Tuberc Respir Dis.
2010 Dec;69(6):450-455.
Usefulness of Serum Cortisol in Assessment for the Severity of Community-Acquired Pneumonia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Respiratory Medicine, Changwon Fatima Hospital, Changwon, Korea. hunpyopark@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Daegu Fatima Hospital, Daegu, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
High cortisol levels are frequently observed in patients with severe infections are of prognostic value in sepsis. The aim of this study was to evaluate the clinical usefulness of serum cortisol in assessment for the severity of community-acquired pneumonia (CAP).
METHODS
This study analyzed the results of 52 CAP subjects admitted in Changwon Fatima Hospital between July 2008 to May 2010. Total serum cortisol, infection markers such as C-reactive protein (CRP), procalcitonin (PCT) and CURB (Confusion, Uremia, Respiratory rate, Blood pressure)-65 were examined retrospectively.
RESULTS
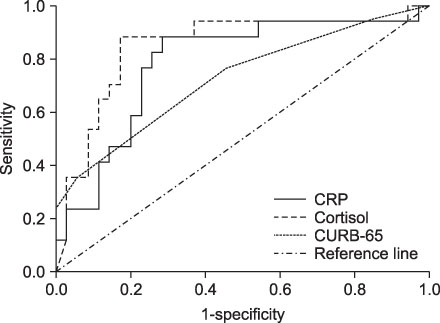
In clinically unstable subjects on admission day 4, baseline serum cortisol, CURB-65, and CRP were elevated significantly compared to those of stable subjects. Area under curve (AUC) of cortisol, CRP, and CURB-65 from ROC curves were 0.847, 0.783, and 0.724 respectively. In the subjects with serum cortisol > or =22.82 microg/dL, CRP, PCT, CURB-65 score, and mortality were significantly elevated.
CONCLUSION
These findings suggest that measurement of serum cortisol in early stage may provide helpful information in the assessment of CAP severity.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Song JH, Jung KS, Kang MW, Kim DJ, Pai H, Suh GY, et al. A Joint committee for CAP Treatment Guideline. Treatment guidelines for community-acquired pneumonia in Korea: an evidence-based approach to appropriate antimicrobial therapy. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2009. 67:281–302.2. Menéndez R, Martínez R, Reyes S, Mensa J, Filella X, Marcos MA, et al. Biomarkers improve mortality prediction by prognostic scales in community-acquired pneumonia. Thorax. 2009. 64:587–591.3. Salluh JI, Bozza FA, Soares M, Verdeal JC, Castro-Faria-Neto HC, Lapa E, Silva JR, et al. Adrenal response in severe community-acquired pneumonia: impact on outcomes and disease severity. Chest. 2008. 134:947–954.4. Kolditz M, Halank M, Schulte-Hubbert B, Höffken G. Adrenal function is related to prognosis in moderate community-acquired pneumonia. Eur Respir J. 2010. 36:615–621.5. Sam S, Corbridge TC, Mokhlesi B, Comellas AP, Molitch ME. Cortisol levels and mortality in severe sepsis. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2004. 60:29–35.6. Jarek MJ, Legare EJ, McDermott MT, Merenich JA, Kollef MH. Endocrine profiles for outcome prediction from the intensive care unit. Crit Care Med. 1993. 21:543–550.7. Drucker D, Shandling M. Variable adrenocortical function in acute medical illness. Crit Care Med. 1985. 13:477–479.8. Rothwell PM, Lawler PG. Prediction of outcome in intensive care patients using endocrine parameters. Crit Care Med. 1995. 23:78–83.9. Christ-Crain M, Stolz D, Jutla S, Couppis O, Müller C, Bingisser R, et al. Free and total cortisol levels as predictors of severity and outcome in community-acquired pneumonia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007. 176:913–920.10. Halm EA, Fine MJ, Marrie TJ, Coley CM, Kapoor WN, Obrosky DS, et al. Time to clinical stability in patients hospitalized with community-acquired pneumonia: implications for practice guidelines. JAMA. 1998. 279:1452–1457.11. El Azab SR, Rosseel PM, de Lange JJ, Groeneveld AB, van Strik R, van Wijk EM, et al. Dexamethasone decreases the pro- to anti-inflammatory cytokine ratio during cardiac surgery. Br J Anaesth. 2002. 88:496–501.12. Barton RN, Stoner HB, Watson SM. Relationships among plasma cortisol, adrenocorticotrophin, and severity of injury in recently injured patients. J Trauma. 1987. 27:384–392.13. Chernow B, Alexander HR, Smallridge RC, Thompson WR, Cook D, Beardsley D, et al. Hormonal responses to graded surgical stress. Arch Intern Med. 1987. 147:1273–1278.14. Cooper MS, Stewart PM. Corticosteroid insufficiency in acutely ill patients. N Engl J Med. 2003. 348:727–734.15. Annane D, Sébille V, Bellissant E. Ger-Inf-05 Study Group. Effect of low doses of corticosteroids in septic shock patients with or without early acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit Care Med. 2006. 34:22–30.16. Confalonieri M, Urbino R, Potena A, Piattella M, Parigi P, Puccio G, et al. Hydrocortisone infusion for severe community-acquired pneumonia: a preliminary randomized study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005. 171:242–248.17. Marik PE, Pastores SM, Annane D, Meduri GU, Sprung CL, Arlt W, et al. Recommendations for the diagnosis and management of corticosteroid insufficiency in critically ill adult patients: consensus statements from an international task force by the American College of Critical Care Medicine. Crit Care Med. 2008. 36:1937–1949.18. The aetiology, management and outcome of severe community-acquired pneumonia on the intensive care unit. The British Thoracic Society Research Committee and The Public Health Laboratory Service. Respir Med. 1992. 86:7–13.19. Fine MJ, Auble TE, Yealy DM, Hanusa BH, Weissfeld LA, Singer DE, et al. A prediction rule to identify low-risk patients with community-acquired pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 1997. 336:243–250.20. Mandell LA, Wunderink RG, Anzueto A, Bartlett JG, Campbell GD, Dean NC, et al. Infectious Diseases Society of America/American Thoracic Society consensus guidelines on the management of community-acquired pneumonia in adults. Clin Infect Dis. 2007. 44:S27–S72.21. Niederman MS. Making sense of scoring systems in community acquired pneumonia. Respirology. 2009. 14:327–335.22. Park HP, Lee JS, Jang YS, Kim MS. Usefulness of procalcitonin in the assessing the severity of community-acquired pneumonia patient. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2009. 67:430–435.23. Musher DM, Montoya R, Wanahita A. Diagnostic value of microscopic examination of Gram-stained sputum and sputum cultures in patients with bacteremic pneumococcal pneumonia. Clin Infect Dis. 2004. 39:165–169.