J Rheum Dis.
2011 Dec;18(4):320-323. 10.4078/jrd.2011.18.4.320.
Tuberculous Peritonitis in a Patient with Rheumatoid Arthritis Treated with Infliximab
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Kwandong University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea.
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. beconst@cau.ac.kr
- KMID: 2223139
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2011.18.4.320
Abstract
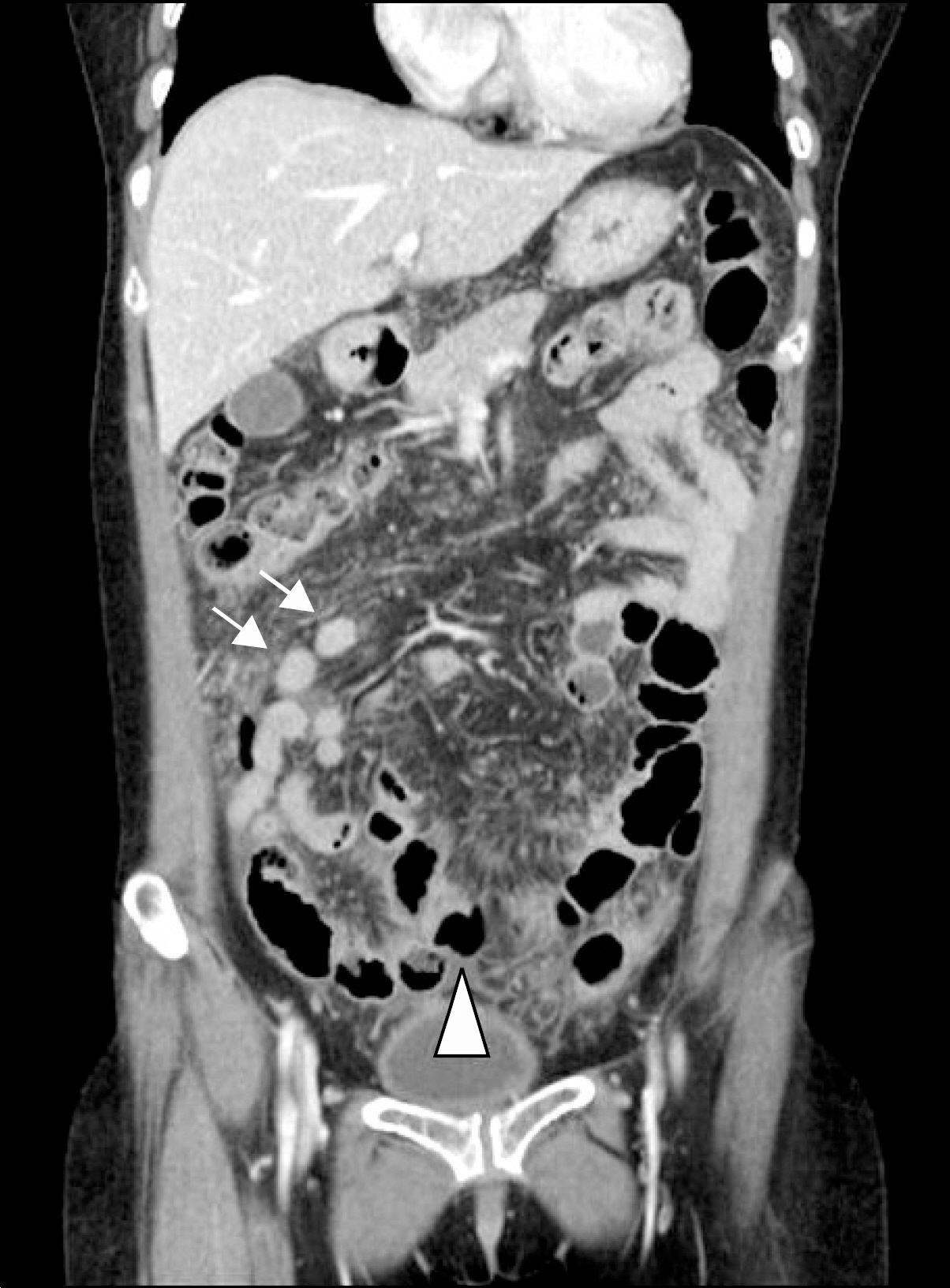
- One of the severe adverse reactions to anti-tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha therapy is the reactivation of tuberculosis. We present a case of tuberculous peritonitis in a 57-year-old woman with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) that appeared during treatment with infliximab. Confirming a diagnosis of tuberculous peritonitis is difficult and can be delayed because of the nonspecific symptoms, the rarity of the disease and the low detection rate of mycobacteria in ascites fluid. This case illustrates that prompt anti-tuberculous therapy is needed for suspected cases of tuberculous peritonitis in RA patients treated with infliximab.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Szerszen A, Gupta S, Seminara D, Jarrett M, Goldstein M. Peritoneal tuberculosis complicated by immune recon- stitution inflammatory syndrome in a patient treated with infliximab?: a case for adjuvant immunosuppressive therapy. J Clin Rheumatol. 2009; 15:417–8.2. Verhave JC, van Altena R, Wijnands MJ, Roerdink HT. Tuberculous peritonitis during infliximab therapy. Neth J Med. 2008; 66:77–80.3. Matsumoto T, Tanaka T, Kawase I. Infliximab for rheumatoid arthritis in a patient with tuberculosis. N Engl J Med. 2006; 355:740–1.
