Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2015 Jul;19(4):309-318. 10.4196/kjpp.2015.19.4.309.
Chronic Alcohol Consumption Results in Greater Damage to the Pancreas Than to the Liver in the Rats
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Bucheon St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, Bucheon 420-717, Korea. sjyoo@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Clinical Neuroscience, Max Planck Institute of Experimental Medicine, Gottingen, Germany DFG Center for Nanoscale Microscopy & Molecular Physiology of the Brain (CNMPB), Gottingen 37075, Germany.
- 3Department of Physiology, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul 137-701, Korea.
- 4Division of Metabolic Disease, Center for Biomedical Sicence, National Institutes of Health, Cheongju 361-951, Korea.
- 5Division of Structural and Functional Genomics, Center for Genome Science, National Institute of Health, Cheongju 361-951, Korea.
- 6Department in Preventive Medicine, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon 443-749, Korea.
- 7Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul 137-701, Korea.
- 8Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Bucheon 420-767, Korea.
- 9Department of Psychiatry, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul 137-701, Korea. kdj922@chollian.net
- KMID: 2285573
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2015.19.4.309
Abstract
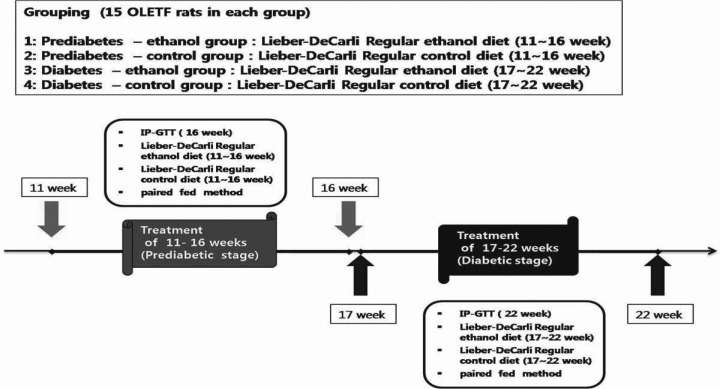
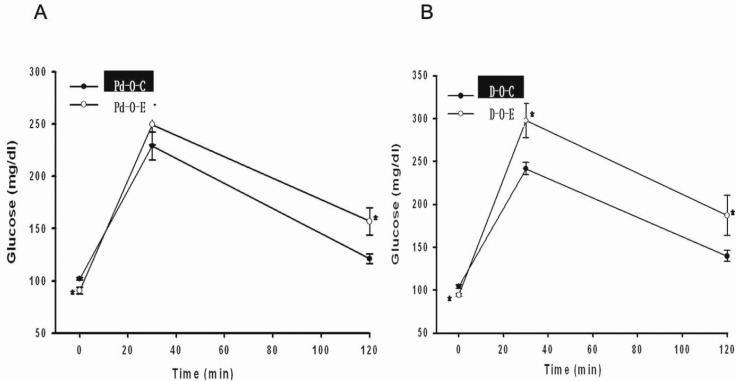
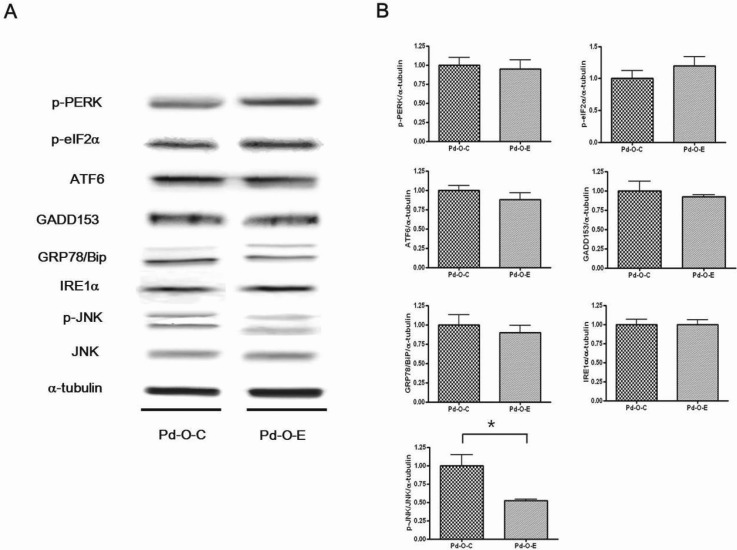
