Anat Cell Biol.
2016 Mar;49(1):50-60. 10.5115/acb.2016.49.1.50.
Characterization of mesenchymal cells beneath cornification of the fetal epithelium and epidermis at the face: an immunohistochemical study using human fetal specimens
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anatomy, Chonbuk National University Medical School, Jeonju, Korea.
- 2Department of Anatomy, Histology and Embryology, Yanbian University Medical College, Yanji, Jilin, China.
- 3Division of Internal Medicine, Iwamizawa Asuka Hospital, Iwamizawa, Japan.
- 4Department of Surgery, Chonbuk National University Hospital, Jeonju, Korea. chobh@jbnu.ac.kr
- 5Research Institute of Clinical Medicine, Chonbuk National University-Biomedical Research Institute, Chonbuk National University Hospital, Jeonju, Korea.
- KMID: 2308931
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.2016.49.1.50
Abstract
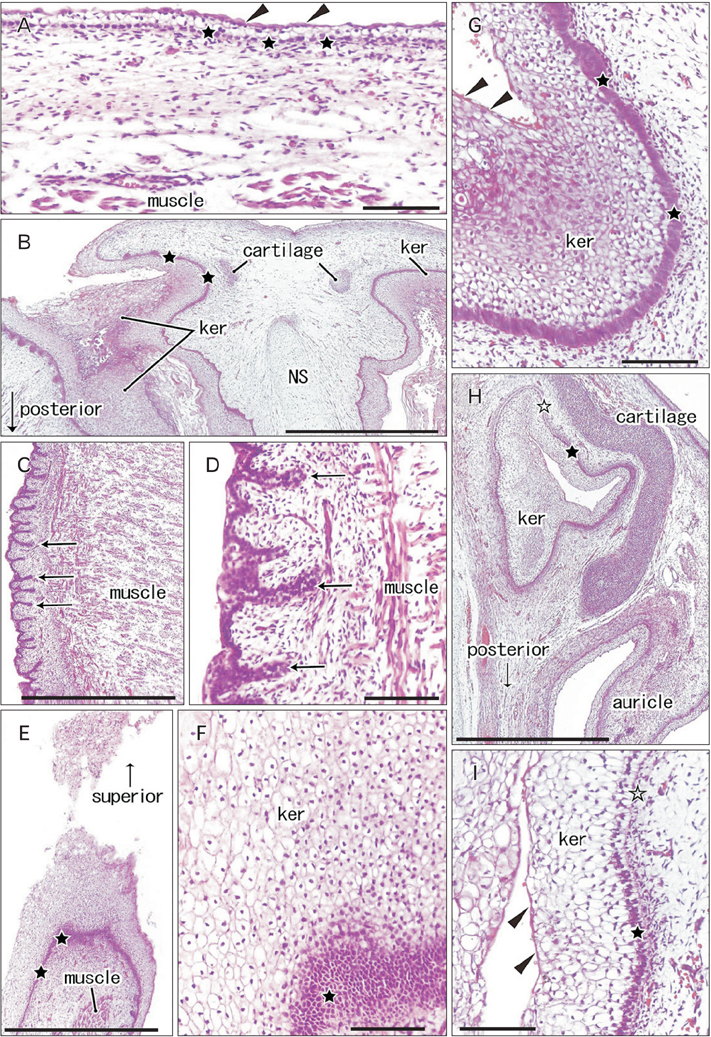
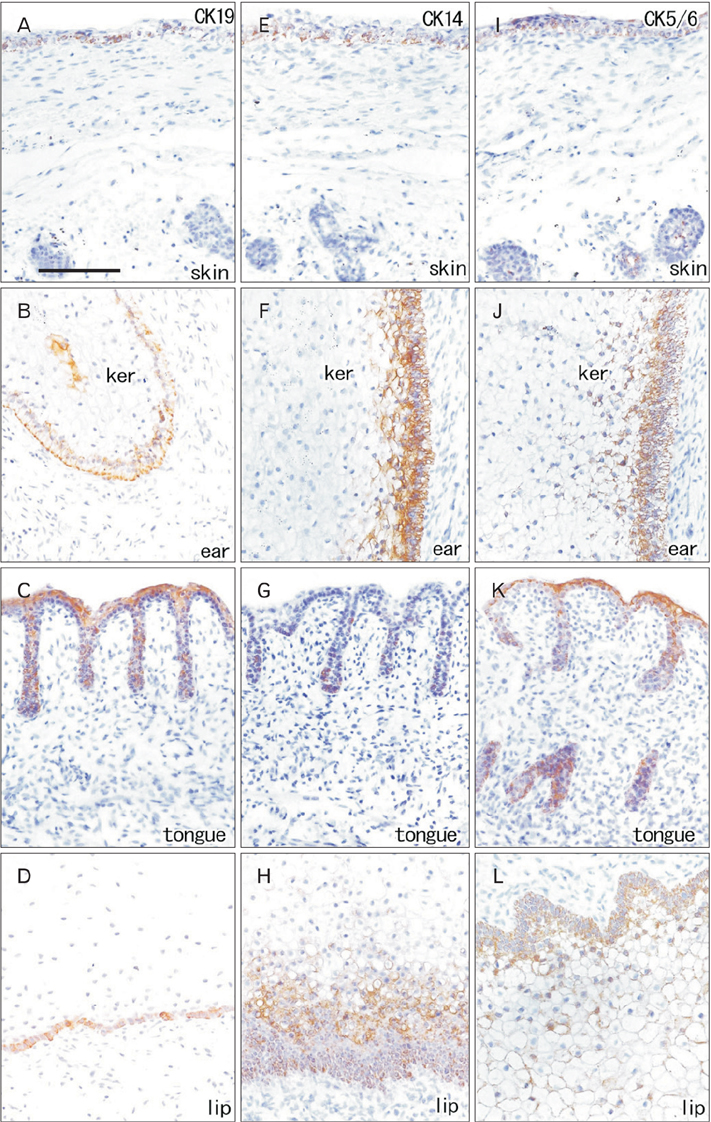
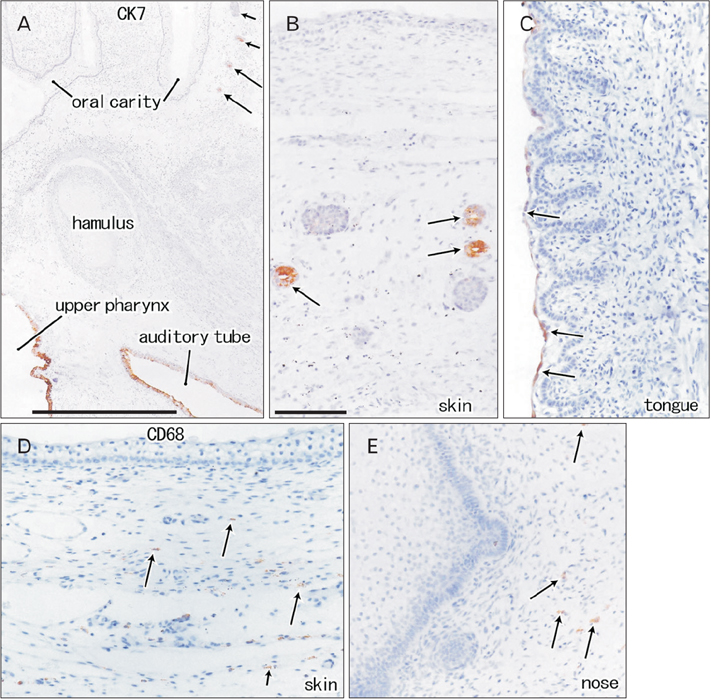
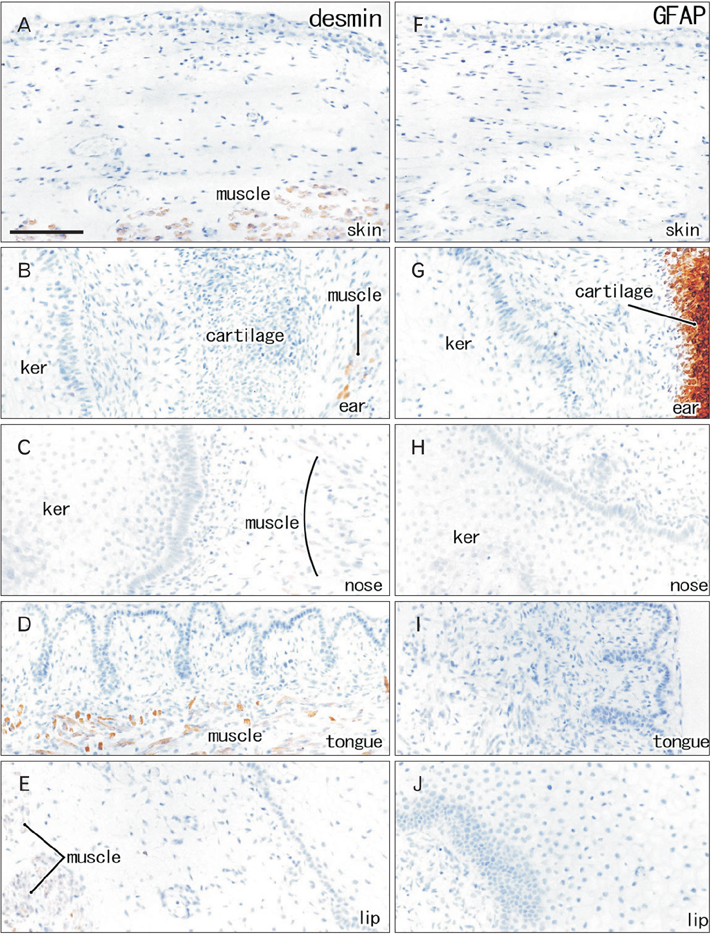
- Fetal development of the face involves a specific type of cornification in which keratinocytes provide a mass or plug to fill a cavity. The epithelial-mesenchymal interaction was likely to be different from that in the usual skin. We examined expression of intermediate filaments and other mesenchymal markers beneath cornification in the fetal face. Using sections from 5 mid-term human fetuses at 14-16 weeks, immunohistochemistry was conducted for cytokeratins (CK), vimentin, nestin, glial fibrilary acidic protein, desmin, CD34, CD68 and proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA). Fetal zygomatic skin was composed of a thin stratum corneum and a stratum basale (CK5/6+, CK14+, and CK19+) and, as the intermediate layer, 2-3 layered large keratinocytes with nucleus. The basal layer was lined by mono-layered mesenchymal cells (CD34+ and nestin+). Some of basal cells were PCNA-positive. In the keratinocyte plug at the external ear and nose, most cell nuclei expressed PCNA, CK5/6, CK14, and CK19. Vimentin-positive mesenchymal cells migrated into the plug. The PCNA-positive nucleus as well as mesenchymal cell migration was not seen in the lip margin in spite of the thick keratinocyte layer. The