Nutr Res Pract.
2023 Dec;17(6):1113-1127. 10.4162/nrp.2023.17.6.1113.
Aqueous extract of Laurus nobilis leaf accelerates the alcohol metabolism and prevents liver damage in singleethanol binge rats
- Affiliations
-
- 1Industry coupled Cooperation Center for Bio Healthcare Materials, Hallym University, Chuncheon 24252, Korea
- 2Department of Food and Nutrition, Sahmyook University, Seoul 01795, Korea
- 3R&D Division, Daehan Chemtech Co. Ltd., Gwacheon 13840, Korea
- KMID: 2548868
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4162/nrp.2023.17.6.1113
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/OBJECTIVES
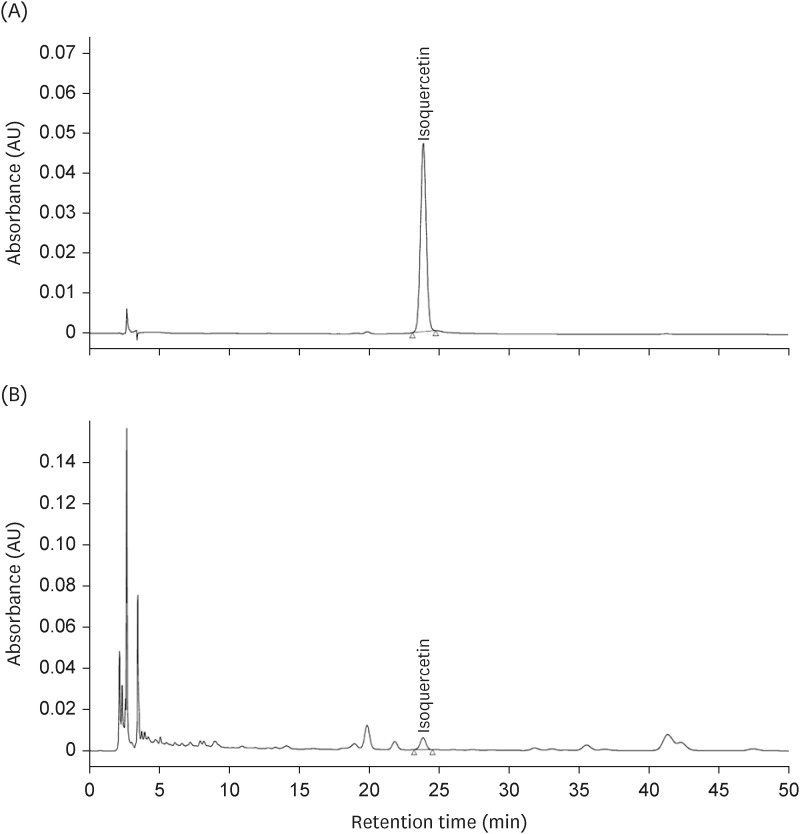
Excessive alcohol consumption has harmful health effects, including alcohol hangovers and alcohol-related liver disease. Therefore, methods to accelerate the alcohol metabolism are needed. Laurus nobilis is a spice, flavoring agent, and traditional herbal medicine against various diseases. This study examined whether the standardized aqueous extract of L. nobilis leaves (LN) accelerates the alcohol metabolism and protects against liver damage in single-ethanol binge Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats.