Article4. Gutié rrez-Macías A, Lizarralde-Palacios E, Martínez-Odriozola P, Miguel-de la Villa F. Tuberculous peritonitis in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis treated with adalimumab. Clin Rheumatol. 2007; 26:452–3.
Article5. Szeto T, Peterson J, Silva F. A case of tuberculous peritonitis in the United States in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis treated with adalimumab. J Clin Rheumatol. 2010; 16:135–7.
Article6. Antolín J, Azahara M, Hernández C, Blanco M, Mao L, Cigüenza R. Tuberculous peritonitis after treatment with adalimumab. Scand J Infect Dis. 2008; 40:677–8.
Article7. Manadan AM, Block JA, Sequeira W. Mycobacteria tuberculosis peritonitis associated with etanercept therapy. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2003; 21:526.8. Park H, Park CW, Kim KB, Lee MJ, Zeon SJ, Shim SC, et al. A case of peritoneal tuberculosis with poncet's disease in a patient treated with infliximab. J Rheum Dis. 2011; 18:55–9.
Article9. Tubach F, Salmon D, Ravaud P, Allanore Y, Goupille P, Bréban M, et al. Research Axed on Tolerance of Biotherapies Group. Risk of tuberculosis is higher with antitumor necrosis factor monoclonal antibody therapy than with soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor therapy: The three-year prospective French Research Axed on Tolerance of Biotherapies registry. Arthritis Rheum. 2009; 60:1884–94.
Article10. Plessner HL, Lin PL, Kohno T, Louie JS, Kirschner D, Chan J, et al. Neutralization of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) by antibody but not TNF receptor fusion molecule exacerbates chronic murine tuberculosis. J Infect Dis. 2007; 195:1643–50.
Article11. Hamdi H, Mariette X, Godot V, Weldingh K, Hamid AM, Prejean MV, et al. RATIO (Recherche sur Anti-TNF et Infections Opportunistes) Study Group. Inhibition of an-ti-tuberculosis T-lymphocyte function with tumour necrosis factor antagonists. Arthritis Res Ther. 2006; 8:R114.12. Chow KM, Chow VC, Hung LC, Wong SM, Szeto CC. Tuberculous peritonitis-associated mortality is high among patients waiting for the results of mycobacterial cultures of ascitic fluid samples. Clin Infect Dis. 2002; 35:409–13.
Article13. Ferrara G, Losi M, D'Amico R, Roversi P, Piro R, Meacci M, et al. Use in routine clinical practice of two commercial blood tests for diagnosis of infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis: a prospective study. Lancet. 2006; 367:1328–34.
Article14. Yuksel H, Akoğlu TF. Serum and synovial fluid adenosine deaminase activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, and reactive arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1988; 47:492–5.
Article15. Riquelme A, Calvo M, Salech F, Valderrama S, Pattillo A, Arellano M, et al. Value of adenosine deaminase (ADA) in ascitic fluid for the diagnosis of tuberculous peritonitis: a meta-analysis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2006; 40:705–10.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Tuberculous Peritonitis in a Patient with Ankylosing Spondylitis during Infliximab Therapy
- A Case of Peritoneal Tuberculosis with Poncet's Disease in a Patient Treated with Infliximab
- Synovial Chondromatosis in Knee Masquerading as Tuberculosis Arthritis
- A Case of Peritoneal Tuberculosis Developed after Infliximab Therapy for Refractory RA
- A Case of Bullous Pemphigoid Arising after Infliximab Therapy in a Patient with Rheumatoid Arthritis