Ann Rehabil Med.
2012 Jun;36(3):311-319. 10.5535/arm.2012.36.3.311.
Effect of Magnetic Stimulation in Spinal Cord on Limb Angiogenesis and Implication: A Pilot Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul 110-744, Korea. kurmguro@paran.com
- KMID: 2266735
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2012.36.3.311
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
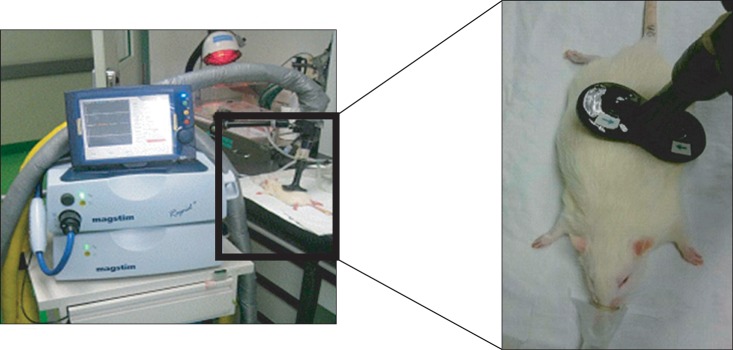
To investigate the effect of repetitive magnetic stimulation (rMS) of the spinal cord on limb angiogenesis in healthy rats and explore its implication for the treatment of lymphedema. METHOD: Twelve adult male Sprague-Dawley rats were divided into four groups as follows: sham rMS followed by tissue harvest 5 minutes later (group 1, n=2), 1 Hz rMS and tissue harvest 5 minutes later (group 2, n=3), 20 Hz rMS and tissue harvest 5 minutes later (group 3, n=3), 20 Hz rMS and tissue harvest 30 minutes later (group 4, n=4). Animals were treated with 20-minute rMS with 120% of the motor threshold on their left side of upper lumbar spinal cord. Expression of angiogenic