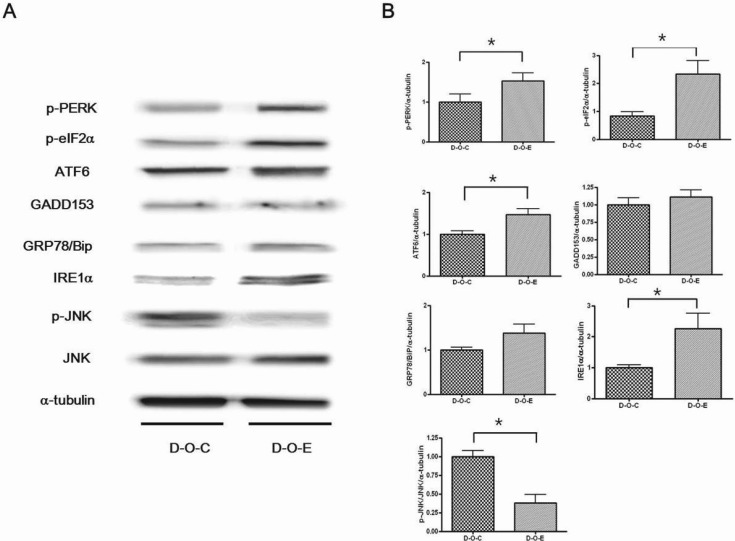
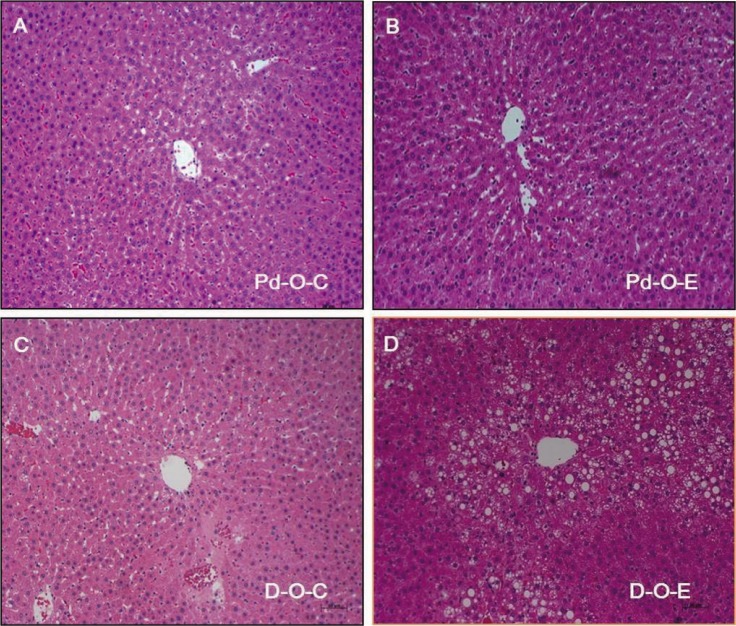
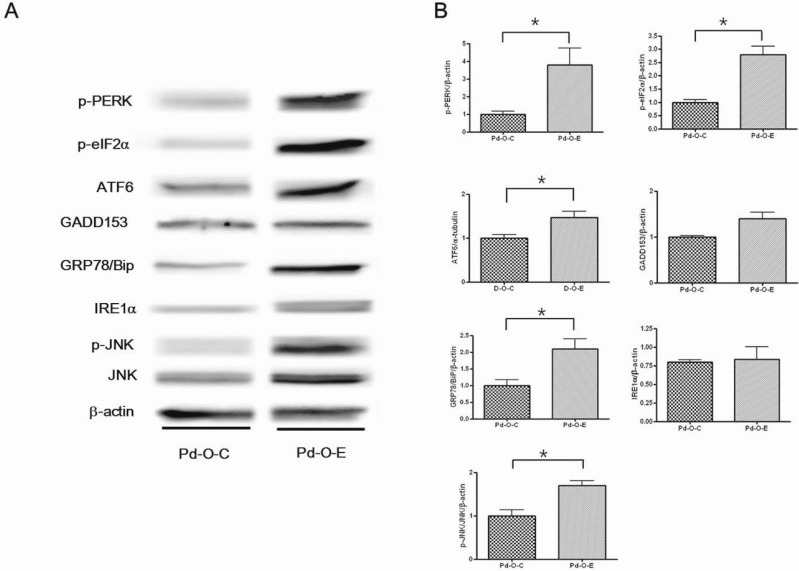
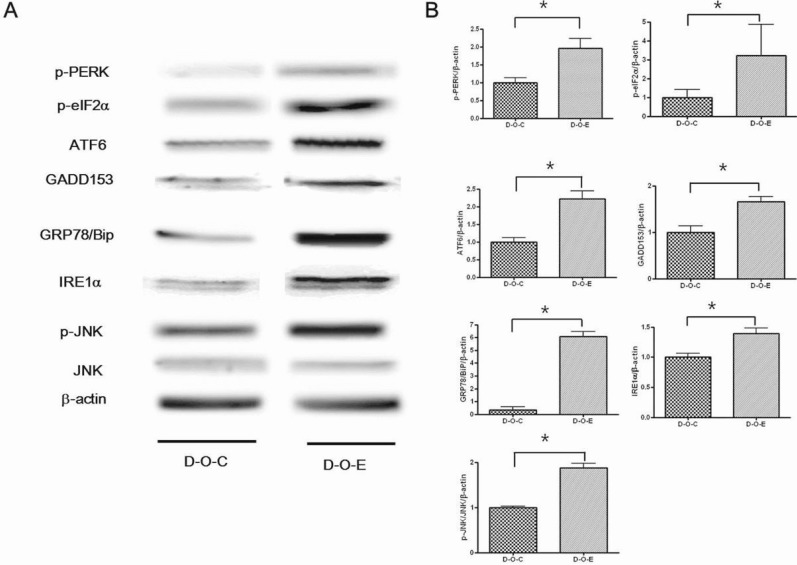
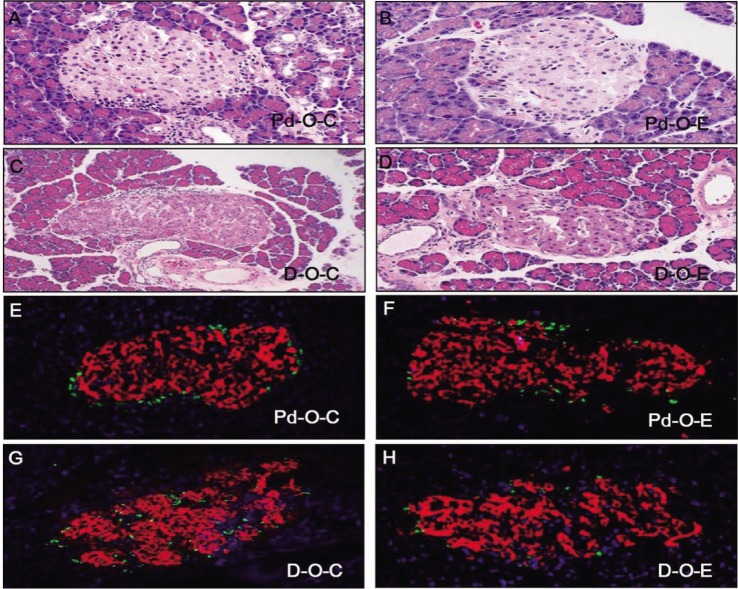
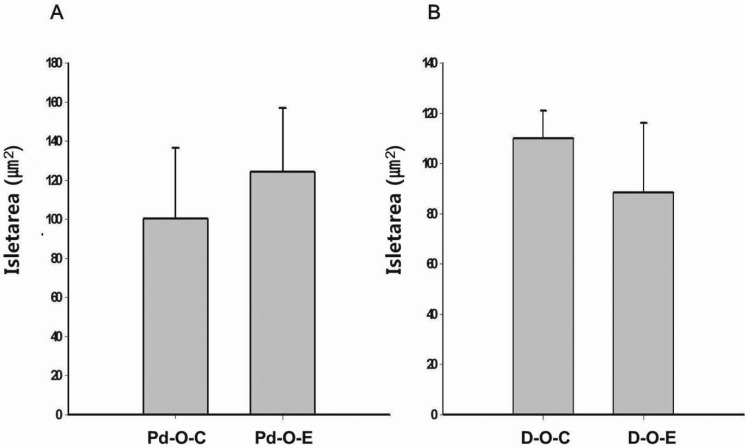
- Alcohol consumption increases the risk of type 2 diabetes. However, its effects on prediabetes or early diabetes have not been studied. We investigated endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress in the pancreas and liver resulting from chronic alcohol consumption in the prediabetes and early stages of diabetes. We separated Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty (OLETF) rats, a type-2 diabetic animal model, into two groups based on diabetic stage: prediabetes and early diabetes were defined as occurrence between the ages of 11 to 16 weeks and 17 to 22 weeks, respectively. The experimental group received an ethanol-containing liquid diet for 6 weeks. An intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test was conducted after 16 and 22 weeks for the prediabetic and early diabetes groups, respectively. There were no significant differences in body weight between the control and ethanol groups. Fasting and 120-min glucose levels were lower and higher, respectively, in the ethanol group than in the control group. In prediabetes rats, alcohol induced significant expression of ER stress markers in the pancreas; however, alcohol did not affect the liver. In early diabetes rats, alcohol significantly increased most ER stress-marker levels in