Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2008 Dec;12(6):307-314. 10.4196/kjpp.2008.12.6.307.
Functional Connectivity Map of Retinal Ganglion Cells for Retinal Prosthesis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physiology, Chungbuk National University School of Medicine, Cheongju 361-763, Korea. ysgoo@chungbuk.ac.kr
- 2Department of Biomedical Engineering, College of Health Science, Yonsei University, Wonju 220-710, Korea.
- 3Nano Artificial Vision Research Center, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul 110-744, Korea.
- KMID: 2285357
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2008.12.6.307
Abstract
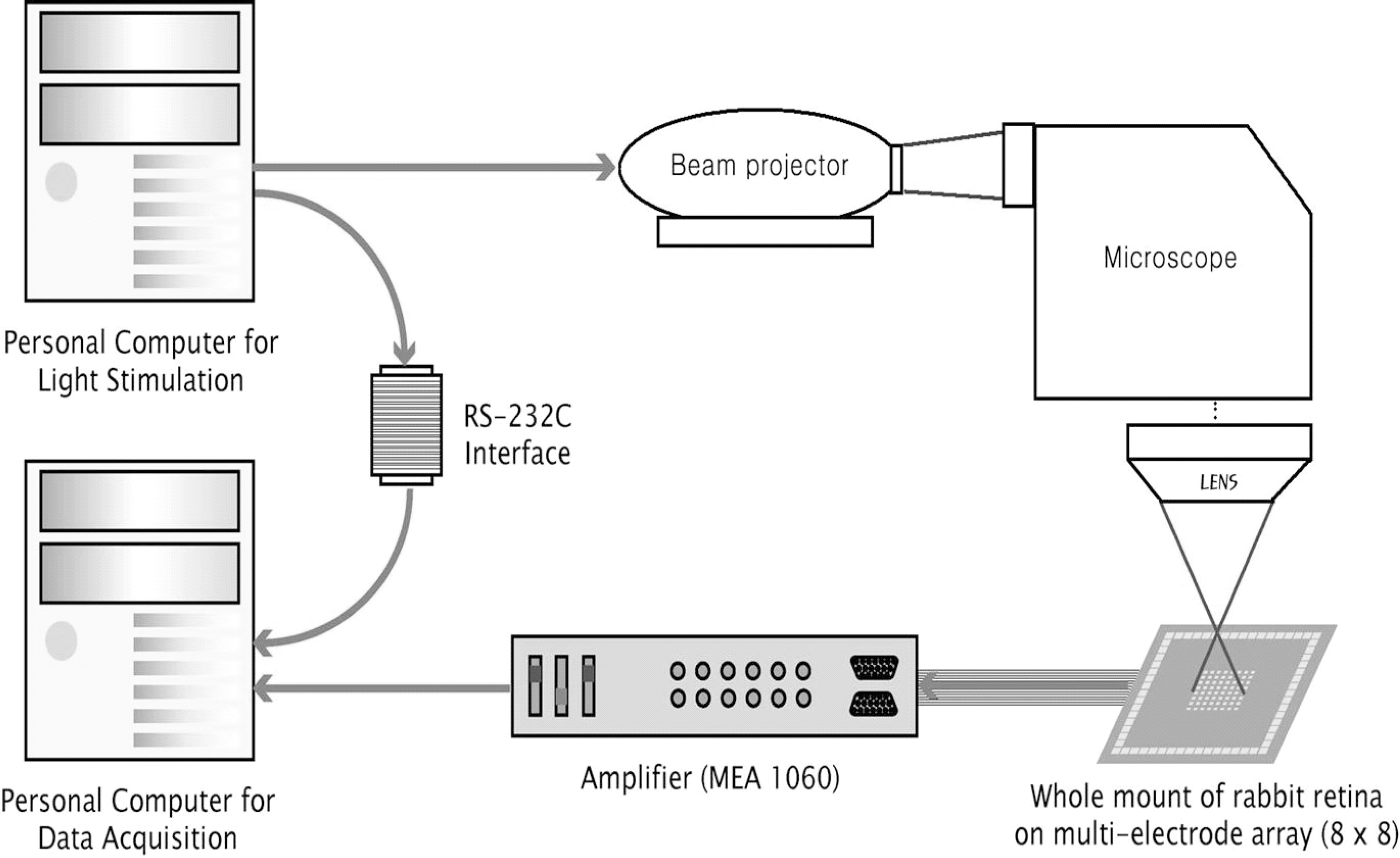