factors, that is, Akt, phospho-Akt (pAkt), endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS), phospho-eNOS (p-eNOS) were measured by western blot. Bilateral hindlimb muscles (quadriceps and gastrocnemius) were harvested.
RESULTS
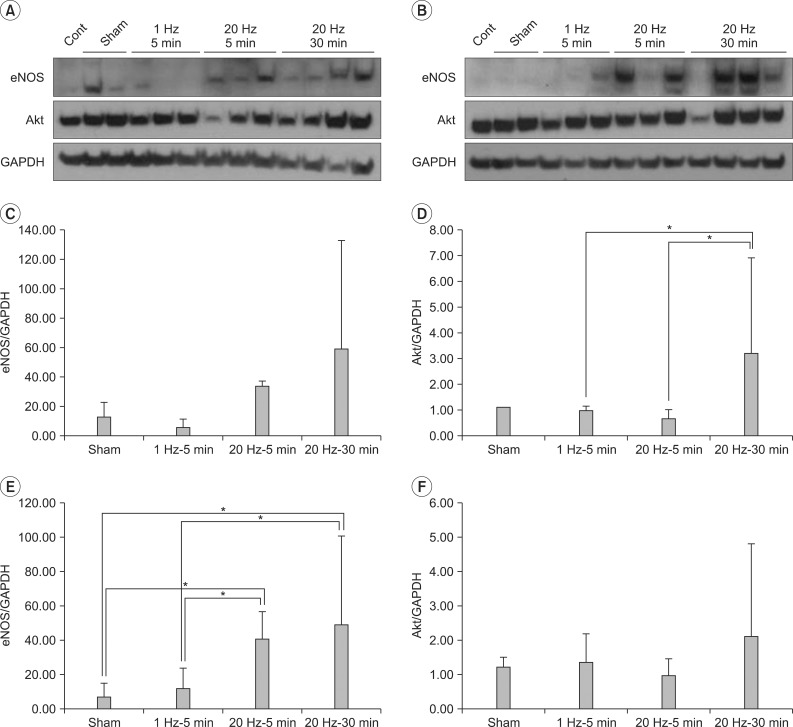
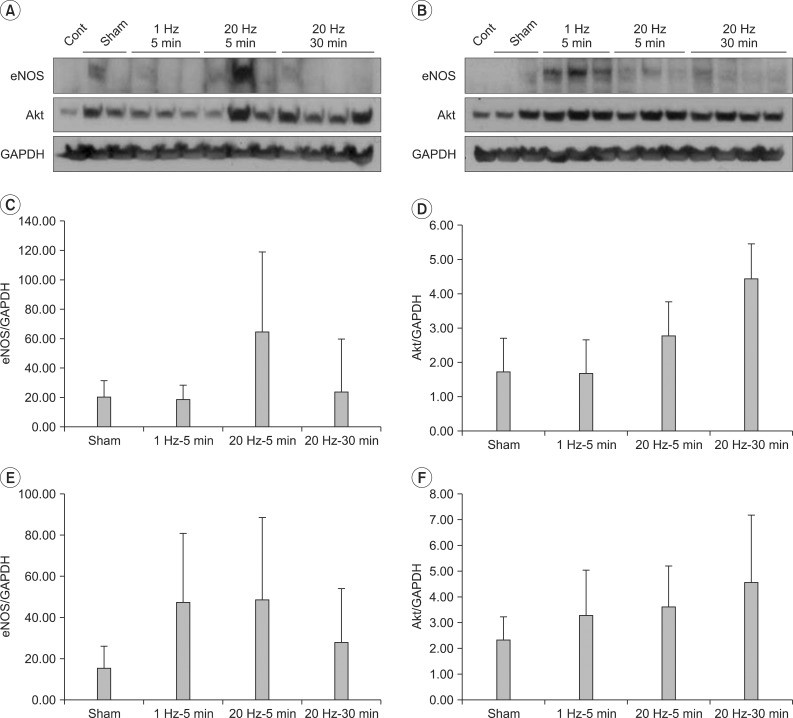
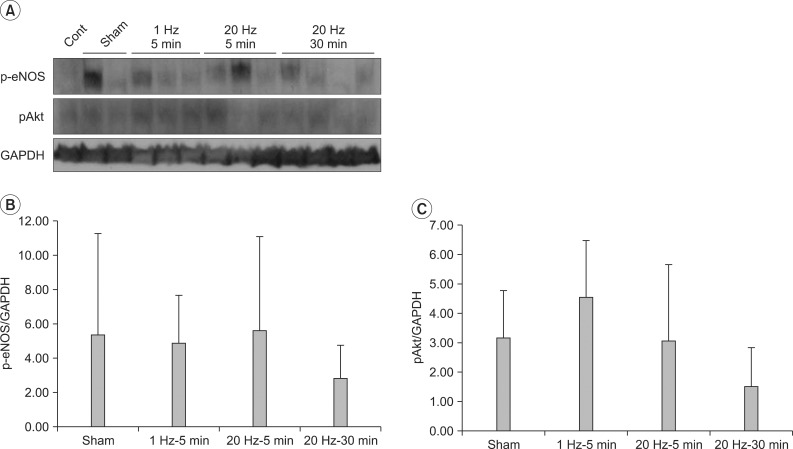
Expression of Akt in left quadriceps increased in group 4 compared with group 2 and 3 (3.4 and 5.3-fold each, p=0.026). Expression of eNOS in left plus right quadriceps markedly increased in group 3 and 4 compared with group 1 and 2 (p=0.007). Expressions of eNOS, Akt and p-eNOS, pAkt in gastrocnemius were not comparable between four groups (p>0.05).
CONCLUSION
Repetitive magnetic stimulation of the spinal cord may exert an angiogenic effect closely linked to lymphangiogenesis. It has clinical implication for the possible therapy of lymphedema caused by breast, cervical or endometrial cancer operation. Future studies with the specific lymphatic endothelial cell markers are required to confirm the effect of rMS on lymphangiogenesis.
