Lab Anim Res.
2013 Sep;29(3):168-173. 10.5625/lar.2013.29.3.168.
Effects of estrogen on food intake, serum leptin levels and leptin mRNA expression in adipose tissue of female rats
- Affiliations
-
- 1Behavioral Neuroscience Laboratory, Graduate School of Veterinary Medicine, Nippon Veterinary and Life Science University, Musashino, Tokyo, Japan. trsaito@nvlu.ac.jp
- 2Department of Laboratory Animal Science, Dokkyo University School of Medicine, Mibu, Tochigi, Japan.
- 3Civil International Corporation, Ueno, Taito, Japan.
- 4Department of Veterinary Anatomy, College of Veterinary Medicine, Chonnam National University, Gwangju, Korea.
- 5Department of Zoology, Faculty of Science, Kasetsart University, Bangkok, Thailand.
- KMID: 2312110
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5625/lar.2013.29.3.168
Abstract
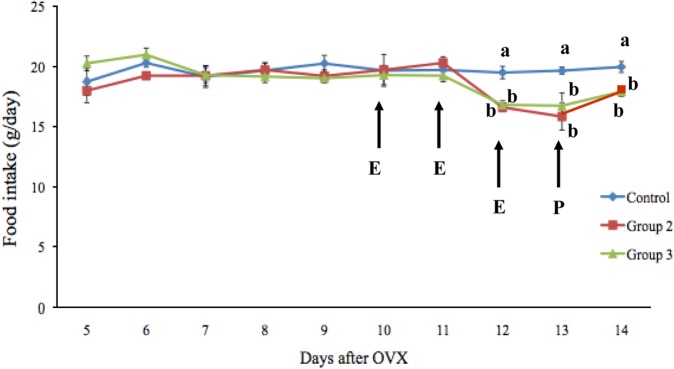
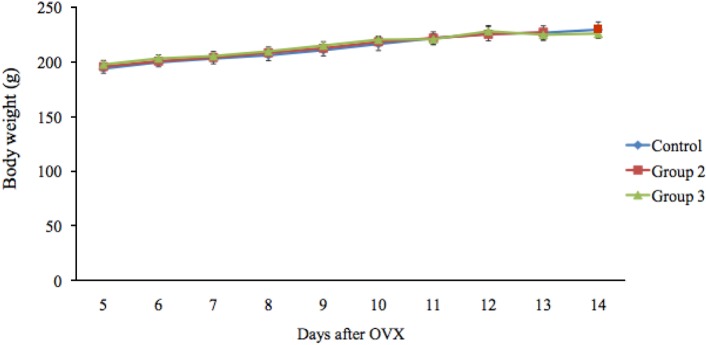
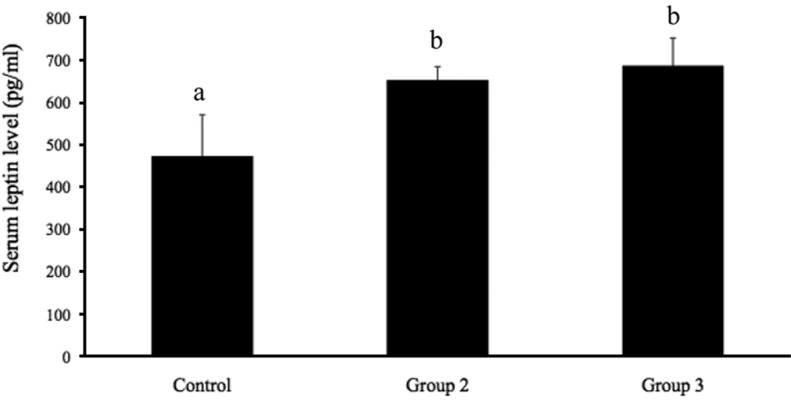
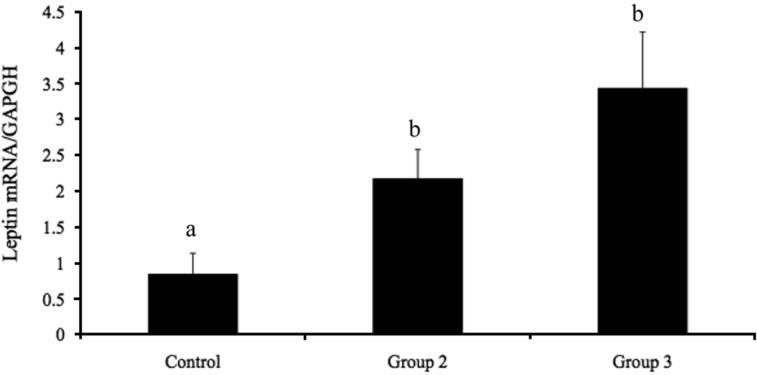
- The integration of metabolism and reproduction involves complex interactions of hypothalamic neuropeptides with metabolic hormones, fuels, and sex steroids. Of these, estrogen influences food intake, body weight, and the accumulation and distribution of adipose tissue. In this study, the effects of estrogen on food intake, serum leptin levels, and leptin mRNA expression were evaluated in ovariectomized rats. Seven-week-old female Wistar-Imamichi rats were ovariectomized and divided into three treatment groups: group 1 (the control group) received sesame oil, group 2 was given 17beta-estradiol benzoate, and group 3 received 17beta-estradiol benzoate plus progesterone. The body weight and food consumption of each rat were determined daily. Serum leptin levels and leptin mRNA expression were measured by ELISA and quantitative RT-PCR, respectively. Food consumption in the control group was significantly higher (P<0.05) than that in groups 2 and 3, although body weight did not significantly differ among the three groups. The serum leptin concentration and leptin mRNA expression were significantly higher (P<0.05) in groups 2 and 3 than in group 1, but no significant difference existed between groups 2 and 3. In conclusion, estrogen influenced food intake via the modulation of leptin signaling pathway in ovariectomized rats.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Zhang Y, Proenca R, Maffei M, Barone M, Leopold L, Friedman JM. Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature. 1994; 372(6505):425–432. PMID: 7984236.