lingual epithelium were characterized by the CK7-positive stratum corneum as well as the thick mesenchymal papilla. CD68-positive macrophages were absent in the epidermis/epithelium. Being different from usual cornification of the skin, loss of a mesenchymal monolayer as well as superficial migration of mesenchymal cells might connect with a specific differentiation of keratinocyte to provide a plug at the fetal nose and ear.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mack JA, Anand S, Maytin EV. Proliferation and cornification during development of the mammalian epidermis. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2005; 75:314–329.2. Mack JA, Li L, Sato N, Hascall VC, Maytin EV. Hoxb13 up-regulates transglutaminase activity and drives terminal differentiation in an epidermal organotypic model. J Biol Chem. 2005; 280:29904–29911.3. Warbrick JG. The early development of the nasal cavity and upper lip in the human embryo. J Anat. 1960; 94:351–362.4. Nishimura Y. Embryological study of nasal cavity development in human embryos with reference to congenital nostril atresia. Acta Anat (Basel). 1993; 147:140–144.5. Kumoi T, Nishimura Y, Shiota K. The embryologic development of the human anterior nasal aperture. Acta Otolaryngol. 1993; 113:93–97.6. Anson BJ, Bast TH, Richany SF. The fetal and early postnatal development of the tympanic ring and related structures in man. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1955; 64:802–823.7. Nishimura Y, Kumoi T. The embryologic development of the human external auditory meatus. Preliminary report. Acta Otolaryngol. 1992; 112:496–503.8. de la Cuadra-Blanco C, Peces-Peña MD, Jáñez-Escalada L, Mérida-Velasco JR. Morphogenesis of the human excretory lacrimal system. J Anat. 2006; 209:127–135.9. Sevel D. Development and congenital abnormalities of the nasolacrimal apparatus. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1981; 18:13–19.10. van der Werff JF, Nievelstein RA, Brands E, Luijsterburg AJ, Vermeij-Keers C. Normal development of the male anterior urethra. Teratology. 2000; 61:172–183.11. van der Putte SC. The devlopment of the perineum in the human: a comprehensive histological study with a special reference to the role of the stromal components. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2005; 177:1–131.12. Masumoto H, Katori Y, Kawase T, Cho BH, Murakami G, Shibata S, Matsubara A. False positive reactivity of a substance P-antibody in the ectodermal/epithelial plug of the nose, ear, eye and perineum of the human and mouse fetuses. Okajimas Folia Anat Jpn. 2010; 87:33–40.13. Franke WW, Grund C, Jackson BW, Illmensee K. Formation of cytoskeletal elements during mouse embryogenesis. IV. Ultra-structure of primary mesenchymal cells and their cell-cell interactions. Differentiation. 1983; 25:121–141.14. Hay ED. Extracellular matrix, cell skeletons, and embryonic development. Am J Med Genet. 1989; 34:14–29.15. Hendrix MJ, Seftor EA, Chu YW, Trevor KT, Seftor RE. Role of intermediate filaments in migration, invasion and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1996; 15:507–525.16. Al Saleh S, Al Mulla F, Luqmani YA. Estrogen receptor silencing induces epithelial to mesenchymal transition in human breast cancer cells. PLoS One. 2011; 6:e20610.17. Jain R, Fischer S, Serra S, Chetty R. The use of cytokeratin 19 (CK19) immunohistochemistry in lesions of the pancreas, gastrointestinal tract, and liver. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2010; 18:9–15.18. Clark BZ, Beriwal S, Dabbs DJ, Bhargava R. Semiquantitative GATA-3 immunoreactivity in breast, bladder, gynecologic tract, and other cytokeratin 7-positive carcinomas. Am J Clin Pathol. 2014; 142:64–71.19. Martins MD, Cavalcanti de Araujo V, Raitz R, Soares de Araujo N. Expression of cytoskeletal proteins in developing human minor salivary glands. Eur J Oral Sci. 2002; 110:316–321.20. Lourenco SV, Coutinho-Camillo CM, Buim ME, Uyekita SH, Soares FA. Human salivary gland branching morphogenesis: morphological localization of claudins and its parallel relation with developmental stages revealed by expression of cytoskeleton and secretion markers. Histochem Cell Biol. 2007; 128:361–369.21. Galou M, Colucci-Guyon E, Ensergueix D, Ridet JL, Gimenez y Ribotta M, Privat A, Babinet C, Dupouey P. Disrupted glial fibrillary acidic protein network in astrocytes from vimentin knockout mice. J Cell Biol. 1996; 133:853–863.22. Shibata S, Cho KH, Kim JH, Abe H, Murakami G, Cho BH. Expression of hyaluronan (hyaluronic acid) in the