Ewha Med J.
2013 Mar;36(1):35-42. 10.12771/emj.2013.36.1.35.
Microarray Analysis after Intravenous Immunoglobulin Treatment in Patients with Kawasaki Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, School of Medicine, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea. ymhong@ewha.ac.kr
- KMID: 2284013
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12771/emj.2013.36.1.35
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
The etiology for Kawasaki disease (KD) remains unknown, but several studies have suggested the involvement of immune dysregulation and genetic factors. The purpose of this study is to compare gene expressions before and after an infusion of intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) in KD patients.
METHODS
Blood was obtained from both acute and sub-acute phases of 4 patients with KD and febrile control children. Blood was collected in PAXgene blood RNA tubes and RNA was extracted using a PAXgene blood RNA isolation kit. Labeled RNAs were analyzed using Roche NimbleGen human whole genome 12-plex array.
RESULTS
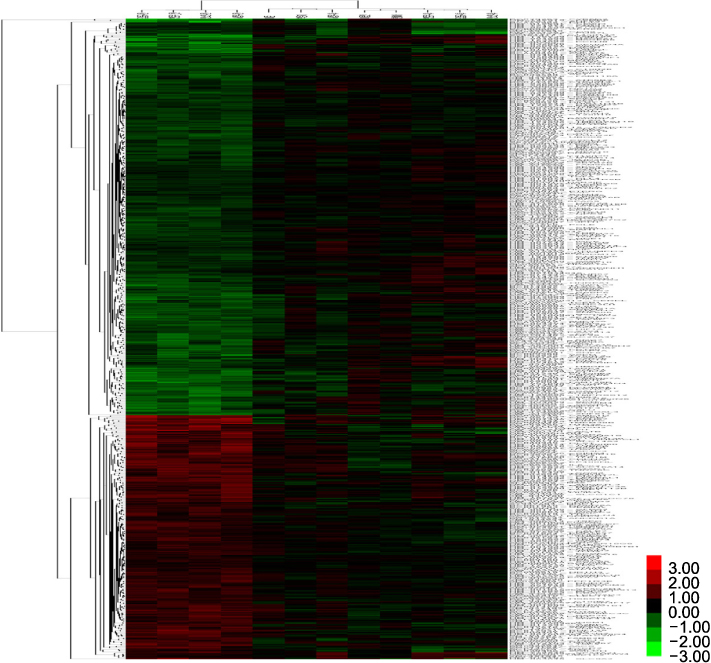
KD patients prior to IVIG injection showed more than a two-fold increase in the expression of 88 genes and more than a two-fold decrease in the expression of 98 genes compared to the control group. They also showed more than two-fold increase in the expression of 226 genes and more than a two-fold decrease in 117 genes in KD patients after IVIG treatment compared to the patients before IVIG injection. Through microarray evaluation, the expressions of genes involved in proliferation, translation, inflammatory response, immune response, cell adhesion, cell migration, cell differentiation, apoptosis, cell growth, transport, cell cycle, transcription, signal transduction and metastasis were observed.
CONCLUSION
Changes in gene expressions in pediatric patients with KD before and after IVIG were observed via microarray evaluation.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Park AH, Batchra N, Rowley A, Hotaling A. Patterns of Kawasaki syndrome presentation. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 1997. 40:41–50.2. Shulman ST, Rowley AH. Etiology and pathogenesis of Kawasaki disease. Prog Pediatr Cardiol. 1997. 6:187–192.3. Fulton DR, Newburger JW. Long term cardiac sequelae of Kawasaki disease. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2000. 2:324–329.4. Crystal MA, Manhiot C, Yeung RSM, Smallhorn JF, McCrindle BW. Coronary artery dilation after Kawasaki disease for children within the normal range. Int J Cardiol. 2009. 136:27–32.5. Newburger JW. Takahashi M, Beiser AS, Burns JC, Bastian J, Chung KJ, et al. Single infusion of intravenous gamma globulin compared to four daily doses in the treatment of acute Kawasaki syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1991. 324:1633–1639.6. Leung DY, Cortran RS, Kurt-Jones E, Burns JC, Newburger JW, Pober JS. Endothelial cell activation and high interleukin-1 secretion in the pathogenesis of acute Kawasaki disease. Lancet. 1989. 334:1298–1302.7. Galeotti C, Bayry J, Kone-Paut I, Kaveri SV. Kawasaki disease: Aetiopathogenesis and therapeutic utility of intravenous immunoglobulin. Autoimmun Rev. 2010. 9:441–448.8. Dajani AS, Taubert KA, Takahashi M, Bierman FZ, Freed MD, Ferrieri P, et al. Guidelines for long term management of patients with Kawasaki disease. Circulation. 1994. 89:916–922.9. Matsuda A, Morita H, Unno H, Saito H, Matsumoto K, Hirao Y, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of high-dose IgG on TNF-α-activated human coronary artery endothelial cells. Eur J Immunol. 2012. 42:2121–2131.10. Rowley AH, Shulman ST. Pathogenesis and management of Kawasaki disease. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2010. 8:197–203.11. Cheung YF, Huang GY, Chen SB, Liu XQ, Xi L, Liang XC, et al. Inflammatory gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to Kawasaki disease and its arterial sequelae. Pediatrics. 2008. 122:e608–e613.12. Ikeda K, Ihara K, Yamaguchi K, Muneuchi J, Ohno T, Mizuno Y, et al. Genetic analysis of MMP gene polymorphisms in patients with Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Res. 2008. 63:182–185.13. Wang CL, Wu YT, Liu CA, Kuo HC, Yang KD. Kawasaki disease infection, immunity and genetics. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2005. 24:998–1004.14. Shimizu C, Matsubara T, Onouchi Y, Jain S, Sun S, Nievergelt CM, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase haplotypes associated with coronary artery aneurysm formation in patients with Kawasaki disease. J Hum Genet. 