both the pancreas and liver. These results indicate that chronic alcohol consumption increased the risk of diabetes in prediabetic and early diabetic OLETF rats; the pancreas was more susceptible to damage than was the liver in the early diabetic stages, and the adaptive and proapoptotic pathway of ER stress may play key roles in the development and progression of diabetes affected by chronic alcohol ingestion.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Research Society on Alcoholism. Impact of Alcoholism and Alcohol Induced Disease on America. In : Alcoholism RSo, editor. Research Society on Alcoholism: Research Society on Alcoholism. 2011. p. 1–6.2. World Health Organization. Global strategy to reduce the harmful use of alcohol. Accessed May 21 2010. Available from: http://www.who.int/substance_abuse/activities/gsrhua/en/.3. Wechsler H, Lee JE, Kuo M, Seibring M, Nelson TF, Lee H. Trends in college binge drinking during a period of increased prevention efforts. Findings from 4 Harvard School of Public Health College Alcohol Study surveys: 1993-2001. J Am Coll Health. 2002; 50:203–217. PMID: 11990979.
Article4. Chung SS, Joung KH. Risk factors of heavy episodic drinking among Korean adolescents. J Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs. 2013; 20:665–671. PMID: 22852763.
Article5. Ozcan U, Cao Q, Yilmaz E, Lee AH, Iwakoshi NN, Ozdelen E, Tuncman G, Görgön C, Glimcher LH, Hotamisligil GS. Endoplasmic reticulum stress links obesity, insulin action, and type 2 diabetes. Science. 2004; 306:457–461. PMID: 15486293.