MATERIALS/METHODS
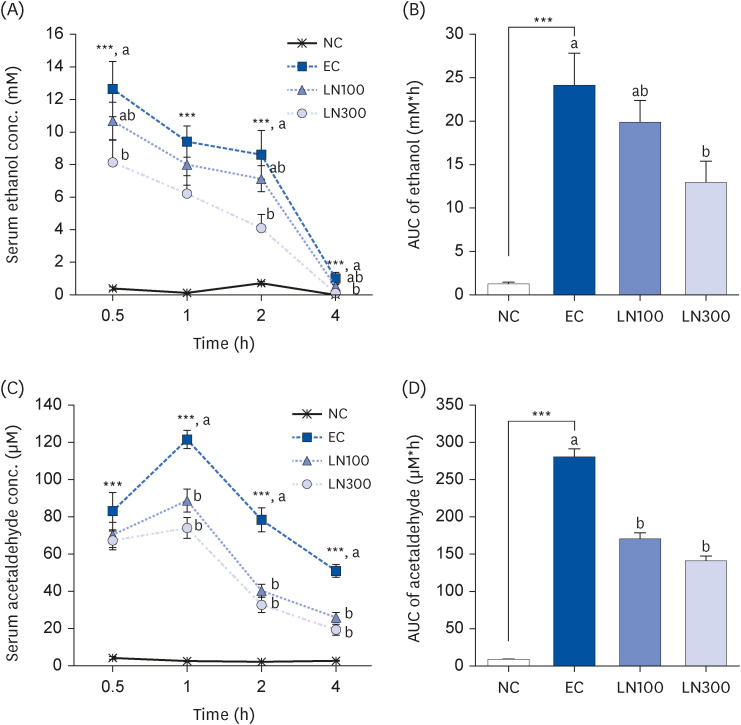
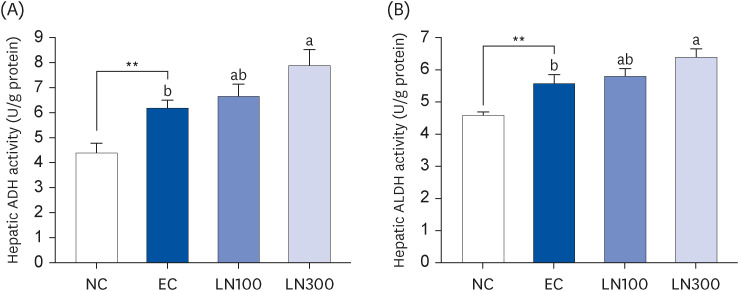
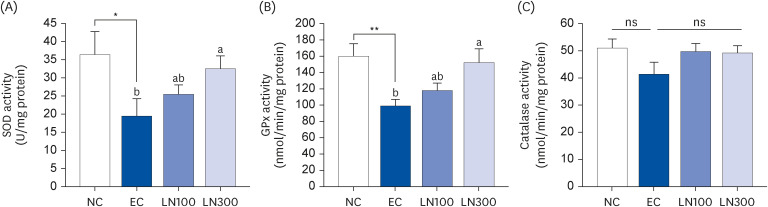
LN was administered orally to SD rats 1 h before ethanol administration (3 g/kg body weight [BW]) at 100 and 300 mg/kg BW. Blood samples were collected 0.5, 1, 2, and 4 h after ethanol administration. The livers were excised 1 h after ethanol administration to determine the hepatic enzyme activity. The alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH), aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and glutathione peroxidase (GPx) activities in the liver tissue were measured.
RESULTS
LN decreased the serum ethanol and acetaldehyde levels in ethanol-administered rats. LN increased the hepatic ADH and ALDH activities but decreased the alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, and gamma-glutamyl transferase activities in the ethanol-administered rats. In addition, LN inhibited lipid peroxidation and increased the activities of SOD and GPx.
