Korean J Urol.
2008 Feb;49(2):160-167.
Changes in Corpus Cavernosum after Partial Bladder Outlet Obstruction in Rat
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, College of Medicine, Dongguk University, Gyeongju, Korea. ksleemd@ dongguk.ac.kr
Abstract
- PURPOSE
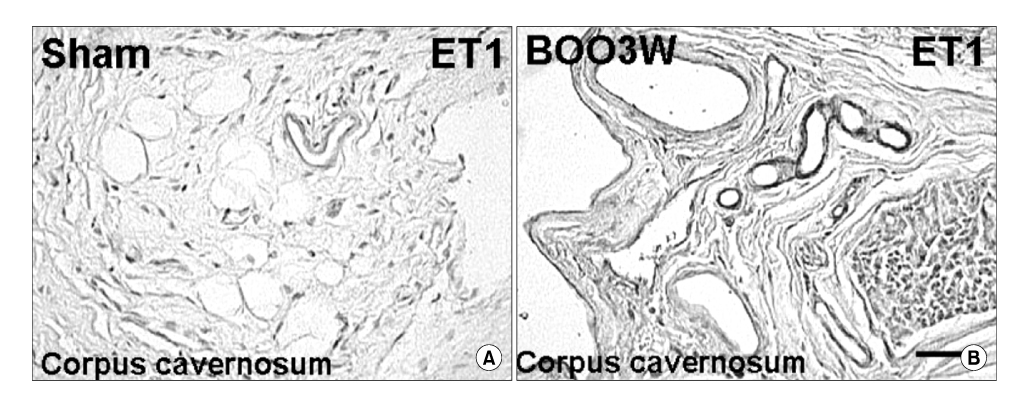
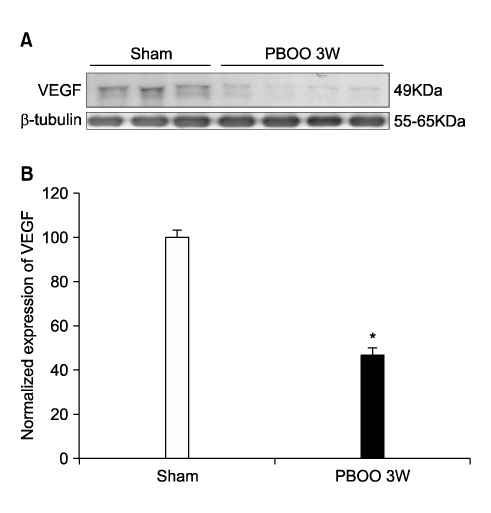
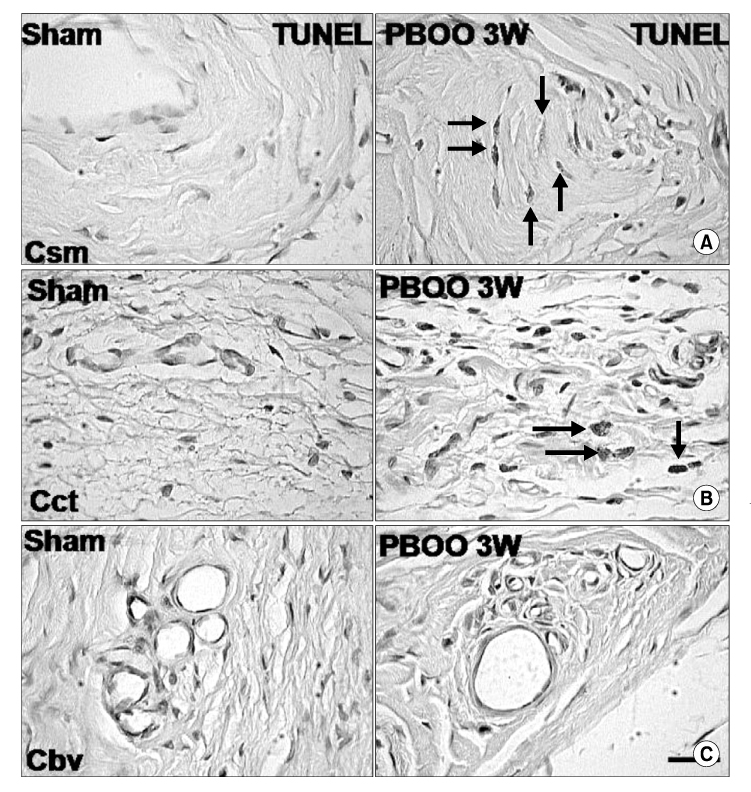
Abnormalities of the relaxation and contraction of the corpus cavernosum can lead to erectile dysfunction. Therefore, we induced a partial bladder outlet obstruction(PBOO) in male rats, and investigated the mechanisms of penile dysfunction with endothelial nitric oxide synthase(eNOS), vascular endothelial growth factor(VEGF), endothelin-1(ET-1), and apoptosis of peri-vascular smooth muscle and connective tissue cells in the corpus cavernosum. MATERIALS AND METHODS: PBOO was induced in 13 Sprague-Dawley rats by placing a 25 gauge needle sheath around the urethra, then ligating the bladder neck with a 3-0 suture. Three week after surgery, distal penile tissues were dissected for immunohistochemical staining, immunoblotting, and TUNEL staining. RESULTS: The expression of eNOS and VEGF were significantly decreased, whereas the expression of ET-1 and apoptosis of perivascular smooth muscle and connective tissue cells were significantly increased in the corpus cavernosum. CONCLUSIONS: The significant increase of ET-1 and apoptosis along with decreased eNOS and VEGF could mediate erectile dysfunction.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Apoptosis
Connective Tissue Cells
Contracts
Endothelin-1
Erectile Dysfunction
Humans
Immunoblotting
In Situ Nick-End Labeling
Male
Muscle, Smooth
Neck
Needles
Nitric Oxide
Nitric Oxide Synthase Type III
Rats
Rats, Sprague-Dawley
Relaxation
Sutures
Urethra
Urinary Bladder
Urinary Bladder Neck Obstruction
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A
Endothelin-1
Nitric Oxide
Nitric Oxide Synthase Type III
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A
Figure
Reference
-
1. Feldman HA, Goldstein I, Hatzichristou DG, Krane RJ, Mc-Kinlay JB. Impotence and its medical and psychosocial correlates: results of the Massachusetts Male Aging Study. J Urol. 1994. 151:54–61.2. Chung WS. The relationship between benign prostate hyperplasia and erectile dysfunction: what is reality? Korean J Androl. 2005. 23:111–115.3. Rosen R, Altwein J, Boyle P, Kirby RS, Lukacs B, Meuleman E, et al. Lower urinary tract symptoms and male sexual dysfunction: the multinational survey of the aging male (MSAM-7). Eur Urol. 2003. 44:637–649.4. Boyle P, Robertson C, Mazzetta C, Keech M, Hobbs R, Fourcade R, et al. The association between lower urinary tract symptoms and erectile dysfunction in four centres: the UrEpik study. BJU Int. 2003. 