Korean J Androl.
2012 Apr;30(1):23-30. 10.5534/kja.2012.30.1.23.
Transforming Growth Factor-beta Type I Receptor Inhibitor Induces Functional and Morphologic Recovery in a Rat Model of Erectile Dysfunction and Cavernous Fibrosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology and National Research Center for Sexual Medicine, Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea. jksuh@inha.ac.kr
- KMID: 2298805
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5534/kja.2012.30.1.23
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To examine the effectiveness of small-molecule inhibitor of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) type I receptor, an activin receptor-like kinase 5 (ALK5), on erectile dysfunction (ED) in a rat model of cavernous fibrosis, in which fibrosis was induced by intracavernous injection of adenovirus expressing TGF-beta1 (Ad-TGF-beta1).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
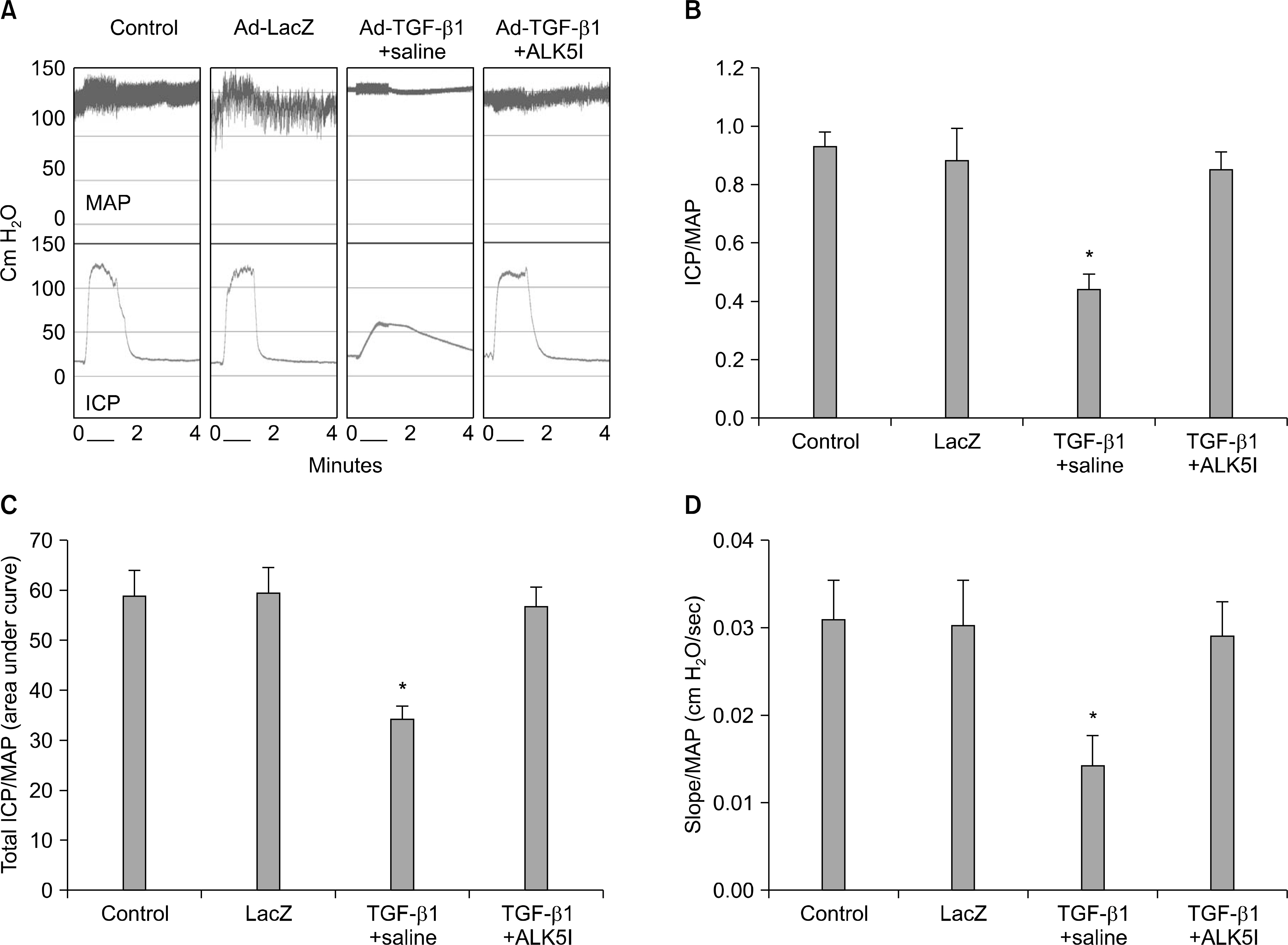
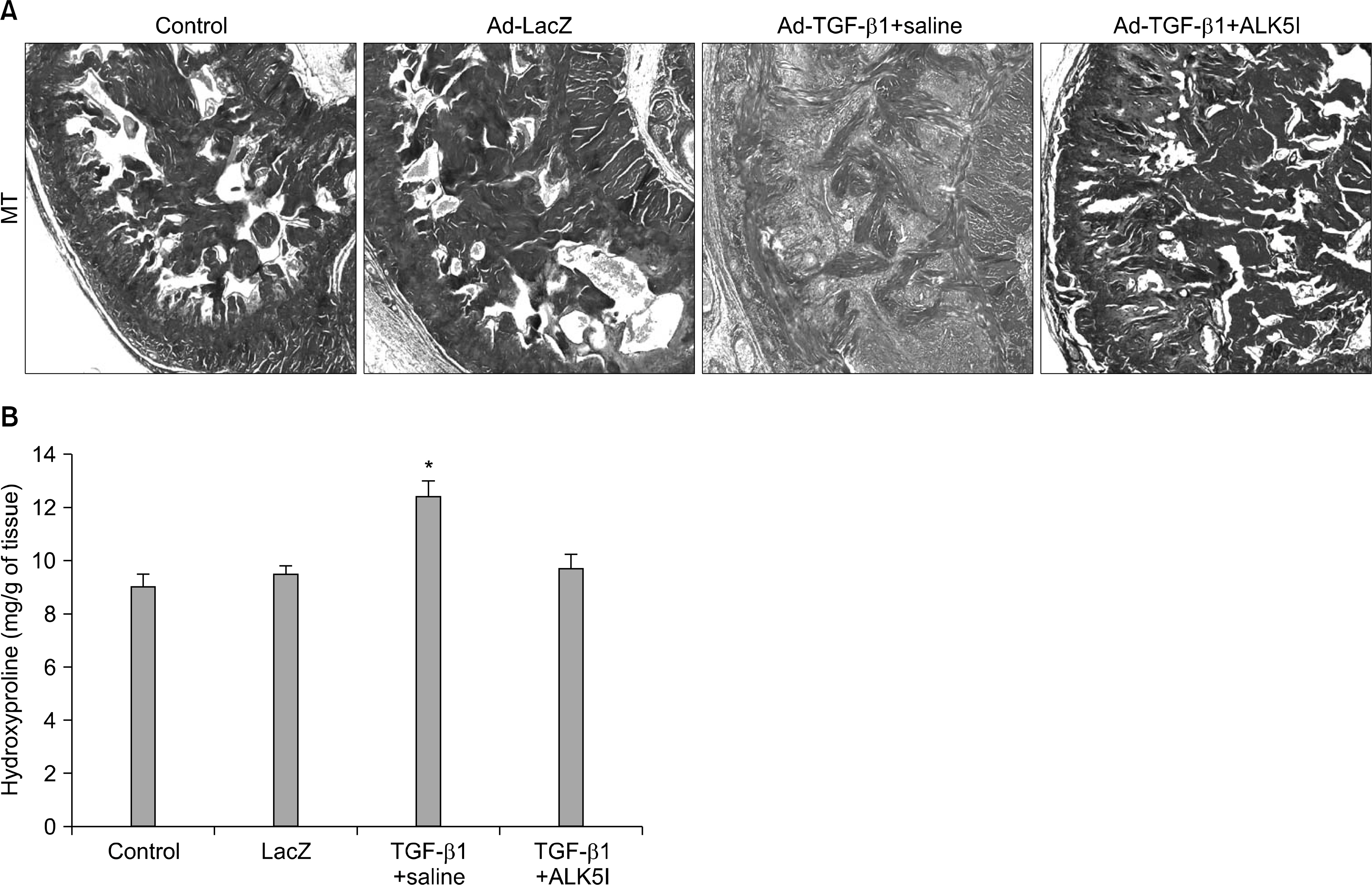
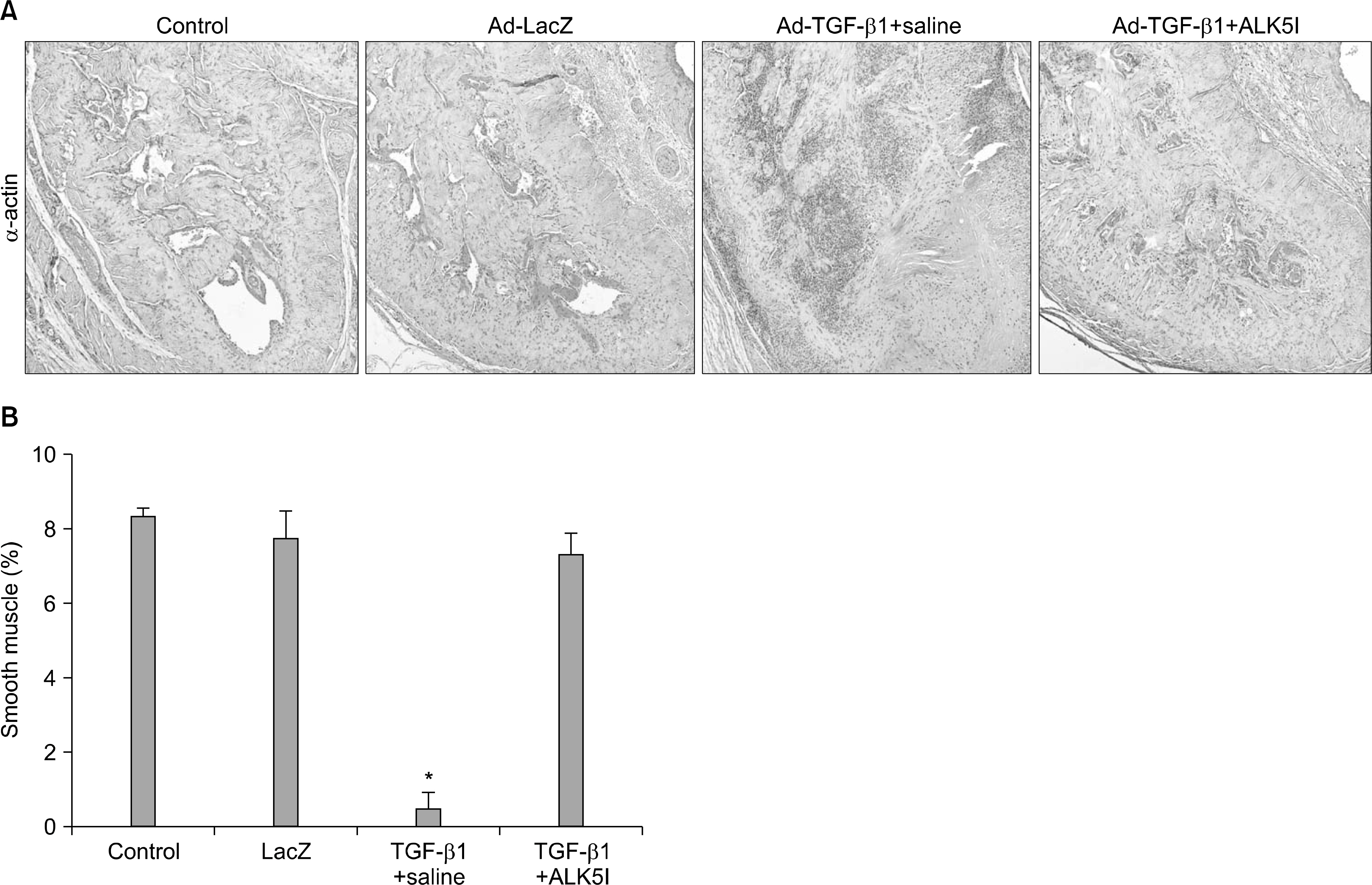
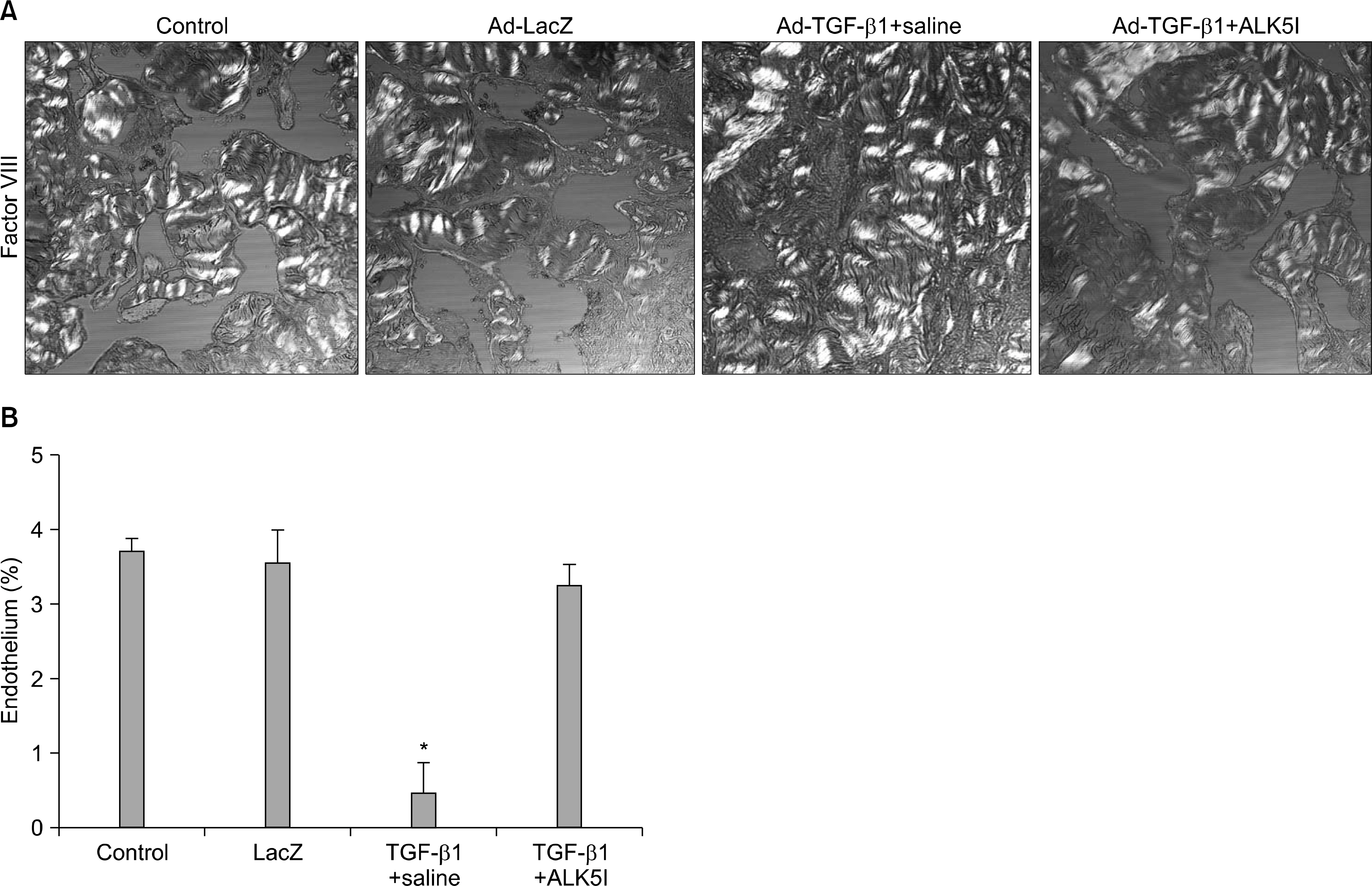
Four-month-old Sprague-Dawley rats were divided into four groups (n=10 per group): age-matched controls without treatment, age-matched controls receiving intracavernous injection of LacZ adenovirus, and cavernous fibrosis rats receiving an intracavernous injection of saline or ALK5 inhibitor (5 mg/kg). ALK5 inhibitor or saline was administered on day 5 after injection of Ad-TGF-beta1. On day 30, erectile function was assessed by electrical stimulation of the cavernous nerve and the penis was then harvested for histologic studies (n=6 per group) and for the measurement of the hydroxyproline level (n=4 per group).
RESULTS
Ad-TGF-beta1-induced cavernous fibrosis rats treated with saline showed a significant decrease in cavernous smooth muscle and endothelial content, and an increase in collagen deposition, which resulted in profound deterioration of all erectile function parameters, such as the ratios of maximal intracavernous pressure (ICP), total ICP, and slope to mean arterial pressure. ALK5 inhibitor significantly restored erectile function in a rat model of cavernous fibrosis by increasing cavernous smooth muscle and endothelial content, and by blocking cavernous fibrosis.