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Angiogenesis Inducing Agents
Animals
Blotting, Western
Breast
Endometrial Neoplasms
Endothelial Cells
Extremities
Female
Hindlimb
Humans
Lymphangiogenesis
Lymphedema
Magnetics
Magnets
Male
Muscles
Nitric Oxide Synthase Type III
Pilot Projects
Rats
Rats, Sprague-Dawley
Salicylamides
Spinal Cord
Angiogenesis Inducing Agents
Nitric Oxide Synthase Type III
Salicylamides
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ohtani O, Ohtani Y. Organization and developmental aspects of lymphatic vessels. Arch Histol Cytol. 2008; 71:1–22. PMID: 18622090.
Article2. McLaughlin SA, Wright MJ, Morris KT, Sampson MR, Brockway JP, Hurley KE, Riedel ER, Van Zee KJ. Prevalence of lymphedema in women with breast cancer 5 years after sentinel lymph node biopsy or axillary dissection: patient perceptions and precautionary behaviors. J Clin Oncol. 2008; 26:5220–5226. PMID: 18838708.
Article3. Erickson VS, Pearson ML, Ganz PA, Adams J, Kahn KL. Arm edema in breast cancer patients. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2001; 93:96–111. PMID: 11208879.
Article4. Bergmark K, Avall-Lundqvist E, Dickman PW, Henningsohn L, Steineck G. Lymphedema and bladder-emptying difficulties after radical hysterectomy for early cervical cancer and among population controls. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2006; 16:1130–1139. PMID: 16803496.
Article5. Beesley V, Janda M, Eakin E, Obermair A, Battistutta D. Lymphedema after gynecological cancer treatment: prevalence, correlates, and supportive care needs. Cancer. 2007; 109:2607–2614. PMID: 17474128.6. Saito Y, Nakagami H, Morishita R, Takami Y, Kikuchi Y, Hayashi H, Nishikawa T, Tamai K, Azuma N, Sasajima T, et al. Transfection of human hepatocyte growth factor gene ameliorates secondary lymphedema via promotion of lymphangiogenesis. Circulation. 2006; 114:1177–1184. PMID: 16952986.
Article7. Amaral SL, Linderman JR, Morse MM, Greene AS. Angiogenesis induced by electrical stimulation is mediated by angiotensin II and VEGF. Microcirculation. 2001; 8:57–67. PMID: 11296854.
Article8. Liu Y, Fang Y, Dong P, Gao J, Liu R, Hhahbaz M, Bi Y, Ding Z, Tian H, Liu Z. Effect of vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGF-C) gene transfer in rat model of secondary lymphedema. Vascul Pharmacol. 2008; 48:150–156. PMID: 18455964.
Article9. Oh BM. Low-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in the early subacute phase of stroke enhances the angiogenic mechanisms in rats [dissertation]. 2010. Seoul: Seoul National University College of Medicine.10. Edwards D, Fregni F. Modulating the healthy and affected motor cortex with repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in stroke: development of new strategies for neurorehabilitation. NeuroRehabilitation. 2008; 23:3–14. PMID: 18356585.
Article11. O'Reardon JP, Solvason HB, Janicak PG, Sampson S, Isenberg KE, Nahas Z, McDonald WM, Avery D, Fitzgerald PB, Loo C, et al. Reply regarding "efficacy and safety of transcranial magnetic stimulation in the acute treatment of major depression: a multisite randomized controlled trial". Biol Psychiatry. 2010; 67:e15–e17. PMID: 19914602.12. Brighina F, Giglia G, Scalia S, Francolini M, Palermo A, Fierro B. Facilitatory effects of 1 Hz rTMS in motor cortex of patients affected by migraine with aura. Exp Brain Res. 2005; 161:34–38. PMID: 15480599.13. Smania N, Corato E, Fiaschi A, Pietropoli P, Aglioti SM, Tinazzi M. Repetitive magnetic stimulation: a novel therapeutic approach for myofascial pain syndrome. J Neurol. 2005; 252:307–314. PMID: 15726272.
Article14. Lefaucheur JP, Drouot X, Menard-Lefaucheur I, Zerah F, Bendib B, Cesaro P, Keravel Y, Nguyen JP. Neurogenic pain relief by repetitive transcranial magnetic cortical stimulation depends on the origin and the site of pain. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2004; 75:612–616. PMID: 15026508.