Article2. Watanobe H, Suda T. A detailed study on the role of sex steroid milieu in determining plasma leptin concentrations in adult male and female rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999; 259(1):56–59. PMID: 10334915.
Article3. Mohamed WF, Alsuwaigh BR, Alsuhaimi EA. Effect of gonadal sex steroid on serum leptin level of both adult male and female rat. Sci J King Faisal Univ (Basic Appl Sci). 2004; 5:239–247.4. Stephens TW, Basinski M, Bristow PK, Bue-Valleskey JM, Burgett SG, Craft L, Hale J, Hoffmann J, Hsiung HM, Kriauciunas A, Mackellar W, Rosteck PR JR, Schoner B, Smith D, Tinsley FC, Zhang XY, Heiman M. The role of neuropeptide Y in the antiobesity action of the obese gene product. Nature. 1995; 377(6549):530–532. PMID: 7566151.
Article5. Halaas JL, Gajiwala KS, Maffei M, Cohen SL, Chait BT, Rabinowitz D, Lallone RL, Burley SK, Friedman JM. Weight-reducing effects of the plasma protein encoded by the obese gene. Science. 1995; 269(5223):543–546. PMID: 7624777.6. Rocha M, Grueso E, Puerta M. The anorectic effect of oestradiol does not involve changes in plasma and cerebrospinal fluid leptin concentrations in the rat. J Endocrinol. 2001; 171(2):349–354. PMID: 11691655.
Article7. Mayes JS, Watson GH. Direct effects of sex steroid hormones on adipose tissues and obesity. Obes Rev. 2004; 5(4):197–216. PMID: 15458395.
Article8. Pelleymounter MA, Baker MB, McCaleb M. Does estradiol mediate leptin's effects on adiposity and body weight? Am J Physiol. 1999; 276:E955–E963. PMID: 10329991.9. Saad MF, Damani S, Gingerich RL, Riad-Gabriel MG, Khan A, Boyadjian R, Jinagouda SD, el-Tawil K, Rude RK, Kamdar V. Sexual dimorphism in plasma leptin concentration. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1997; 82(2):579–584. PMID: 9024258.10. Demerath EW, Towne B, Wisemandle W, Blangero J, Chumlea WC, Siervogel RM. Serum leptin concentration, body composition, and gonadal hormones during puberty. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1999; 23(7):678–685. PMID: 10454100.
Article11. Pinilla L, Seoane LM, Gonzalez L, Carro E, Aguilar E, Casanueva FF, Dieguez C. Regulation of serum leptin levels by gonadal function in rats. Eur J Endocrinol. 1999; 140(5):468–473. PMID: 10229915.
Article12. Tanaka M, Nakaya S, Kumai T, Watanabe M, Tateishi T, Shimizu H, Kobayashi S. Effects of estrogen on serum leptin levels and leptin mRNA expression in adipose tissue in rats. Horm Res. 2001; 56(3-4):98–104. PMID: 11847470.