CONCLUSIONS
The results suggest that inhibition of the TGF-beta pathway is a promising therapeutic strategy for the treatment of ED related to cavernous fibrosis from various causes.
MeSH Terms
-
Activin Receptors
Adenoviridae
Animals
Arterial Pressure
Caves
Collagen
Electric Stimulation
Erectile Dysfunction
Fibrosis
Hydroxyproline
Male
Muscle, Smooth
Penis
Protein-Serine-Threonine Kinases
Rats
Rats, Sprague-Dawley
Receptors, Transforming Growth Factor beta
Transforming Growth Factor beta
Transforming Growth Factor beta1
Activin Receptors
Collagen
Hydroxyproline
Protein-Serine-Threonine Kinases
Receptors, Transforming Growth Factor beta
Transforming Growth Factor beta
Transforming Growth Factor beta1
Figure
Reference
-
1). Sullivan ME, Keoghane SR, Miller MA. Vascular risk factors and erectile dysfunction. BJU Int. 2001; 87:838–45.
Article2). Martin-Morales A, Sanchez-Cruz JJ, Saenz de Tejada I, Rodriguez-Vela L, Jimenez-Cruz JF, Burgos- Rodriguez R. Prevalence and independent risk factors for erectile dysfunction in Spain: results of the Epidemiologia de la Disfuncion Erectil Masculina Study. J Urol. 2001; 166:569–74.
Article3). Feldman HA, Goldstein I, Hatzichristou DG, Krane RJ, McKinlay JB. Impotence and its medical and psychosocial correlates: results of the Massachusetts Male Aging Study. J Urol. 1994; 151:54–61.
Article4). Ryu JK, Han JY, Chu YC, Song SU, Lee KH, Yoon SM, et al. Expression of cavernous transforming growth factor-beta1 and its type II receptor in patients with erectile dysfunction. Int J Androl. 2004; 27:42–9.
Article5). Ryu JK, Shin HY, Song SU, Oh SM, Piao S, Han JY, et al. Downregulation of angiogenic factors and their downstream target molecules affects the deterioration of erectile function in a rat model of hypercholesterolemia. Urology. 2006; 67:1329–34.
Article6). Zhang LW, Piao S, Choi MJ, Shin HY, Jin HR, Kim WJ, et al. Role of increased penile expression of transforming growth factor-beta1 and activation of the Smad signaling pathway in erectile dysfunction in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J Sex Med. 2008; 5:2318–29.7). Nehra A, Goldstein I, Pabby A, Nugent M, Huang YH, de las Morenas A, et al. Mechanisms of venous leakage: a prospective clinicopathological correlation of corporeal function and structure. J Urol. 1996; 156:1320–9.
Article8). Ahn GJ, Sohn YS, Kang KK, Ahn BO, Kwon JW, Kang SK, et al. The effect of PDE5 inhibition on the erectile function in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Int J Impot Res. 2005; 17:134–41.
Article9). Moreland RB, Traish A, McMillin MA, Smith B, Goldstein I, Saenz de Tejada I. PGE1 suppresses the induction of collagen synthesis by transforming growth factor-beta 1 in human corpus cavernosum smooth muscle. J Urol. 1995; 153:826–34.10). Ryu JK, Song SU, Han JY, Chu YC, Lee M, Kim JS, et al. Establishment of penile fibrosis model in a rat using mouse NIH 3T3 fibroblasts expressing transforming growth factor beta1. Biol Reprod. 2005; 72:916–21.11). Ryu JK, Oh SM, Jin HR, Kim DK, Kang YJ, Jang JH, et al. Establishment of a cavernous fibrosis model in a rat using adenovirus expressing transforming growth factor-beta1. Korean J Androl. 2010; 28:100–6.12). Grygielko ET, Martin WM, Tweed C, Thornton P, Harling J, Brooks DP, et al. Inhibition of gene markers of fibrosis with a novel inhibitor of transforming growth factor-beta type I receptor kinase in puromycin-induced nephritis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005; 313:943–51.13). Bonniaud P, Margetts PJ, Kolb M, Schroeder JA, Kapoun AM, Damm D, et al. Progressive transforming growth factor beta1-induced lung fibrosis is blocked by an orally active ALK5 kinase inhibitor. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005; 171:889–98.14). de Gouville AC, Boullay V, Krysa G, Pilot J, Brusq JM, Loriolle F, et al. Inhibition of TGF-beta signaling by an ALK5 inhibitor protects rats from dimethylnitrosamine-induced liver fibrosis. Br J Pharmacol. 2005; 145:166–77.15). Ryu JK, Piao S, Shin HY, Choi MJ, Zhang LW, Jin HR, et al. IN-1130, a novel transforming growth factor-beta type I receptor kinase (activin receptor-like kinase 5) inhibitor, promotes regression of fibrotic plaque and corrects penile curvature in a rat model of Peyronie's disease. J Sex Med. 2009; 6:1284–96.16). Piao S, Choi MJ, Tumurbaatar M, Kim WJ, Jin HR, Shin SH, et al. Transforming growth factor (TGF)-β type I receptor kinase (ALK5) inhibitor alleviates profibrotic TGF-β1 responses in fibroblasts derived from Peyronie's plaque. J Sex Med. 2010; 7:3385–95.