92:719–725.5. Braun MH, Sommer F, Haupt G, Mathers MJ, Reifenrath B, Engelmann UH. Lower urinary tract symptoms and erectile dysfunction: co-morbidity or typical "Aging Male" symptoms? results of the "Cologne Male Survey". Eur Urol. 2003. 44:588–594.6. Anderson KE. Pharmacology of lower urinary tract smooth muscles and penile erectile tissues. Pharmacol Rev. 1993. 45:253–308.7. Chang S, Hypolite JA, Zderic SA, Wein AJ, Chacko S, DiSanto ME. Enhanced force generation by corpus cavernosum smooth muscle in rabbits with partial bladder outlet obstruction. J Urol. 2002. 167:2636–2644.8. Becker AJ, Uckert S, Stief CG, Scheller F, Knapp WH, Machtens SA, et al. Systemic and cavernous plasma levels of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide during sexual arousal in healthy males. World J Urol. 2002. 20:59–63.9. Huggins JP, Pelton JT, Miller RC. The structure and specificity of endothelin receptors: their importance in physiology and medicine. Pharmacol Ther. 1993. 59:55–123.10. Blanker MH, Bohnen AM, Groeneveld FP, Bernsen RM, Prins A, Thomas S, et al. Correlates for erectile and ejaculatory dysfunction in older Dutch men: a community-based study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2001. 49:436–442.11. Ignarro LJ, Bush PA, Buga GM, Wood KS, Fukuto JM, Rajfer J. Nitric oxide and cyclic GMP formation upon electrical field stimulation cause relaxation of corpus cavernosum smooth muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990. 170:843–850.12. Podlasek CA, Zelner DJ, Bervig TR, Gonzalez CM, McKenna KE, McVary KT. Characterization and localaization of nitric oxide synthtase isoform in the BB/WOR diabetic rat. J Urol. 2001. 166:746–755.13. Sairam K, Kulinskaya E, McNicholas TA, Boustead GB, Hanbury DC. Sildenafil influences lower urinary tract symptoms. BJU Int. 2002. 90:836–839.14. Schulz E, Anter E, Keaney JF Jr. Oxidative stress, antioxidants, and endothelial function. Curr Med Chem. 2004. 11:1093–1104.15. Cai H, Harrison DG. Endothelial dysfunction in cardiovascular disease: the role of oxidant stress. Circ Res. 2000. 87:840–844.16. Zalba G, Beaumont J, San Jose G, Fortuno A, Fortuno MA, Diez J. Vascular oxidant stress: molecular mechanisms pathophysiological implications. J Physiol Biochem. 2000. 56:57–64.17. Burnett AL, Lowenstein CJ, Bredt DS, Chang TS, Snyder SH. Nitric oxide: a physiologic mediator of penile erection. Science. 1992. 257:401–403.18. Arai H, Hori S, Aramori I, Ohkubo H, Nakanishi S. Cloning and expression of a cDNA encoding an endothelin receptor. Nature. 1990. 348:730–732.19. Chang S, Hypolite JA, Zderic SA, Wein AJ, Chacko S, Disanto ME. Increased corpus cavernosum smooth muscle tone associated with partial bladder outlet obstruction is mediated via Rho-kinase. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2005. 289:R1124–R1130.20. Khan MA, Dashwood MR, Thompson CS, Auld J, Morgan RJ, Mikhailidis DP. Down-regulation of endothelin-B receptor sites in cavernosal tissue of a rabbit model of partial bladder outlet obstruction: potential clinical relevance. World J Urol. 1999. 17:290–295.21. Hirata Y, Takagi Y, Fukuda Y, Marumo F. Endothelin is a potent mitogen for rat vascular smooth muscle cells. Atherosclerosis. 1989. 78:225–228.22. Warner TD, De Nucci G, Vane JR. Rat endothelin is a vasodilator in the isolated perfused mesentery of the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989. 159:325–326.23. Saenz de Tejada I, Carson MP, de las Morenas A, Goldstein I, Traish AM. Endothelin: localization, synthesis, activity, and receptor types in human penile corpus cavernosum. Am J Physiol. 1991. 261:H1078–H1085.24. Sullivan ME, Dashwood MR, Thompson CS, Muddle JR, Mikhailidis DP, Morgan RJ. Alterations in endothelin B receptor sites in cavernosal tissue of diabetic rabbits: potential relevance to the pathogenesis of erectile dysfunction. J Urol. 1997. 158:1966–1972.25. Rajasekaran M, Kasyan A, Jain A, Kim SW, Monga M. Altered growth factor expression in the aging penis: the Brown-Norway rat model. J Androl. 2002. 23:393–399.26. Park K, Ahn KY, Kim MK, Lee SE, Kang TW, Ryu SB. Intracavernosal injection of vascular endothelial growth factor improves erectile function in aged rats. Eur Urol. 2004. 46:403–407.27. Lin CS, Ho HC, Chen KC, Lin G, Nunes L, Lue TF. Intracavernosal injection of vascular endothelial growth factor induces nitric oxide synthase isoforms. BJU Int. 2002. 89:955–960.28. Yamanaka M, Shirai M, Shiina H, Tanaka Y, Enokida H, Tsujimura A, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor restores erectile function through inhibition of apoptosis in diabetic rat penile crura. J Urol. 2005. 173:318–323.29. Azadzoi KM, Master TA, Siroky MB. Effect of chronic ischemia on constitutive and inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in erectile tissue. J Androl. 2004. 25:382–388.30. Yamanaka M, Shirai M, Shiina H, Shirai M, Tanaka Y, Fujime M, et al. Loss of anti-apoptotic genes in aging rat crura. J Urol. 2002. 168:2296–2300.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Expression of eNOS and ET-1 in Corpus Cavernosum in Male Rat with Partial Bladder Outlet Obstruction
- Changes of Endothelin-1 in Rats Corpus Cavernosum Smooth Muscle of Partial Bladder Outlet Obstruction
- Effect of Bladder Outlet Obstruction on Blood Flow and Tissue Collagen in Rat Bladder
- The Role of Peripheral and Spinal alpha1-adrenoceptor in Bladder Overactivity Induced by Partial Bladder Outlet Obstruction in Rat
- Ultrastructural Changes of Detrusor Muscle by Partial Obstruction of the Bladder Outlet in the Rat