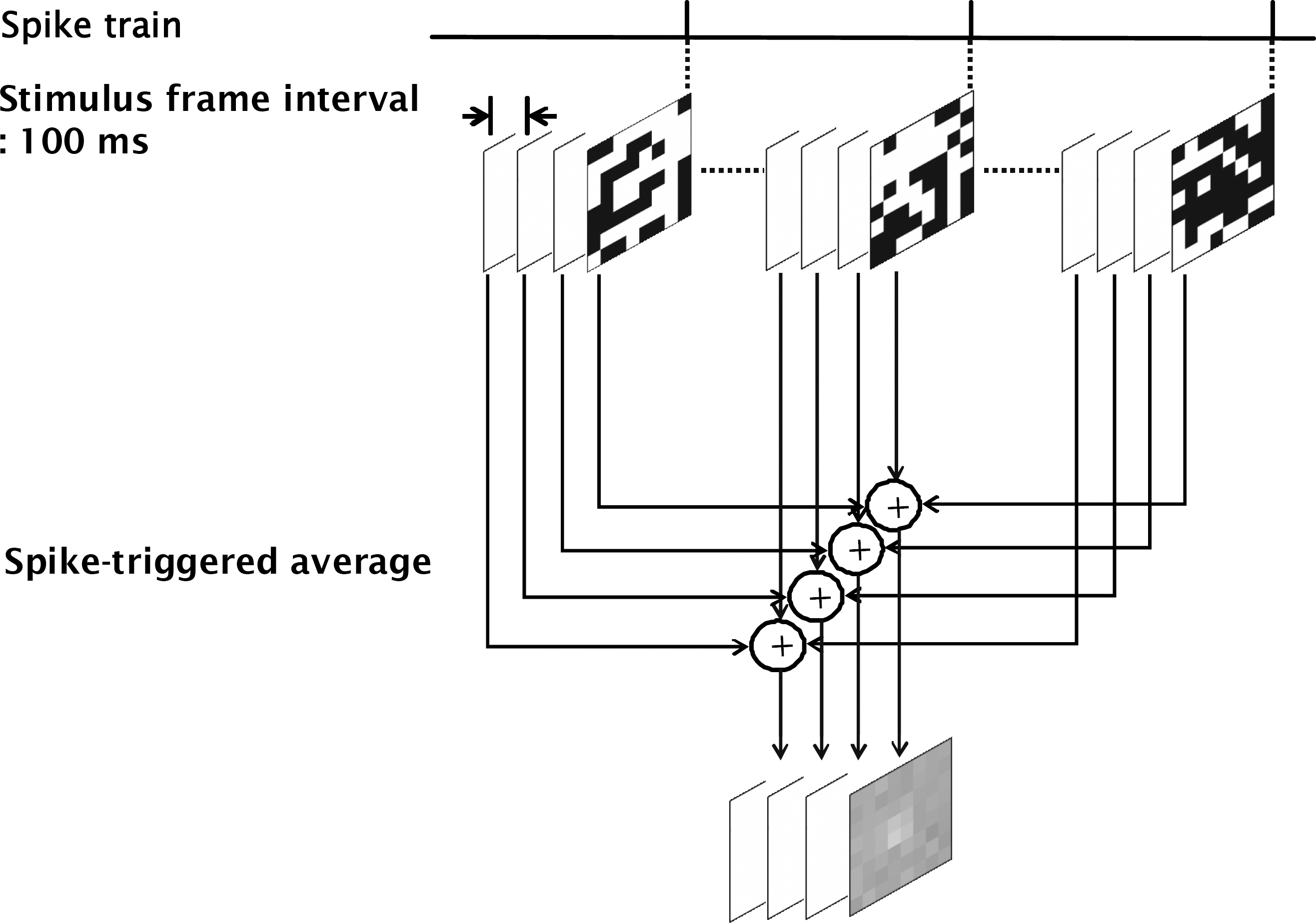
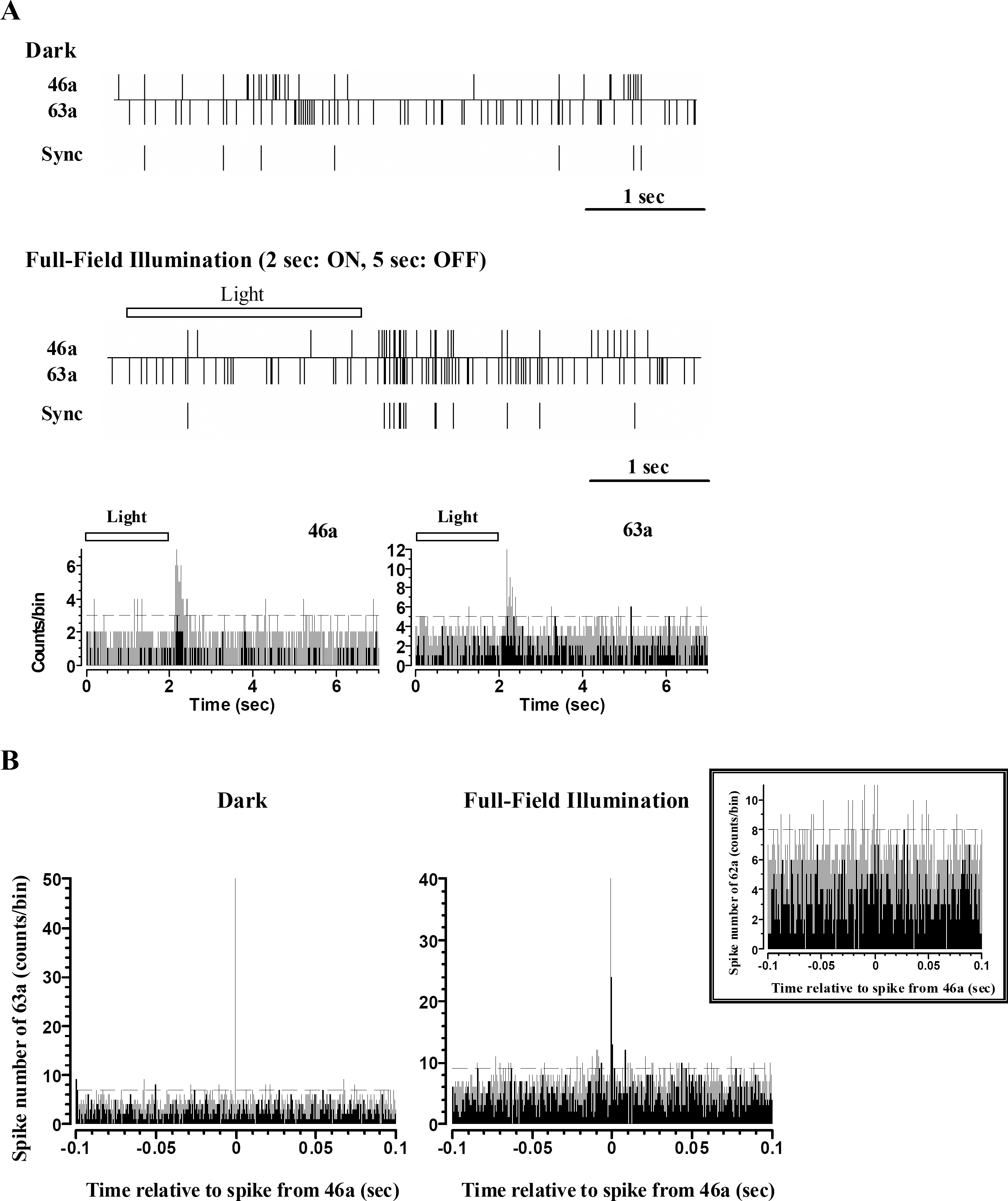
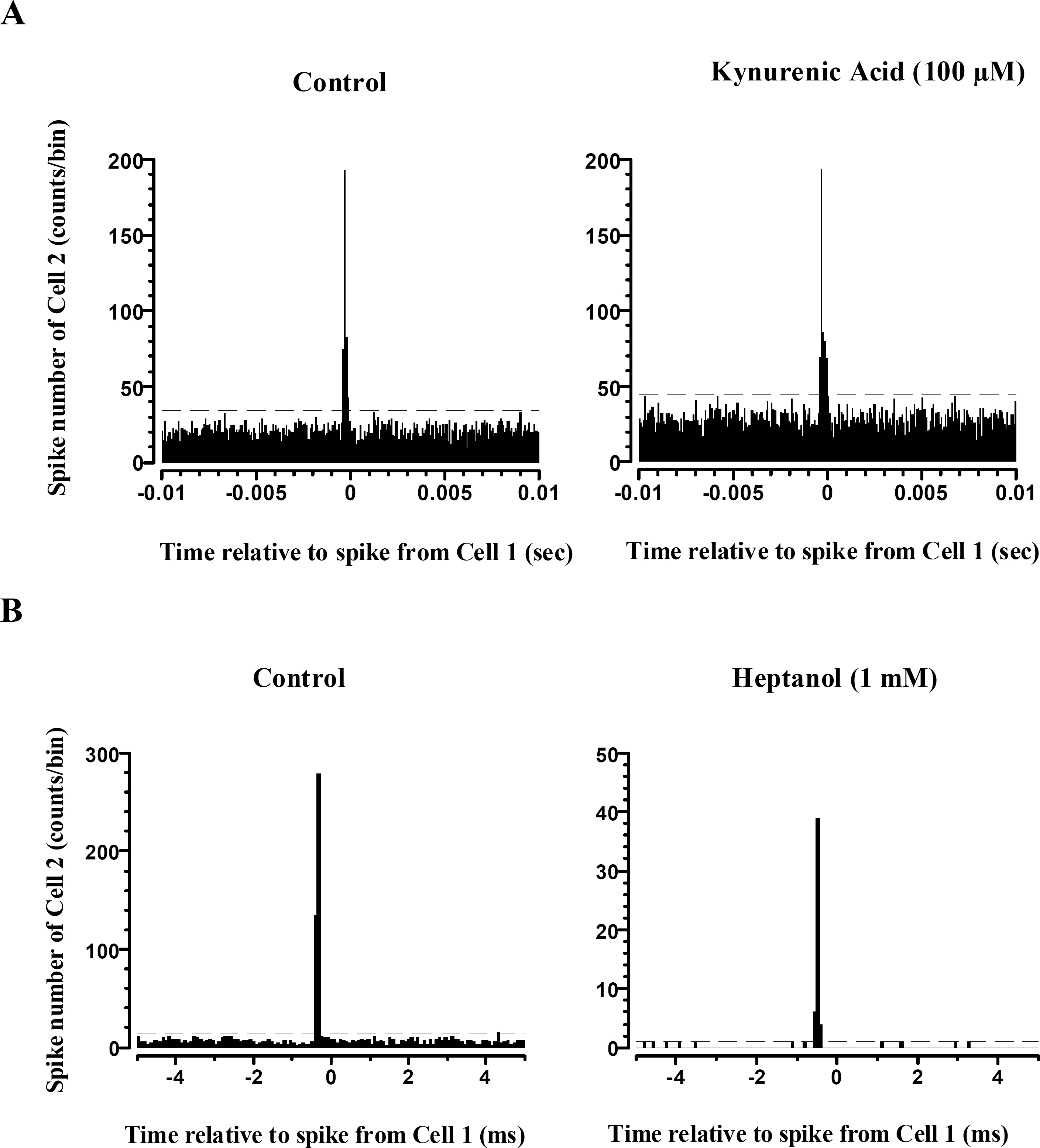
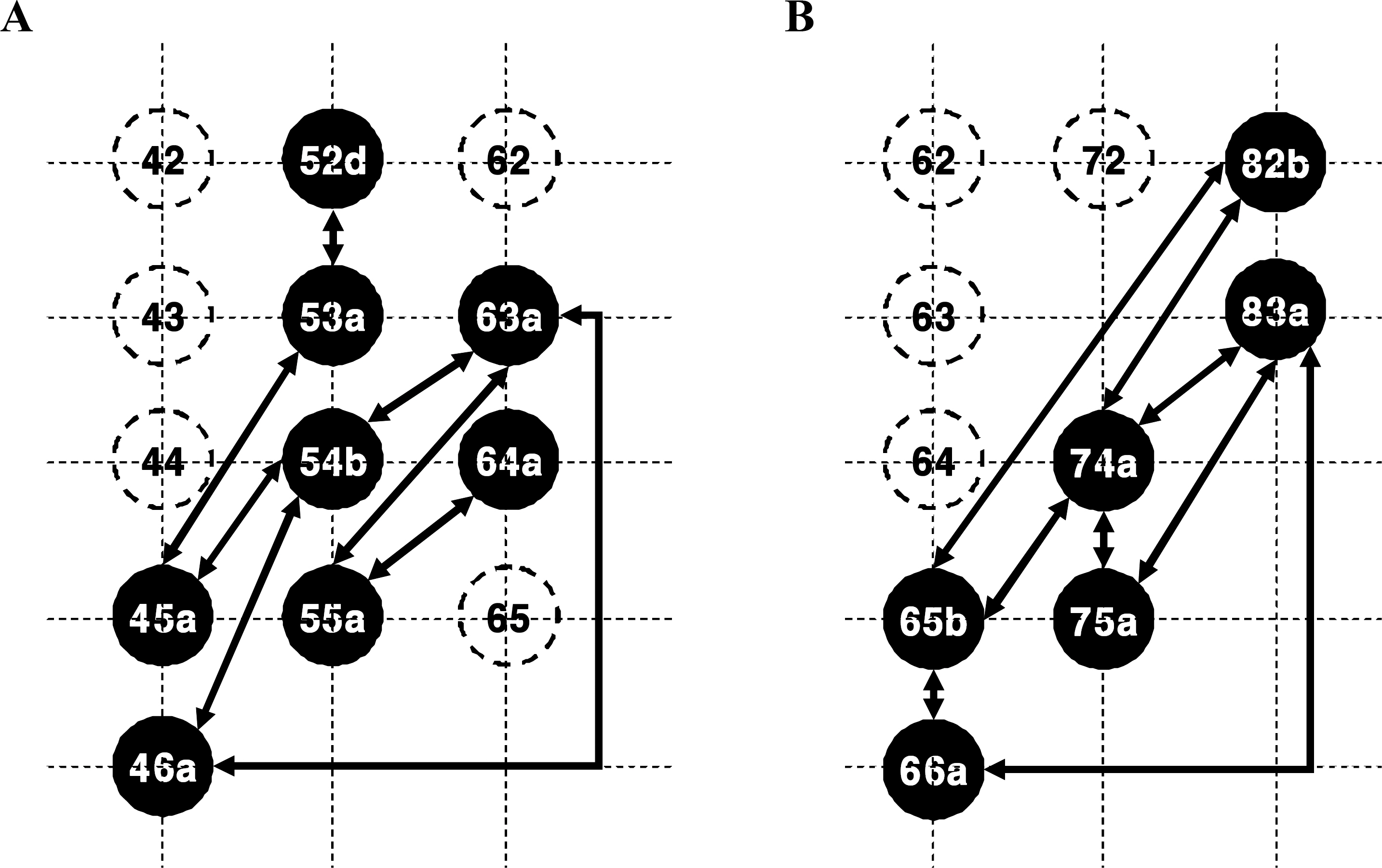
- Retinal prostheses are being developed to restore vision for the blind with retinal diseases such as retinitis pigmentosa (RP) or age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Among the many issues for prosthesis development, stimulation encoding strategy is one of the most essential electrophysiological issues. The more we understand the retinal circuitry how it encodes and processes visual information, the greater it could help decide stimulation encoding strategy for retinal prosthesis. Therefore, we examined how retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) in in-vitro retinal preparation act together to encode a visual scene with multielectrode array (MEA). Simultaneous recording of many RGCs with MEA showed that nearby neurons often fired synchronously, with spike delays mostly within 1 ms range. This synchronized firing - narrow correlation - was blocked by gap junction blocker, heptanol, but not by glutamatergic synapse blocker, kynurenic acid. By tracking down all the RGC pairs which showed narrow correlation, we could harvest 40 functional connectivity maps of RGCs which showed the cell cluster firing together. We suggest that finding functional connectivity map would be useful in stimulation encoding strategy for the retinal prosthesis since stimulating the cluster of RGCs would be more efficient than separately stimulating each individual RGC.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Effect of Stimulus Waveform of Biphasic Current Pulse on Retinal Ganglion Cell Responses in Retinal Degeneration (
rd1 ) mice
Kun No Ahn, Jeong Yeol Ahn, Jae-hyung Kim, Kyoungrok Cho, Kyo-in Koo, Solomon S. Senok, Yong Sook Goo
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2015;19(2):167-175. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2015.19.2.167.Accurate Representation of Light-intensity Information by the Neural Activities of Independently Firing Retinal Ganglion Cells
Sang Baek Ryu, Jang Hee Ye, Chi Hyun Kim, Yong Sook Goo, Kyung Hwan Kim
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2009;13(3):221-227. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2009.13.3.221.
Reference
-
Amthor FR., Takahashi ES., Oyster CW. Morphologies of rabbit retinal ganglion cells with concentric receptive fields. J Comp Neurol. 280:72–96. 1989a.
ArticleAmthor FR., Takahashi ES., Oyster CW. Morphologies of rabbit retinal ganglion cells with complex receptive fields. J Comp Neurol. 280:97–121. 1989b.
ArticleArnett D., Spraker TE. Cross-correlation analysis of the maintained discharge of rabbit retinal ganglion cells. J Physiol (London). 317:29–47. 1981.