developing laminar architecture of the human fetal brain. Ann Anat. 2013; 195:424–430.23. Kim JH, Parkkila S, Shibata S, Fujimiya M, Murakami G, Cho BH. Expression of carbonic anhydrase IX in human fetal joints, ligaments and tendons: a potential marker of mechanical stress in fetal development? Anat Cell Biol. 2013; 46:272–284.24. Katori Y, Kawase T, Ho Cho K, Abe H, Rodríguez-Vázquez JF, Murakami G, Fujimiya M. Suprahyoid neck fascial configuration, especially in the posterior compartment of the parapharyngeal space: a histological study using late-stage human fetuses. Clin Anat. 2013; 26:204–212.25. Abe S, Rhee SK, Osonoi M, Nakamura T, Cho BH, Murakami G, Ide Y. Expression of intermediate filaments at muscle insertions in human fetuses. J Anat. 2010; 217:167–173.26. Yang Y, Makita T. Immunocytochemical colocalization of desmin and vimentin in human fetal skeletal muscle cells. Anat Rec. 1996; 246:64–70.27. Kopher RA, Penchev VR, Islam MS, Hill KL, Khosla S, Kaufman DS. Human embryonic stem cell-derived CD34+ cells function as MSC progenitor cells. Bone. 2010; 47:718–728.28. Lin CS, Xin ZC, Deng CH, Ning H, Lin G, Lue TF. Defining adipose tissue-derived stem cells in tissue and in culture. Histol Histopathol. 2010; 25:807–815.29. Young HE, Steele TA, Bray RA, Hudson J, Floyd JA, Hawkins K, Thomas K, Austin T, Edwards C, Cuzzourt J, Duenzl M, Lucas PA, Black AC Jr. Human reserve pluripotent mesenchymal stem cells are present in the connective tissues of skeletal muscle and dermis derived from fetal, adult, and geriatric donors. Anat Rec. 2001; 264:51–62.30. Katori Y, Kiyokawa H, Kawase T, Murakami G, Cho BH. CD34-positive primitive vessels and other structures in human fetuses: an immunohistochemical study. Acta Otolaryngol. 2011; 131:1086–1090.31. Abe S, Suzuki M, Cho KH, Murakami G, Cho BH, Ide Y. CD34-positive developing vessels and other structures in human fetuses: an immunohistochemical study. Surg Radiol Anat. 2011; 33:919–927.32. Shuler CF, Schwartz SA. Embryogenesis of stratified squamous epithelium. I. Tissue-specific expression of keratin proteins. Exp Cell Biol. 1986; 54:301–309.33. Sawaf MH, Shabana AH, Pelissier A, Forest N, Ouhayoun JP. Characterization of cytokeratin patterns in the developing human tongue. Int J Dev Biol. 1991; 35:91–100.34. Iwasaki S, Aoyagi H, Yoshizawa H. Localization of keratins 13 and 14 in the lingual mucosa of rats during the morphogenesis of circumvallate papillae. Acta Histochem. 