Article13. Fungfuang W, Nakada T, Nakao N, Terada M, Yokosuka M, Gizurarson S, Hau J, Moon C, Saito TR. Serum leptin concentrations, leptin mRNA expression, and food intake during the estrous cycle in rats. Lab Anim Res. 2013; 29(1):1–6. PMID: 23573101.
Article14. Eckel LA. Estradiol: a rhythmic, inhibitory, indirect control of meal size. Physiol Behav. 2004; 82(1):35–41. PMID: 15234587.
Article15. Yoneda N, Saito S, Kimura M, Yamada M, Iida M, Murakami T, Irahara M, Shima K, Aono T. The influence of ovariectomy on ob gene expression in rats. Horm Metab Res. 1998; 30(5):263–265. PMID: 9660086.16. Brown LM, Gent L, Davis K, Clegg DJ. Metabolic impact of sex hormones on obesity. Brain Res. 2010; 1350:77–85. PMID: 20441773.
Article17. Liang YQ, Akishita M, Kim S, Ako J, Hashimoto M, Iijima K, Ohike Y, Watanabe T, Sudoh N, Toba K, Yoshizumi M, Ouchi Y. Estrogen receptor beta is involved in the anorectic action of estrogen. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2002; 26:1103–1109. PMID: 12119576.18. Rivera HM, Eckel LA. Activation of central, but not peripheral, estrogen receptors is necessary for estradiol's anorexigenic effect in ovariectomized rats. Endocrinology. 2010; 151(12):5680–5688. PMID: 21068154.
Article19. Brown LM, Clegg DJ. Central effects of estradiol in the regulation of food intake, body weight, and adiposity. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2010; 122(1-3):65–73. PMID: 20035866.
Article20. Okamoto S, Shimizu M, Mizuno A, Higuchi T. Estrogens inhibit food intake in CCK-1 receptor-deficient rats. J Physiol Sci. 2010; 60(4):267–271. PMID: 20495898.
Article21. Bennett PA, Lindell K, Wilson C, Carlsson LM, Carlsson B, Robinson IC. Cyclical variations in the abundance of leptin receptors, but not in circulating leptin, correlate with NPY expression during the oestrous cycle. Neuroendocrinology. 1999; 69(6):417–423. PMID: 10364693.
Article22. Shimizu H, Shimomura Y, Nakanishi Y, Futawatari T, Ohtani K, Sato N, Mori M. Estrogen increases in vivo leptin production in rats and human subjects. J Endocrinol. 1997; 154(2):285–292. PMID: 9291839.
Article23. Henson MC, Castracane VD. Leptin in pregnancy: an update. Biol Reprod. 2006; 74(2):218–229. PMID: 16267210.24. Kristensen K, Pedersen SB, Richelsen B. Regulation of leptin by steroid hormones in rat adipose tissue. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999; 259(3):624–630. PMID: 10364468.
Article25. Alonso A, Fernández R, Moreno M, Ordóñez P, Díaz F, González C. Leptin and its receptor are controlled by 17beta-estradiol in peripheral tissues of ovariectomized rats. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2007; 232(4):542–549. PMID: 17392490.26. Gambino YP, Maymó JL, Pérez-Pérez A, Dueñas JL, Sánchez-Margalet V, Calvo JC, Varone CL. 17Beta-estradiol enhances leptin expression in human placental cells through genomic and nongenomic actions. Biol Reprod. 2010; 83(1):42–51. PMID: 20237333.27. Clegg DJ, Brown LM, Woods SC, Benoit SC. Gonadal hormones determine sensitivity to central leptin and insulin. Diabetes. 2006; 55(4):978–987. PMID: 16567519.
Article28. O'Neil JS, Burow ME, Green AE, McLachlan JA, Henson MC. Effects of estrogen on leptin gene promoter activation in MCF-7 breast cancer and JEG-3 choriocarcinoma cells: selective regulation via estrogen receptors alpha and beta. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2001; 176(1-2):67–75. PMID: 11369444.29. Yi KW, Shin JH, Seo HS, Lee JK, Oh MJ, Kim T, Saw HS, Kim SH, Hur JY. Role of estrogen receptor-alpha and -beta in regulating leptin expression in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2008; 16(11):2393–2399. PMID: 18719660.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Serum leptin concentrations, leptin mRNA expression, and food intake during the estrous cycle in rats
- Metformin Enhances Leptin Sensitivity in Aged Rats
- Changes of Lipogenic and Lipolytic Activities Following Repeated Fasting and Refeeding in Rat
- A study on changes of serum leptin and its expression in CAPD animal model
- Serum Leptin Levels in Children according to Pubertal Stage