ArticleBrivanlou IH., Warland DK., Meister M. Mechanisms of concerted firing among retinal ganglion cells. Neuron. 20:527–539. 1998.
ArticleBrown SP., He S., Masland RH. Receptive field microstructure and dendritic geometry of retinal ganglion cells. Neuron. 27:371–383. 2000.
ArticleCaldwell JH., Daw NW. New properties of rabbit retinal ganglion cells. J Physiol (Lond.). 276:257–276. 1978.
ArticleDeVries SH., Baylor DA. Mosaic arrangement of ganglion cell receptive fields in rabbit retina. J Neurophysiol. 78:2048–2060. 1997.
ArticleDeVries SH. Correlated firing in rabbit retinal ganglion cells. J Neurophysiol. 81:908–920. 1999.
ArticleEgert U., Schlosshauer B., Fennrich S., Nisch W., Fejtl M., Knott T., Muller T., Hammerle H. A novel organotypic long-term culture of the rat hippocampus on substrate-integrated multielectrode arrays. Brain Res Protoc. 2:229–242. 1998.
ArticleGuenther E., Herrmann T., Stett A. The retina sensor: An in vitro tool to study drug effects on retinal signaling. Taketani M, Baudry M, editors. ed,. Advances in Network Electrophysiology Using Multi-electrode Arrays. 1st ed.Springer;New York: p. p. 321–331. 2006.Humayun MS., Weiland JD., Fujii GY., Greenberg R., Williamson R., Little J., Mech G., Cimmarusti V., Boemel GV., Dagnelie G., de Juan Jr E. Visual perception in a blind subject with a chronic microelectronic retinal prosthesis. Vis Res. 43:2573–2581. 2003.
ArticleLowenstein JI., Montezuma SR., Rizzo III JF. Outer retinal degeneration: an electronic retinal prosthesis as a treatment strategy. Archives of Ophthalmology. 122:588–596. 2004.Margolis DJ., Detwilder PB. Different mechanisms generate maintained activity in ON and OFF retinal ganglion cells. J Neurosci. 27:5994–6005. 2007.
ArticleMastronarde DN. Interactions between ganglion cells in cat retina. J Neurophysiol. 49:350–365. 1983.
ArticleMeister M., Pine J., Baylor DA. Multi-neuronal signals from the retina: acquisition and analysis. J Neurosci Methods. 51:95–106. 1994.
ArticleMeister M., Lagnado L., Baylor DA. Concerted signaling by retinal ganglion cells. Science. 270:1207–1210. 1995.
ArticleMeister M. Multineuronal codes in retinal signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 93:609–614. 1996.
ArticleMeister M., Berry MJ 2nd. The neural code of the retina. Neuron. 22:435–450. 1999.
ArticleNakatani K., Tamura T., Yau KW. Light adaptation in retinal rods of the rabbit and two other nonprimate mammals. J Gen Physiol. 97:413–435. 1991.
ArticleRizzo JF III., Wyatt J., Lowenstein J., Kelly S., Shire D. Perceptual efficacy of electrical stimulation of human retina with a microelectrode array during short-term surgical trials. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 44:5362–5369. 2003.Seo J., Zhou J., Kim E., Koo K., Ye JH., Kim SJ., Chung H., Cho DD., Goo YS., Yu YS. A retinal implant system based on flexible polymer microelectrode array for electrical stimulation. Tombran-Tink J, Barnstable C, Rizzo JF, editors. ed,. Visual Prosthesis and Ophthalmic Devices: New Hope in Sight. 1st ed.Humana Press Inc;New Jersey: p. p. 107–119. 2007.
ArticleStett A., Barth W., Weiss S., Haemmerle H., Zrenner E. Electrical multisite stimulation of isolated chicken retina. Vis Res. 40:1785–1795. 2000.Zrenner E., Besch D., Bartz-Schmidt KU., Gekeler F., Gabriel VP., Kuttenkeuler C., Sachs H., Saier H., Wilhelm B., Wilke R. Subretinal chronic multi-electrode arrays implanted in blind patients. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 47:E Abstract 1538. 2006.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Changes of the Retinal Ganglional Cells in the Pressure-induced Ischemic Rabbit Retina
- NF-kappa B activation following optic nerve transection
- Accurate Representation of Light-intensity Information by the Neural Activities of Independently Firing Retinal Ganglion Cells
- Comparison of Retinal Waveform between Normal and rd/rd Mouse
- Characteristics of Light-evoked Retinal Ganglion Cell Activity with Postnatal Maturation in SD Rat