Article6. Ji C. Mechanisms of alcohol-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress and organ injuries. Biochem Res Int. 2012; 2012:216450. PMID: 22110961.
Article7. Marciniak SJ, Ron D. Endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling in disease. Physiol Rev. 2006; 86:1133–1149. PMID: 17015486.
Article8. Bernales S, Papa FR, Walter P. Intracellular signaling by the unfolded protein response. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2006; 22:487–508. PMID: 16822172.
Article9. Ron D, Walter P. Signal integration in the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007; 8:519–529. PMID: 17565364.
Article10. Zhang K, Kaufman RJ. From endoplasmic-reticulum stress to the inflammatory response. Nature. 2008; 454:455–462. PMID: 18650916.
Article11. Minamino T, Komuro I, Kitakaze M. Endoplasmic reticulum stress as a therapeutic target in cardiovascular disease. Circ Res. 2010; 107:1071–1082. PMID: 21030724.
Article12. Hendershot LM. The ER function BiP is a master regulator of ER function. Mt Sinai J Med. 2004; 71:289–297. PMID: 15543429.13. Ron D. Translational control in the endoplasmic reticulum stress response. J Clin Invest. 2002; 110:1383–1388. PMID: 12438433.
Article14. Rasheva VI, Domingos PM. Cellular responses to endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis. Apoptosis. 2009; 14:996–1007. PMID: 19360473.
Article15. Xu C, Bailly-Maitre B, Reed JC. Endoplasmic reticulum stress: cell life and death decisions. J Clin Invest. 2005; 115:2656–2664. PMID: 16200199.