Article15. Hirayama A, Saitoh Y, Kishima H, Shimokawa T, Oshino S, Hirata M, Kato A, Yoshimine T. Reduction of intractable deafferentation pain by navigation-guided repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation of the primary motor cortex. Pain. 2006; 122:22–27. PMID: 16495011.
Article16. Di Lazzaro V, Pilato F, Dileone M, Profice P, Capone F, Ranieri F, Musumeci G, Cianfoni A, Pasqualetti P, Tonali PA. Modulating cortical excitability in acute stroke: a repetitive TMS study. Clin Neurophysiol. 2008; 119:715–723. PMID: 18165149.
Article17. Mansur CG, Fregni F, Boggio PS, Riberto M, Gallucci-Neto J, Santos CM, Wagner T, Rigonatti SP, Marcolin MA, Pascual-Leone A. A sham stimulation-controlled trial of rTMS of the unaffected hemisphere in stroke patients. Neurology. 2005; 64:1802–1804. PMID: 15911819.
Article18. Fehlings MG, Tator CH. The effect of direct current field polarity on recovery after acute experimental spinal cord injury. Brain Res. 1992; 579:32–42. PMID: 1623405.
Article19. Lin VW, Hsiao I, Kingery WS. High intensity magnetic stimulation over the lumbosacral spine evokes antinociception in rats. Clin Neurophysiol. 2002; 113:1006–1012. PMID: 12088693.
Article20. Ohkuma M. Treatment of peripheral lymphedema by concomitant application of magnetic fields, vibration and hyperthermia: a preliminary report. Lymphology. 2002; 35:87–90. PMID: 12081056.21. Girouard H, Iadecola C. Neurovascular coupling in the normal brain and in hypertension, stroke, and Alzheimer disease. J Appl Physiol. 2006; 100:328–335. PMID: 16357086.
Article22. Iadecola C. Neurovascular regulation in the normal brain and in Alzheimer's disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2004; 5:347–360. PMID: 15100718.
Article23. Allen EA, Pasley BN, Duong T, Freeman RD. Transcranial magnetic stimulation elicits coupled neural and hemodynamic consequences. Science. 2007; 317:1918–1921. PMID: 17901333.
Article24. Lohela M, Bry M, Tammela T, Alitalo K. VEGFs and receptors involved in angiogenesis versus lymphangiogenesis. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2009; 21:154–165. PMID: 19230644.
Article25. Benest AV, Harper SJ, Herttuala SY, Alitalo K, Bates DO. VEGF-C induced angiogenesis preferentially occurs at a distance from lymphangiogenesis. Cardiovasc Res. 2008; 78:315–323. PMID: 18065770.
Article26. Salvador R, Miranda PC. Transcranial magnetic stimulation of small animals: a modeling study of the influence of coil geometry, size and orientation. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2009; 2009:674–677. PMID: 19964482.
Article27. Yambe T, Inoue A, Sekine K, Shiraishi Y, Watanabe M, Yamaguchi T, Shibata M, Maruyama M, Konno S, Nitta S. Effect of the alternative magnetic stimulation on peripheral circulation for regenerative medicine. Biomed Pharmacother. 2005; 59(Suppl 1):S174–S176. PMID: 16275489.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Spinal Cauda Equina Stimulation for Alternative Location of Spinal Cord Stimulation in Intractable Phantom Limb Pain Syndrome: A Case Report
- Posterior Cord Syndrome After Spinal Cord Stimulation Electrode Lead Insertion: A Case Report
- An Unexpected Improvement of the Symptom from Herniated Intervertebral Disc during Trial of Spinal Cord Stimulation for the Post-herpetic Neuralgia: A case report
- Spinal Cord Stimulation for Refractory Neuropathic Pain of Neuralgic Amyotrophy
- Atypical Supernumerary Phantom Limb and Phantom Limb Pain in a Patient With Spinal Cord Injury: Case Report