CONCLUSIONS
LN modulates the mediators of various etiological effects of excessive alcohol consumption and enhances the alcohol metabolism and antioxidant activity, making it a potential candidate for hangover treatments.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Verster JC, Scholey A, van de Loo AJ, Benson S, Stock AK. Updating the definition of the alcohol hangover. J Clin Med. 2020; 9:823. PMID: 32197381.2. Wiese JG, Shlipak MG, Browner WS. The alcohol hangover. Ann Intern Med. 2000; 132:897–902. PMID: 10836917.3. Gyamfi MA, Wan YJ. Pathogenesis of alcoholic liver disease: the role of nuclear receptors. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2010; 235:547–560. PMID: 20463294.4. Jiang Y, Zhang T, Kusumanchi P, Han S, Yang Z, Liangpunsakul S. Alcohol metabolizing enzymes, microsomal ethanol oxidizing system, cytochrome P450 2E1, catalase, and aldehyde dehydrogenase in alcohol-associated liver disease. Biomedicines. 2020; 8:50. PMID: 32143280.5. Mackus M, Loo AJ, Garssen J, Kraneveld AD, Scholey A, Verster JC. The role of alcohol metabolism in the pathology of alcohol hangover. J Clin Med. 2020; 9:3421. PMID: 33113870.6. Niemelä O, Parkkila S, Ylä-Herttuala S, Villanueva J, Ruebner B, Halsted CH. Sequential acetaldehyde production, lipid peroxidation, and fibrogenesis in micropig model of alcohol-induced liver disease. Hepatology. 1995; 22:1208–1214. PMID: 7557872.7. Kang KK, Seo MS, Sung SE, Choi JH, Lee S, Kim K, Jang W, Lee HS. Effects of Raphanus sativus var. niger (black radish) fermented with Lactobacillus plantarum on alcohol metabolism in rats. Food Suppl Biomater Health. 2021; 1:e22.8. Palmer E, Tyacke R, Sastre M, Lingford-Hughes A, Nutt D, Ward RJ. Alcohol Hangover: underlying biochemical, inflammatory and neurochemical mechanisms. Alcohol Alcohol. 2019; 54:196–203. PMID: 30916313.9. Ceni E, Mello T, Galli A. Pathogenesis of alcoholic liver disease: role of oxidative metabolism. World J Gastroenterol. 2014; 20:17756–17772. PMID: 25548474.10. Wang F, Li Y, Zhang YJ, Zhou Y, Li S, Li HB. Natural products for the prevention and treatment of hangover and alcohol use disorder. Molecules. 2016; 21:64. PMID: 26751438.11. Jayawardena R, Thejani T, Ranasinghe P, Fernando D, Verster JC. Interventions for treatment and/or prevention of alcohol hangover: systematic review. Hum Psychopharmacol. 2017; 32:e2600.12. Pittler MH, Ernst E. Systematic review: hepatotoxic events associated with herbal medicinal products. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2003; 18:451–471. PMID: 12950418.13. dela Pena IJ, dela Pena JB, Yoon SY, Kim HJ, Lee JH, Paek SH, et al. Supplementation of Laurus nobilis attenuate ethanol-induced psychomotor alterations in rats. Nat Prod Sci. 2014; 20:44–50.14. Simić M, Kundaković T, Kovacević N. Preliminary assay on the antioxidative activity of Laurus nobilis extracts. Fitoterapia. 2003; 74:613–616. PMID: 12946729.15. Dadalioǧlu I, Evrendilek GA. Chemical compositions and antibacterial effects of essential oils of Turkish oregano (Origanum minutiflorum), bay laurel (Laurus nobilis), Spanish lavender (Lavandula stoechas L.), and fennel (Foeniculum vulgare) on common foodborne pathogens. J Agric Food Chem. 2004; 52:8255–8260. PMID: 15612826.16. Ferreira A, Proença C, Serralheiro ML, Araújo ME. The in vitro screening for acetylcholinesterase inhibition and antioxidant activity of medicinal plants from Portugal. J Ethnopharmacol. 2006; 108:31–37. PMID: 16737790.17. Dhifi W, Bellili S, Jazi S, Nasr SB, El-Beyrouthy M, Mnif W. Phytochemical composition and antioxidant activity of Tunisian Laurus nobilis . Pak J Pharm Sci. 2018; 31:2397–2402. PMID: 30473510.18. Lee EH, Shin JH, Kim SS, Lee H, Yang SR, Seo SR. Laurus nobilis leaf extract controls inflammation by suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome activation. J Cell Physiol. 2019; 234:6854–6864. PMID: 30387132.19. Bouadid I, Amssayef A, Eddouks M. Study of the anti-hypertensive effect of Laurus nobilis in rats. Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 2023; 21:42–54. PMID: 35549860.20. Mohammed RR, Omer AK, Yener Z, Uyar A, Ahmed AK. Biomedical effects of Laurus nobilis L. leaf extract on vital organs in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats: Experimental research. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2020; 61:188–197. PMID: 33520200.21. Qnais EY, Abdulla FA, Kaddumi EG, Abdalla SS. Antidiarrheal activity of Laurus nobilis L. leaf extract in rats. J Med Food. 2012; 15:51–57. PMID: 22082096.22. Marza Hamza N, Malik Yasir S, Abdulsajjad M Hussain K. Biological effects of aqueous extract of Laurus noboilis L. leaves on some histological and immunological parameters in male rat liver affected by aluminum chloride. Arch Razi Inst. 2021; 76:1745–1753. PMID: 35546977.23. Matsuda H, Shimoda H, Ninomiya K, Yoshikawa M. Inhibitory mechanism of costunolide, a sesquiterpene lactone isolated from Laurus nobilis, on blood-ethanol elevation in rats: involvement of inhibition of gastric emptying and increase in gastric juice secretion. Alcohol Alcohol. 2002; 37:121–127. PMID: 11912066.24. Dobroslavić E, Repajić M, Dragović-Uzelac V, Elez Garofulić I. Isolation of Laurus nobilis leaf polyphenols: a review on current techniques and future perspectives. Foods. 2022; 11:235. PMID: 35053967.25. Paparella A, Nawade B, Shaltiel-Harpaz L, Ibdah M. A review of the botany, volatile composition, biochemical and molecular aspects, and traditional uses of Laurus nobilis . Plants. 2022; 11:1209. PMID: 35567209.26. Yoshikawa M, Shimoda H, Uemura T, Morikawa T, Kawahara Y, Matsuda H. Alcohol absorption inhibitors from bay leaf (Laurus nobilis): structure-requirements of sesquiterpenes for the activity. Bioorg Med Chem. 2000; 8:2071–2077. PMID: 11003152.27. Tinoco MT, Ramos P, Candeias MF. Effects of a hexane extract from Laurus novocanariensis leaves on the ethanol metabolism of Wistar rats. Fitoterapia. 2009; 80:130–133. PMID: 19166918.28. Medeiros-Fonseca B, Mestre VF, Colaço B, Pires MJ, Martins T, Gil da Costa RM, Neuparth MJ, Medeiros R, Moutinho MS, Dias MI, et al. Laurus nobilis (laurel) aqueous leaf extract’s toxicological and anti-tumor activities in HPV16-transgenic mice. Food Funct. 2018; 9:4419–4428. PMID: 30066000.29. Vidal F, Toda R, Gutiérrez C, Broch M, Fernández-Muixí F, Lorenzo A, Richart C. Influence of chronic alcohol abuse and liver disease on hepatic aldehyde dehydrogenase activity. Alcohol. 1998; 15:3–8. PMID: 9426831.30. Mackus M, van de Loo AJ, Garssen J, Kraneveld AD, Scholey A, Verster JC. The association between ethanol elimination rate and hangover severity. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020; 17:4324. PMID: 32560357.31. Contreras-Zentella ML, Villalobos-García D, Hernández-Muñoz R. Ethanol metabolism in the liver, the induction of oxidant stress, and the antioxidant defense system. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022; 11:1258. PMID: 35883749.32. Yang Z, Gao Y, Wu W, Mu H, Liu R, Fang X, Gao H, Chen H. The mitigative effect of lotus root (Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn) extract on acute alcoholism through activation of alcohol catabolic enzyme, reduction of oxidative stress, and protection of liver function. Front Nutr. 2023; 9:1111283. PMID: 36712522.33. Kang HW, Yu KW, Jun WJ, Chang IS, Han SB, Kim HY, Cho HY. Isolation and characterization of alkyl peroxy radical scavenging compound from leaves of Laurus nobilis . Biol Pharm Bull. 2002; 25:102–108. PMID: 11824536.34. Lee HY, Lee GH, Hoang TH, Kim SW, Kang CG, Jo JH, Chung MJ, Min K, Chae HJ. Turmeric extract (Curcuma longa L.) regulates hepatic toxicity in a single ethanol binge rat model. Heliyon. 2022; 8:e10737. PMID: 36193527.35. Lee S, Lee J, Lee H, Sung J. Relative protective activities of quercetin, quercetin-3-glucoside, and rutin in alcohol-induced liver injury. J Food Biochem. 