2011; 113:395–401.35. Moll I, Heid H, Franke WW, Moll R. Distribution of a special subset of keratinocytes characterized by the expression of cytokeratin 9 in adult and fetal human epidermis of various body sites. Differentiation. 1987; 33:254–265.36. Michaels L, Soucek S. Development of the stratified squamous epithelium of the human tympanic membrane and external canal: the origin of auditory epithelial migration. Am J Anat. 1989; 184:334–344.37. Scott RJ, Hall PA, Haldane JS, van Noorden S, Price Y, Lane DP, Wright NA. A comparison of immunohistochemical markers of cell proliferation with experimentally determined growth fraction. J Pathol. 1991; 165:173–178.38. Onuma H, Mastui C, Morohashi M. Quantitative analysis of the proliferation of epidermal cells using a human skin organ culture system and the effect of DbcAMP using markers of proliferation (BrdU, Ki-67, PCNA). Arch Dermatol Res. 2001; 293:133–138.39. Lippens S, Kockx M, Knaapen M, Mortier L, Polakowska R, Verheyen A, Garmyn M, Zwijsen A, Formstecher P, Huylebroeck D, Vandenabeele P, Declercq W. Epidermal differentiation does not involve the pro-apoptotic executioner caspases, but is associated with caspase-14 induction and processing. Cell Death Differ. 2000; 7:1218–1224.40. Langbein L, Pape UF, Grund C, Kuhn C, Praetzel S, Moll I, Moll R, Franke WW. Tight junction-related structures in the absence of a lumen: occludin, claudins and tight junction plaque proteins in densely packed cell formations of stratified epithelia and squamous cell carcinomas. Eur J Cell Biol. 2003; 82:385–400.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Immunohistochemical Detection of Keratin and Prekeratin in Human Fetal Nail Unit
- Immunohistochemical Expression of E-Cadherin and Ur-Catenin in Fetal Skin
- Immunohistochemical Expression of the alpha- and gamma-Catenin in the Fetal Skin Development
- Regional Morphological Study on the Development of the Human Embryonic and Fetal periderm
- Differentiation characteristics of cholesteatoma epithelium determined by expression of transglutaminase isoenzymes