Article16. Kawano K, Hirashima T, Mori S, Natori T. OLETF (Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty) rat: a new NIDDM rat strain. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1994; 24(Suppl):S317–S320. PMID: 7859627.
Article17. Moran TH, Katz LF, Plata-Salaman CR, Schwartz GJ. Disordered food intake and obesity in rats lacking cholecystokinin A receptors. Am J Physiol. 1998; 274:R618–R625. PMID: 9530226.18. Seo E, Park EJ, Park MK, Kim DK, Lee HJ, Hong SH. Differential expression of metabolism-related genes in liver of diabetic obese rats. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2010; 14:99–103. PMID: 20473381.
Article19. Kloner RA, Rezkalla SH. To drink or not to drink? That is the question. Circulation. 2007; 116:1306–1317. PMID: 17846344.
Article20. Grauvogel J, Daemmrich TD, Ryschich E, Gebhard MM, Werner J. Chronic alcohol intake increases the severity of pancreatitis induced by acute alcohol administration, hyperlipidemia and pancreatic duct obstruction in rats. Pancreatology. 2010; 10:603–612. PMID: 20980778.
Article21. de la M Hall P, Lieber CS, DeCarli LM, French SW, Lindros KO, Järveläinen H, Bode C, Parlesak A, Bode JC. Models of alcoholic liver disease in rodents: a critical evaluation. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2001; 25(5 Suppl ISBRA):254S–261S. PMID: 11391080.22. Baliunas DO, Taylor BJ, Irving H, Roerecke M, Patra J, Mohapatra S, Rehm J. Alcohol as a risk factor for type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Care. 2009; 32:2123–2132. PMID: 19875607.23. Lieber CS, DeCarli LM. The feeding of alcohol in liquid diets: two decades of applications and 1982 update. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1982; 6:523–531. PMID: 6758624.
Article24. Lieber CS, DeCarli LM, Sorrell MF. Experimental methods of ethanol administration. Hepatology. 1989; 10:501–510. PMID: 2673971.
Article25. Tang SM, Gabelaia L, Gauthier TW, Brown LA. N-acetylcysteine improves group B streptococcus clearance in a rat model of chronic ethanol ingestion. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2009; 33:1197–1201. PMID: 19389194.
Article26. Kim MK, Park KG. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and diabetes. J Korean Endocr Soc. 2008; 23:1–8.
Article27. Ji C, Mehrian-Shai R, Chan C, Hsu YH, Kaplowitz N. Role of CHOP in hepatic apoptosis in the murine model of intragastric ethanol feeding. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2005; 29:1496–1503. PMID: 16131858.
Article28. Harding HP, Zeng H, Zhang Y, Jungries R, Chung P, Plesken H, Sabatini DD, Ron D. Diabetes mellitus and exocrine pancreatic dysfunction in perk-/- mice reveals a role for translational control in secretory cell survival. Mol Cell. 2001; 7:1153–1163. PMID: 11430819.
Article29. Seo HY, Kim YD, Lee KM, Min AK, Kim MK, Kim HS, Won KC, Park JY, Lee KU, Choi HS, Park KG, Lee IK. Endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced activation of activating transcription factor 6 decreases insulin gene expression via up-regulation of orphan nuclear receptor small heterodimer partner. Endocrinology. 2008; 149:3832–3841. PMID: 18450959.
Article30. Arky RA, Veverbrants E, Abramson EA. Irreversible hypoglycemia. A complication of alcohol and insulin. JAMA. 1968; 206:575–578. PMID: 5695576.
Article31. Calfon M, Zeng H, Urano F, Till JH, Hubbard SR, Harding HP, Clark SG, Ron D. IRE1 couples endoplasmic reticulum load to secretory capacity by processing the XBP-1 mRNA. Nature. 2002; 415:92–96. PMID: 11780124.
Article32. Allagnat F, Christulia F, Ortis F, Pirot P, Lortz S, Lenzen S, Eizirik DL, Cardozo AK. Sustained production of spliced X-box binding protein 1 (XBP1) induces pancreatic beta cell dysfunction and apoptosis. Diabetologia. 2010; 53:1120–1130. PMID: 20349222.