Article17). Reddy GK, Enwemeka CS. A simplified method for the analysis of hydroxyproline in biological tissues. Clin Biochem. 1996; 29:225–9.18). Burchardt T, Burchardt M, Karden J, Buttyan R, Shabsigh A, de la Taille A, et al. Reduction of endothelial and smooth muscle density in the corpora cavernosa of the streptozotocin induced diabetic rat. J Urol. 2000; 164:1807–11.
Article19). Chitaley K, Luttrell I. Strain differences in susceptibility to in vivo erectile dysfunction following 6 weeks of induced hyperglycemia in the mouse. J Sex Med. 2008; 5:1149–55.
Article20). Wingard C, Fulton D, Husain S. Altered penile vascular reactivity and erection in the Zucker obese-diabetic rat. J Sex Med. 2007; 4:348–62.
Article21). Leask A, Abraham DJ. TGF-beta signaling and the fibrotic response. FASEB J. 2004; 18:816–27.22). Grainger DJ, Kemp PR, Witchell CM, Weissberg PL, Metcalfe JC. Transforming growth factor beta decreases the rate of proliferation of rat vascular smooth muscle cells by extending the G2 phase of the cell cycle and delays the rise in cyclic AMP before entry into M phase. Biochem J. 1994; 299:227–35.23). Reddy KB, Howe PH. Transforming growth factor beta 1-mediated inhibition of smooth muscle cell proliferation is associated with a late G1 cell cycle arrest. J Cell Physiol. 1993; 156:48–55.24). Redondo S, Ruiz E, Santos-Gallego CG, Padilla E, Tejerina T. Pioglitazone induces vascular smooth muscle cell apoptosis through a peroxisome proliferator- activated receptor-gamma, transforming growth factor-beta1, and a Smad2-dependent mechanism. Diabetes. 2005; 54:811–7.25). Goumans MJ, Valdimarsdottir G, Itoh S, Rosendahl A, Sideras P, ten Dijke P. Balancing the activation state of the endothelium via two distinct TGF-beta type I receptors. EMBO J. 2002; 21:1743–53.
Article26). Watabe T, Nishihara A, Mishima K, Yamashita J, Shimizu K, Miyazawa K, et al. TGF-beta receptor kinase inhibitor enhances growth and integrity of embryonic stem cell-derived endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 2003; 163:1303–11.27). Castañares C, Redondo-Horcajo M, Magán-Marchal N, ten Dijke P, Lamas S, Rodríguez-Pascual F. Signaling by ALK5 mediates TGF-beta-induced ET-1 expression in endothelial cells: a role for migration and proliferation. J Cell Sci. 2007; 120:1256–66.28). Moon JA, Kim HT, Cho IS, Sheen YY, Kim DK. IN-1130, a novel transforming growth factor-beta type I receptor kinase (ALK5) inhibitor, suppresses renal fibrosis in obstructive nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2006; 70:1234–43.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Establishment of a Cavernous Fibrosis Model in a Rat Using Adenovirus Expressing Transforming Growth Factor-beta1
- Pathophysiologic Investigation of Vasculogenic Erectile Dysfunction Using Newly Developed Rat Model
- Effects of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on Erectile Dysfunction in a Rat Model of Atherosclerosis-induced Chronic Pelvic Ischemia
- Erectile Function and Cavernosal TGF-beta Expression in the OLETF Rats
- Expressions of transforming growth factor beta in patients with rheumatioid arthritis and osteoarthritis