Ann Rehabil Med.
2013 Dec;37(6):901-906. 10.5535/arm.2013.37.6.901.
Atypical Supernumerary Phantom Limb and Phantom Limb Pain in a Patient With Spinal Cord Injury: Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, National Health Insurance Corporation Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- 2Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Spinal Cord Injury Rehabilitation, National Rehabilitation Center, Seoul, Korea. zeeahan@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2266572
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2013.37.6.901
Abstract
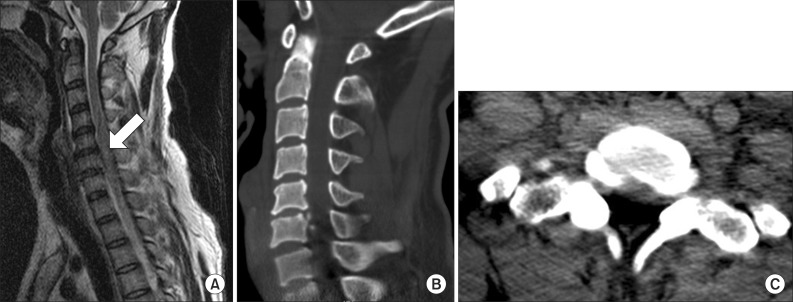
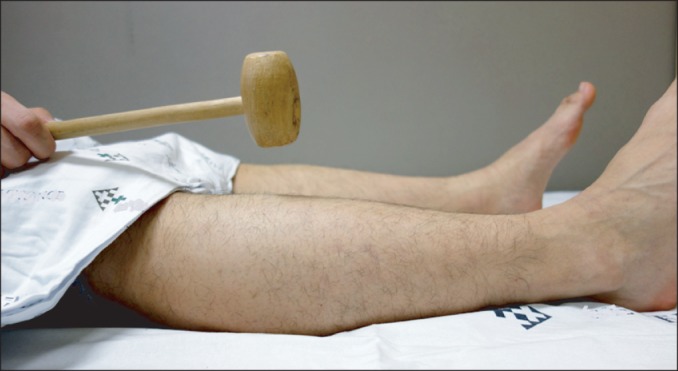
- Supernumerary phantom limb (SPL) resulting from spinal cord lesions are very rare, with only sporadic and brief descriptions in the literature. Furthermore, the reported cases of SPL typically occurred in neurologically incomplete spinal cord patients. Here, we report a rare case of SPL with phantom limb pain that occurred after traumatic spinal cord injury in a neurologically complete patient. After a traffic accident, a 43-year-old man suffered a complete spinal cord injury with a C6 neurologic level of injury. SPL and associated phantom limb pain occurred 6 days after trauma onset. The patient felt the presence of an additional pair of legs that originated at the hip joints and extended medially, at equal lengths to the paralyzed legs. The intensity of SPL and associated phantom limb pain subsequently decreased after visual-tactile stimulation treatment, in which the patient visually identified the paralyzed limbs and then gently tapped them with a wooden stick. This improvement continued over the 2 months of inpatient treatment at our hospital and the presence of the SPLs was reduced to 20% of the real paralyzed legs. This is the first comprehensive report on SPLs of the lower extremities after neurologically complete spinal cord injury.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Brugger P. Phantom limb to phantom body. In : Knoblich G, Thornton IM, Grosjean M, Shiffrar M, editors. Human body perception from the inside out. Oxford: Oxford University Press;2005. p. 171–209.2. Davis R. Pain and suffering following spinal cord injury. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1975; (112):76–80. PMID: 1192653.
Article3. Fredericks J. Phantom limb and phantom limb pain. In : Fredericks J, editor. Clinical neuropsychology. Amsterdam: Elsevier;1985. p. 373–393.4. Halligan PW, Marshall JC, Wade DT. Three arms: a case study of supernumerary phantom limb after right hemisphere stroke. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1993; 56:159–166. PMID: 8437005.
Article5. Curt A, Yengue CN, Hilti LM, Brugger P. Supernumerary phantom limbs in spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord. 2011; 49:588–595. PMID: 21079624.
Article6. Grossi D, Di Cesare G, Tamburro RP. On the syndrome of the "spare limb": one case. Percept Mot Skills. 2002; 94:476–478. PMID: 12027341.
Article7. Brugger P. Supernumerary phantoms: a comment on Grossi, et al.'s (2002) spare thoughts on spare limbs. Percept Mot Skills. 2003; 97:3–10. PMID: 14604017.
Article8. Head H, Holmes G. Sensory disturbances from cerebral lesions. Brain. 1911; 34:102–254.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Atypical Supernumerary Phantom Limb and Phantom Limb Pain in Two Patients with Pontine Hemorrhage
- Letter to the Editor: The Supernumerary Phantom Limb and Phantom Limb Pain-Important Facts
- Effect of Epidural Block with Meperidine in Patient with Phantom Limb Pain: A case report
- Spinal Cauda Equina Stimulation for Alternative Location of Spinal Cord Stimulation in Intractable Phantom Limb Pain Syndrome: A Case Report
- Mirror Therapy for Phantom Limb Pain