Tuberc Respir Dis.
2012 Mar;72(3):284-292.
Prognosis of Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in Patients with Hematologic Diseases in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- 2Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, The Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. symonlee@catholic.ac.kr
- 4Catholic Blood and Marrow Transplantation Center, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
The aim of this study was to investigate therapeutic outcomes and assess factors associated with therapeutic outcomes in hematologic patients with invasive pulmonary aspergillosis (IPA).
METHODS
We analyzed all consecutive cases of IPA in adults with hematologic diseases from January 2008 to January 2009 at a Catholic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation (HSCT) Center in Seoul, Korea.
RESULTS
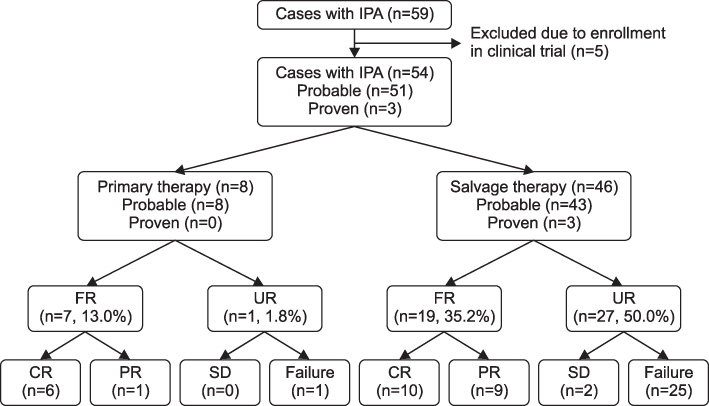
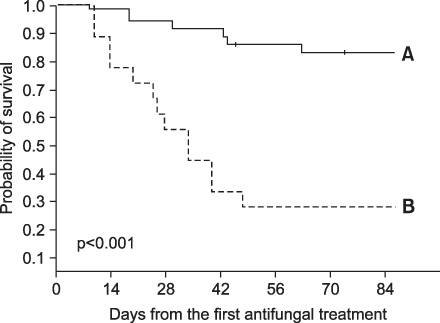
A total of 54 patients were identified. Underlying diseases were acute myelogenous leukemia (n=25), acute lymphoblastic leukemia (n=10), myelodysplastic syndrome (n=7), chronic myelogenous leukemia (n=3), multiple myeloma (n=3), severe aplastic anemia (n=2) and other hematologic diseases (n=4). Twenty six patients (48.2%) were assessed as having a favorable response, of which 16 patients (29.6%) showed complete response. Overall 12-week mortality and IPA attributable mortality were 38.9% (n=21) and 33.3% (n=18), respectively. In multivariate analysis, uncontrolled underlying disease (odds ratio [OR], 7.31; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.49~35.94; p=0.014) was associated with an unfavorable response, and for 12-week mortality, uncontrolled underlying disease (OR, 11.79; 95% CI, 1.49~93.46; p=0.020) and hypoalbuminemia (OR, 9.89; 95% CI, 1.42~68.99; p=0.021) were significantly poor prognostic factors.
CONCLUSION
IPA still remains as a poor therapeutic outcome, especially in patients with refractory hematologic diseases.
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Anemia, Aplastic
Hematologic Diseases
Hematology
Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
Humans
Hypoalbuminemia
Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis
Korea
Leukemia, Myelogenous, Chronic, BCR-ABL Positive
Leukemia, Myeloid, Acute
Multiple Myeloma
Multivariate Analysis
Myelodysplastic Syndromes
Precursor Cell Lymphoblastic Leukemia-Lymphoma
Prognosis
Figure
Reference
-
1. Wald A, Leisenring W, van Burik JA, Bowden RA. Epidemiology of Aspergillus infections in a large cohort of patients undergoing bone marrow transplantation. J Infect Dis. 1997. 175:1459–1466.2. Subirà M, Martino R, Franquet T, Puzo C, Altés A, Sureda A, et al. Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in patients with hematologic malignancies: survival and prognostic factors. Haematologica. 2002. 87:528–534.3. Wheat LJ, Walsh TJ. Diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis by galactomannan antigenemia detection using an enzyme immunoassay. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2008. 27:245–251.4. Herbrecht R, Denning DW, Patterson TF, Bennett JE, Greene RE, Oestmann JW, et al. Voriconazole versus amphotericin B for primary therapy of invasive aspergillosis. N Engl J Med. 2002. 347:408–415.5. Nivoix Y, Velten M, Letscher-Bru V, Moghaddam A, Natarajan-Amé S, Fohrer C, et al. Factors associated with overall and attributable mortality in invasive aspergillosis. Clin Infect Dis. 2008. 47:1176–1184.6. Yoo JH, Choi SM, Lee DG, Choi JH, Shin WS, Min WS, et al. Prognostic factors influencing infection-related mortality in patients with acute leukemia in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2005. 20:31–35.7. Parody R, Martino R, Sánchez F, Subirá M, Hidalgo A, Sierra J. Predicting survival in adults with invasive aspergillosis during therapy for hematological malignancies or after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: single-center analysis and validation of the Seattle, French, and Strasbourg prognostic indexes. Am J Hematol. 2009. 84:571–578.8. Gallien S, Fournier S, Porcher R, Bottero J, Ribaud P, Sulahian A, et al. Therapeutic outcome and prognostic factors of invasive aspergillosis in an infectious disease department: a review of 34 cases. Infection. 2008. 36:533–538.9. Ascioglu S, Rex JH, de Pauw B, Bennett JE, Bille J, Crokaert F, et al. Defining opportunistic invasive fungal infections in immunocompromised patients with cancer and hematopoietic stem cell transplants: an international consensus. Clin Infect Dis. 2002. 34:7–14.10. Herbrecht R, Letscher-Bru V, Oprea C, Lioure B, Waller J, Campos F, et al. Aspergillus galactomannan detection in the diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis in cancer patients. J Clin Oncol. 2002. 20:1898–1906.11. Marr KA, Balajee SA, McLaughlin L, Tabouret M, Bentsen C, Walsh TJ. Detection of galactomannan antigenemia by enzyme immunoassay for the diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis: variables that affect performance. J Infect Dis. 2004. 