J Rheum Dis.
2014 Oct;21(5):274-277. 10.4078/jrd.2014.21.5.274.
A Case of Infliximab-induced Psoriasis in Treatment of Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Maryknoll Medical Center, Busan, Korea. ete@lycos.co.kr
- KMID: 2222954
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2014.21.5.274
Abstract
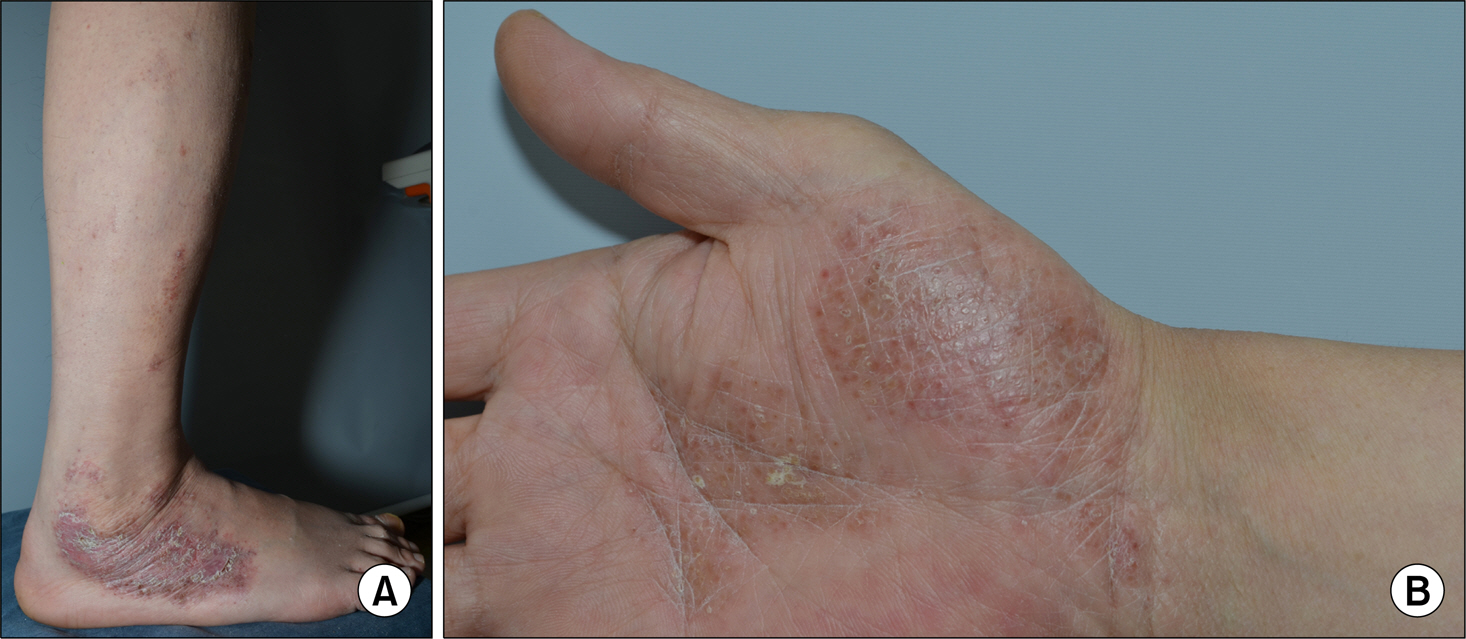
- Infliximab, which is indicated for refractory rheumatoid arthritis (RA), ankylosing spondylitis (AS) and Crohn's disease, has cutaneous adverse events including skin rash, urticaria, pruritus, and lupus-like eruption. Psoriasis induced by infliximab is very rare. In Korea, it is infrequently reported in Crohn's disease or RA and never reported in AS. We encountered a case of psoriasis induced by infliximab treatment for AS, and report here on this case along with a review of the relevant literature.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Flendrie M, Vissers WH, Creemers MC, de Jong EM, van de Kerkhof PC, van Riel PL. Dermatological conditions during TNF-alpha-blocking therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a prospective study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2005; 7:R666–76.2. Famenini S, Wu JJ. Infliximab-induced psoriasis in treatment of Crohn's disease-associated ankylosing spondylitis: case report and review of 142 cases. J Drugs Dermatol. 2013; 12:939–43.3. Kim JY, Choi M, Cho KH. A case of pustular psoriasis developed during infliximab treatment for crohn's disease. Korean J Dermatol. 2012; 50:810–3.4. Jwa YJ, Kim NH, Park HJ, Park JS, Bae WK, Kim KA, et al. A case of psoriasis induced by infliximab treatment for Crohn's disease. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2010; 56:324–8.
Article5. Park BC, Lim HJ, Kim BS, Lee WJ, Kim do W, Lee SJ. Repeated Paradoxical Aggravation of Preexisting Psoriasis during Infliximab Treatment for Crohn's Disease. Ann Dermatol. 2009; 21:60–2.
Article6. Choi YJ, Kim DS, Park JM, Oh SH, Park YK, Lee JH. A case of psoriasiform eruption triggered by tumor necrosis factor-alpha antagonist therapy. Korean J Dermatol. 2008; 46:721–3.7. Kim SY, Kim GM, Kim SY. Case of recurrent generalized pustular psoriasis treated with a combination of infliximab with methotrexate and retinoid. Korean J Dermatol. 2006; 44:67–70.8. Oh JM, Koh EM, Kim H, Lee J, Ahn JK, Cha HS, et al. Exacerbation of psoriatic skin lesion followed by tnfalpha antagonist treatment. J Korean Rheum Assoc. 2010; 17:200–4.9. Park JJ, Lee SC. A Case of Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha Inhibitors-induced Pustular Psoriasis. Ann Dermatol. 2010; 22:212–5.10. Hahn HJ, Jung JW, Park HJ, Lee YW, Choe YB, Ahn KJ. A case of psoriasiform dermatitis following adalimumab injection for treatment of ankylosing spondylitis. Korean J Dermatol. 2013; 51:743–5.11. Nestle FO, Kaplan DH, Barker J. Psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2009; 361:496–509.
Article12. Fidder H, Schnitzler F, Ferrante M, Noman M, Katsanos K, Segaert S, et al. Long-term safety of infliximab for the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease: a single-centre cohort study. Gut. 2009; 58:501–8.
Article13. Joyau C, Veyrac G, Dixneuf V, Jolliet P. Anti-tumour necrosis factor alpha therapy and increased risk of de novo psoriasis: is it really a paradoxical side effect? Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2012; 30:700–6.14. Gilliet M, Conrad C, Geiges M, Cozzio A, Thürlimann W, Burg G, et al. Psoriasis triggered by toll-like receptor 7 agonist imiquimod in the presence of dermal plasmacytoid dendritic cell precursors. Arch Dermatol. 2004; 140:1490–5.
Article15. Aeberli D, Seitz M, Jüni P, Villiger PM. Increase of peripheral CXCR3 positive T lymphocytes upon treatment of RA patients with TNF-alpha inhibitors. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2005; 44:172–5.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Development of Renal Disorder in a Patient Receiving Infliximab (Remicade(R)) for Psoriasis
- A Case of Hypopigmented Mycosis Fungoides in a Patient with Ankylosing Spondylitis during Treatment with Infliximab
- Occurrence of tuberculous pleurisy associated with infliximab therapy
- A Case of Tuberculous Peritonitis in a Patient with Ankylosing Spondylitis during Infliximab Therapy
- TNF Inhibitors and Uveitis in Ankylosing Spondylitis