2010. 55:779–784.15. Abe J, Hibiki T, Noma S, Nakajima T, Saito H, Terai M. Gene expression profiling of the effect of high dose intravenous Ig in patients with Kawasaki disease. J Immunol. 2005. 174:5837–5845.16. Nomura I, Abe J, Noma S, Saito H, Gao B, Wheeler G, et al. Adrenomedullin is highly expressed in blood monocytes associated with acute Kawasaki disease: A microarray gene expression study. Pediatr Res. 2005. 57:49–55.17. Popper SJ, Shimizu C, Shike H, Kanegaye JT, Newburger JW, SundelRP , et al. Gene expression patterns reveal underlying biological processes in Kawasaki disease. Genome Biol. 2007. 8:R261.18. Nakamura Y, Yashiro M, Uehara R, Sadakane A, Tsuboi S, Aoyama Y, et al. Epidemiologic features of Kawasaki disease in Japan: results of the 2009-2010 nationwide survey. J Epidemiol. 2012. 22:216–221.19. Matsubara T, Ichiyma T, Furukawa S. Immunological profile of peripheral blood lymphocytes and monocytes/macrophages in Kawasaki disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 2005. 141:381–387.20. Gupta M, Noel GJ, Schaefer M, Friedman D, Bussel J, Johann-Liang R. Cytokine modulation with immune gamma-globulin in peripheral blood of normal children and its implications in Kawasaki disease treatment. J Clin Immunol. 2001. 21:193–199.21. Ikeda K, Yamaguchi K, Tanaka T, Mizuno Y, Hijikata A, Ohara O, et al. Unique activation status of peripheral blood mononuclear cells at acute phase of Kawasaki disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 2009. 160:246–255.22. Chang LY, Lin YC, Mahalingam J, Huang CT, Chen TW, Kang CW, et al. Tumor derived chemokine CCL5 enhances TGF-β mediated killing of CD8+ T cells in colon cancer by T regulatory cells. Cancer Res. 2012. 72:1092–1102.23. Mamtani M, Matsubara T, Shimizu C, Furukawa S, Akagi T, Onouchi Y, et al. Association of CCR2-CCR5 haplotypes and CCL3L1 copy number with Kawasaki disease, coronary artery lesions, and IVIG responses in Japanese Children. PLoS One. 2010. 5:e11458.24. Furuno K, Takada H, Yamamoto K, Ikeda K, Ohno T, Khajoee V, et al. Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 2 and coronary artery lesions in Kawasaki disease. J Pediatr. 2007. 151:155–160.25. Lau AC, Duong TT, Ito S, Yeung RSM. Matrix metalloproteinase 9 activity leads to elastin breakdown in an animal model of Kawasaki disease. Arthritis Rheum. 2008. 58:854–863.26. Jian P, Yanfang T, Zhuan Z, Jian W, Xueming Z, Jian Ni. MMP 28(epilysin) as a novel promoter of invasion and metastasis in gastric cancer. BMC Cancer. 2011. 11:200–208.27. Overall CM, Kleifeld O. Towards third generation matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors for cancer therapy. Br J Cancer. 2006. 94:941–946.28. Khajoee V, Kariyazono H, Ohno T, Ihara K, Mizuno Y, Kusuhara K, et al. Inducible and endothelial constitutive nitric oxide synthase gene polymorphisms in Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Int. 2003. 45:130–134.29. Xu MG, Men LN, Zhao CY, Zhao X, Wang UX, Meng XC, et al. The number and function of circulating endothelial progenitor cells in patients with Kawasaki disease. Eur J Pediatr. 2010. 169:289–296.30. Wang CL, Wu YT, Lee CJ, Liu HC, Huang LT, Yang KD. Decreased nitric oxide production after intravenous immunoglobulin treatment in patients with Kawasaki disease. J Pediatr. 2002. 141:560–565.31. Blaisdell LL, Hayman JA, Moran AM. Infliximab treatment for pediatric refractory Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Cardiol. 2011. 32:1023–1027.32. Kuo HC, Yang KD, Chang WC, Ger LP. Hsieh KS. Kawasaki disease: An update on diagnosis and treatment. Pediatr Neonatol. 2012. 53:4–11.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Efficacy and Safety of High-Dose Intravenous Immunoglobulin in the Treatment of Kawasaki Disease: How Can We Predict Resistance to Intravenous Immunoglobulin Treatment of Kawasaki Disease?
- A Comparison of Concentrations of TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma between the Dose of Intravenous Immunoglobulin 1 gm/kg and 2 gm/kg in the Patients with Kawasaki Disease
- Predictors and management of intravenous immunoglobulin-resistant Kawasaki disease
- Factors Predicting Resistance to Intravenous Immunoglobulin and Coronary Complications in Kawasaki Disease: IVIG Resistance in Kawasaki Disease
- The Effect of Early Immunoglobulin Treatment on the Course of Kawasaki Disease