Article33. Kato H, Nakajima S, Saito Y, Takahashi S, Katoh R, Kitamura M. mTORC1 serves ER stress-triggered apoptosis via selective activation of the IRE1-JNK pathway. Cell Death Differ. 2012; 19:310–320. PMID: 21779001.
Article34. Tan TC, Crawford DH, Jaskowski LA, Subramaniam VN, Clouston AD, Crane DI, Bridle KR, Anderson GJ, Fletcher LM. Excess iron modulates endoplasmic reticulum stress-associated pathways in a mouse model of alcohol and high-fat diet-induced liver injury. Lab Invest. 2013; 93:1295–1312. PMID: 24126888.
Article35. Zhang K, Wang S, Malhotra J, Hassler JR, Back SH, Wang G, Chang L, Xu W, Miao H, Leonardi R, Chen YE, Jackowski S, Kaufman RJ. The unfolded protein response transducer IRE1α prevents ER stress-induced hepatic steatosis. EMBO J. 2011; 30:1357–1375. PMID: 21407177.
Article36. Kaneto H, Nakatani Y, Kawamori D, Miyatsuka T, Matsuoka TA, Matsuhisa M, Yamasaki Y. Role of oxidative stress, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and c-Jun N-terminal kinase in pancreatic beta-cell dysfunction and insulin resistance. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2005; 37:1595–1608. PMID: 15878838.37. Kaneto H, Matsuoka TA, Nakatani Y, Kawamori D, Miyatsuka T, Matsuhisa M, Yamasaki Y. Oxidative stress, ER stress, and the JNK pathway in type 2 diabetes. J Mol Med (Berl). 2005; 83:429–439. PMID: 15759102.
Article38. Kim JY, Lee DY, Lee YJ, Park KJ, Kim KH, Kim JW, Kim WH. Chronic alcohol consumption potentiates the development of diabetes through pancreatic β-cell dysfunction. World J Biol Chem. 2015; 6:1–15. PMID: 25717351.
Article39. Cullinan SB, Diehl JA. Coordination of ER and oxidative stress signaling: the PERK/Nrf2 signaling pathway. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2006; 38:317–332. PMID: 16290097.
Article40. Hotamisligil GS. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and the inflammatory basis of metabolic disease. Cell. 2010; 140:900–917. PMID: 20303879.
Article41. Dembele K, Nguyen KH, Hernandez TA, Nyomba BL. Effects of ethanol on pancreatic beta-cell death: interaction with glucose and fatty acids. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2009; 25:141–152. PMID: 18330713.
Article42. Ji C. Dissection of endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling in alcoholic and non-alcoholic liver injury. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008; 23(Suppl 1):S16–S24. PMID: 18336657.
Article43. Ji C. New Insights into the Pathogenesis of alcohol-induced ER stress and liver diseases. Int J Hepatol. 2014; 2014:513787. PMID: 24868470.
Article44. Esfandiari F, Villanueva JA, Wong DH, French SW, Halsted CH. Chronic ethanol feeding and folate deficiency activate hepatic endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway in micropigs. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2005; 289:G54–G63. PMID: 15705656.
Article45. Hamelet J, Demuth K, Paul JL, Delabar JM, Janel N. Hyperhomocysteinemia due to cystathionine beta synthase deficiency induces dysregulation of genes involved in hepatic lipid homeostasis in mice. J Hepatol. 2007; 46:151–159. PMID: 17030070.
Article46. van der Kallen CJ, van Greevenbroek MM, Stehouwer CD, Schalkwijk CG. Endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis in the development of diabetes: is there a role for adipose tissue and liver? Apoptosis. 2009; 14:1424–1434. PMID: 19757063.
Article47. Werstuck GH, Lentz SR, Dayal S, Hossain GS, Sood SK, Shi YY, Zhou J, Maeda N, Krisans SK, Malinow MR, Austin RC. Homocysteine-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress causes dysregulation of the cholesterol and triglyceride biosynthetic pathways. J Clin Invest. 2001; 107:1263–1273. PMID: 11375416.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The effect of moderate alcohol drinking in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- Epidemiology of Alcoholic Liver Disease in Korea
- The effects of moderate alcohol consumption on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- Effects of Moderate Alcohol Drinking in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
- Aqueous extract of Laurus nobilis leaf accelerates the alcohol metabolism and prevents liver damage in singleethanol binge rats