compensate the tuberculin skin test (TST) for screening for latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI). Although it improved the detection of LTBI before treatment with tumor necrosis factor blocker, its application to immune suppressed patients is limited. We report a case of peritoneal tuberculosis (TB) developed in a patient who tested positive for TST and QuantiFERON-TB Gold (QFT-G) before infliximab therapy, to emphasize the importance of monitoring during treatment. A 52-year-old woman presented with abdominal distension. She had been diagnosed with seropositive rheumatoid arthritis six years ago. She had started taking infliximab six months ago. All screening tests for TB were performed and the results of all were negative. At admission, the results of repeated TST and QFT-G tests were positive. Histopathological examination confirmed peritoneal TB. The patient started anti-TB therapy and the symptoms were relieved.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kievit W, Fransen J, Adang EM, den Broeder AA, Bernelot Moens HJ, Visser H, et al. Long-term effectiveness and safety of TNF-blocking agents in daily clinical practice: results from the Dutch Rheumatoid Arthritis Monitoring register. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2011. 50:196–203.2. Dixon WG, Hyrich KL, Watson KD, Lunt M, Galloway J, Ustianowski A, et al. Drug-specific risk of tuberculosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with anti-TNF therapy: results from the British Society for Rheumatology Biologics Register (BSRBR). Ann Rheum Dis. 2010. 69:522–528.3. Wolfe F, Michaud K, Anderson J, Urbansky K. Tuberculosis infection in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and the effect of infliximab therapy. Arthritis Rheum. 2004. 50:372–379.4. Seong SS, Choi CB, Woo JH, Bae KW, Joung CL, Uhm WS, et al. Incidence of tuberculosis in Korean patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA): effects of RA itself and of tumor necrosis factor blockers. J Rheumatol. 2007. 34:706–711.5. Keane J, Gershon S, Wise RP, Mirabile-Levens E, Kasznica J, Schwieterman WD, et al. Tuberculosis associated with infliximab, a tumor necrosis factor alpha-neutralizing agent. N Engl J Med. 2001. 345:1098–1104.6. Kwok SK, Park SH. Guidelines for prevention of tuberculosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with TNF-alpha blockers. J Korean Rheum Assoc. 2007. 14:105–111.7. Gómez-Reino JJ, Carmona L, Valverde VR, Mola EM, Montero MD. BIOBADASER Group. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with tumor necrosis factor inhibitors may predispose to significant increase in tuberculosis risk: a multicenter active-surveillance report. Arthritis Rheum. 2003. 48:2122–2127.8. Kang YA, Lee HW, Yoon HI, Cho B, Han SK, Shim YS, et al. Discrepancy between the tuberculin skin test and the whole-blood interferon gamma assay for the diagnosis of latent tuberculosis infection in an intermediate tuberculosis-burden country. JAMA. 2005. 293:2756–2761.9. Furst DE, Wallis R, Broder M, Beenhouwer DO. Tumor necrosis factor antagonists: different kinetics and/or mechanisms of action may explain differences in the risk for developing granulomatous infection. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2006. 36:159–167.10. Ponce de León D, Acevedo-Vásquez E, Sánchez-Torres A, Cucho M, Alfaro J, Perich R, et al. Attenuated response to purified protein derivative in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: study in a population with a high prevalence of tuberculosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005. 64:1360–1361.11. Ponce de Leon D, Acevedo-Vasquez E, Alvizuri S, Gutierrez C, Cucho M, Alfaro J, et al. Comparison of an interferon-gamma assay with tuberculin skin testing for detection of tuberculosis (TB) infection in patients with rheumatoid arthritis in a TB-endemic population. J Rheumatol. 2008. 35:776–781.12. Park H, Park CW, Kim KB, Lee MJ, Zeon SJ, Shim SC, et al. A case of peritoneal tuberculosis with Poncet's disease in a patient treated with infliximab. J Rheum Dis. 2011. 18:55–59.13. Kim IT, Park HB, Lee SH, Hyun YK, Kim YJ, Lee YW, et al. Tuberculous peritonitis in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis treated with infliximab. J Rheum Dis. 2011. 18:320–323.14. Park JH, Seo GY, Lee JS, Kim TH, Yoo DH. Positive conversion of tuberculin skin test and performance of interferon release assay to detect hidden tuberculosis infection during anti-tumor necrosis factor agent trial. J Rheumatol. 2009. 36:2158–2163.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Infliximab-induced Psoriasis in Treatment of Ankylosing Spondylitis
- A Case of Miliary Tuberculosis in a Patient with Behcet's Disease and Uveitis Receiving Infliximab
- Tuberculous Peritonitis in a Patient with Rheumatoid Arthritis Treated with Infliximab
- Multidrug-resistant Disseminated Tuberculosis Related to Infliximab in a Patient with Ulcerative Colitis and Negative Evaluation for Latent Tuberculosis
- A Case of Multiple Tuberculosis Associated with Infliximab Therapy in Crohn's Disease