190:641–649.12. Upton A, Kirby KA, Carpenter P, Boeckh M, Marr KA. Invasive aspergillosis following hematopoietic cell transplantation: outcomes and prognostic factors associated with mortality. Clin Infect Dis. 2007. 44:531–540.13. De Pauw B, Walsh TJ, Donnelly JP, Stevens DA, Edwards JE, Calandra T, et al. Revised definitions of invasive fungal disease from the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer/Invasive Fungal Infections Cooperative Group and the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Mycoses Study Group (EORTC/MSG) Consensus Group. Clin Infect Dis. 2008. 46:1813–1821.14. Walsh TJ, Anaissie EJ, Denning DW, Herbrecht R, Kontoyiannis DP, Marr KA, et al. Treatment of aspergillosis: clinical practice guidelines of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2008. 46:327–360.15. von Eiff M, Roos N, Schulten R, Hesse M, Zühlsdorf M, van de Loo J. Pulmonary aspergillosis: early diagnosis improves survival. Respiration. 1995. 62:341–347.16. Greene RE, Schlamm HT, Oestmann JW, Stark P, Durand C, Lortholary O, et al. Imaging findings in acute invasive pulmonary aspergillosis: clinical significance of the halo sign. Clin Infect Dis. 2007. 44:373–379.17. Lin SJ, Schranz J, Teutsch SM. Aspergillosis case-fatality rate: systematic review of the literature. Clin Infect Dis. 2001. 32:358–366.18. Park SH, Choi SM, Lee DG, Choi JH, Yoo JH, Lee JW, et al. Current trends of infectious complications following hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in a single center. J Korean Med Sci. 2006. 21:199–207.19. Yeghen T, Kibbler CC, Prentice HG, Berger LA, Wallesby RK, McWhinney PH, et al. Management of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in hematology patients: a review of 87 consecutive cases at a single institution. Clin Infect Dis. 2000. 31:859–868.20. Pagano L, Akova M, Dimopoulos G, Herbrecht R, Drgona L, Blijlevens N. Risk assessment and prognostic factors for mould-related diseases in immunocompromised patients. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2011. 66:Suppl 1. i5–i14.21. Pagano L, Caira M, Candoni A, Offidani M, Martino B, Specchia G, et al. Invasive aspergillosis in patients with acute myeloid leukemia: a SEIFEM-2008 registry study. Haematologica. 2010. 95:644–650.22. Freifeld AG, Bow EJ, Sepkowitz KA, Boeckh MJ, Ito JI, Mullen CA, et al. Clinical practice guideline for the use of antimicrobial agents in neutropenic patients with cancer: 2010 update by the infectious diseases society of america. Clin Infect Dis. 2011. 52:e56–e93.23. Cornillet A, Camus C, Nimubona S, Gandemer V, Tattevin P, Belleguic C, et al. Comparison of epidemiological, clinical, and biological features of invasive aspergillosis in neutropenic and nonneutropenic patients: a 6-year survey. Clin Infect Dis. 2006. 43:577–584.24. Maertens J, Buvé K, Theunissen K, Meersseman W, Verbeken E, Verhoef G, et al. Galactomannan serves as a surrogate endpoint for outcome of pulmonary invasive aspergillosis in neutropenic hematology patients. Cancer. 2009. 115:355–362.25. Woods G, Miceli MH, Grazziutti ML, Zhao W, Barlogie B, Anaissie E. Serum Aspergillus galactomannan antigen values strongly correlate with outcome of invasive aspergillosis: a study of 56 patients with hematologic cancer. Cancer. 2007. 110:830–834.26. Silvestre J, Póvoa P, Coelho L, Almeida E, Moreira P, Fernandes A, et al. Is C-reactive protein a good prognostic marker in septic patients? Intensive Care Med. 2009. 35:909–913.27. Pettilä V, Pentti J, Pettilä M, Takkunen O, Jousela I. Predictive value of antithrombin III and serum C-reactive protein concentration in critically ill patients with suspected sepsis. Crit Care Med. 2002. 30:271–275.28. Claeys R, Vinken S, Spapen H, ver Elst K, Decochez K, Huyghens L, et al. Plasma procalcitonin and C-reactive protein in acute septic shock: clinical and biological correlates. Crit Care Med. 2002. 30:757–762.29. Chai LA, Netea MG, Teerenstra S, Earnest A, Vonk AG, Schlamm HT, et al. Early proinflammatory cytokines and C-reactive protein trends as predictors of outcome in invasive Aspergillosis. J Infect Dis. 2010. 202:1454–1462.30. Kontoyiannis DP. Are serum cytokines sensitive and specific enough to prognosticate in aspergillosis? J Infect Dis. 2011. 203:1503.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pulmonary Resection for Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in Hematological Malignancy Patients
- A Case of Acute Interstitial Pneumonia with Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis
- Surgical Management of Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in Hemtologic Malignancy Patients: Report of 2 cases
- A Case of chronic necrotizing pulmonary aspergillosis with pulmonary artery aneurysm
- Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis Invaded to Thoracic Vertebra in a Immunocompetent Host: A case report