2019; 43:e13002. PMID: 31378953.36. Lee HJ, Saravana PS, Ho TC, Cho YJ, Park JS, Lee SG, Chun BS. In vivo protective effect against ethanol metabolism and liver injury of oyster (Crassostrea gigas) extracts obtained via subcritical water processing. Food Sci Biotechnol. 2021; 30:1063–1074. PMID: 34471560.37. Kitakaze T, Inoue M, Ashida H. Aged garlic extract prevents alcohol-induced cytotoxicity through induction of aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 in the liver of mice. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2023; 67:e2200627. PMID: 36856009.38. Wu D, Cederbaum A. Glutathione depletion in CYP2E1-expressing liver cells induces toxicity due to the activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and reduction of nuclear factor-κB DNA binding activity. Mol Pharmacol. 2004; 66:749–760. PMID: 15322268.39. Ali H, Assiri MA, Shearn CT, Fritz KS. Lipid peroxidation derived reactive aldehydes in alcoholic liver disease. Curr Opin Toxicol. 2019; 13:110–117. PMID: 31263795.40. Cederbaum AI, Lu Y, Wu D. Role of oxidative stress in alcohol-induced liver injury. Arch Toxicol. 2009; 83:519–548. PMID: 19448996.41. Ezhilarasan D. Oxidative stress is bane in chronic liver diseases: clinical and experimental perspective. Arab J Gastroenterol. 2018; 19:56–64. PMID: 29853428.42. De Minicis S, Brenner DA. Oxidative stress in alcoholic liver disease: role of NADPH oxidase complex. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008; 23(Suppl 1):S98–103. PMID: 18336675.43. Cederbaum AI. Cytochrome P450 2E1-dependent oxidant stress and upregulation of anti-oxidant defense in liver cells. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006; 21(Suppl 3):S22–S25. PMID: 16958665.44. Wang F, Zhang YJ, Zhou Y, Li Y, Zhou T, Zheng J, Zhang JJ, Li S, Xu DP, Li HB. Effects of beverages on alcohol metabolism: Potential health benefits and harmful impacts. Int J Mol Sci. 2016; 17:354. PMID: 27005619.45. Lee JY, An YJ, Kim JW, Choi HK, Lee YH. Effect of Angelica keiskei Koidzumi extract on alcohol-induced hepatotoxicity in vitro and in vivo . J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 2016; 45:1391–1397.46. Li BY, Li HY, Zhou DD, Huang SY, Luo M, Gan RY, Mao QQ, Saimaiti A, Shang A, Li HB. Effects of different green tea extracts on chronic alcohol induced-fatty liver disease by ameliorating oxidative stress and inflammation in mice. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021; 2021:5188205. PMID: 35003517.47. Li HY, Gan RY, Shang A, Mao QQ, Sun QC, Wu DT, Geng F, He XQ, Li HB. Plant-based foods and their bioactive compounds on fatty liver disease: effects, mechanisms, and clinical application. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021; 2021:6621644. PMID: 33728021.48. Li S, Gan LQ, Li SK, Zheng JC, Xu DP, Li HB. Effects of herbal infusions, tea and carbonated beverages on alcohol dehydrogenase and aldehyde dehydrogenase activity. Food Funct. 2014; 5:42–49. PMID: 24162728.49. Manir MM, Kim JK, Lee BG, Moon SS. Tea catechins and flavonoids from the leaves of Camellia sinensis inhibit yeast alcohol dehydrogenase. Bioorg Med Chem. 2012; 20:2376–2381. PMID: 22377672.50. Yamashita H, Goto M, Matsui-Yuasa I, Kojima-Yuasa A. Ecklonia cava polyphenol has a protective effect against ethanol-induced liver injury in a cyclic AMP-dependent manner. Mar Drugs. 2015; 13:3877–3891. PMID: 26096275.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Chronic-Binge Ethanol Drinking Exacerbates Liver Damage through Oxidative/Nitrosative Stress
- In Vivo Assessment of Punica granatum Leaf Extract: Anti-Urolithiatic and Nephroprotective Effects
- A comparative study on the hepatoprotective effect of selenium-nanoparticles and dates flesh extract on carbon tetrachloride induced liver damage in albino rats
- Pretreatment of Albino Rats with Methanolic Fruit Extract of Randia Dumetorum (L.) Protects against Alcohol Induced Liver Damage
- Postprandial hypoglycemic effect of mulberry leaf in Goto-Kakizaki rats and counterpart control Wistar rats