Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2013 Jul;5(4):216-223. 10.4168/aair.2013.5.4.216.
Rhinovirus-Infected Epithelial Cells Produce More IL-8 and RANTES Compared With Other Respiratory Viruses
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, School of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. pedjsyoon@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2260315
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2013.5.4.216
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The environmental factors human rhinoviruses (HRVs) and house dust mites (HDMs) are the most common causes of acute exacerbations of asthma. The aim of this study was to compare the chemokine production induced by HRVs in airway epithelial cells with that induced by other respiratory viruses, and to investigate synergistic interactions between HRVs and HDMs on the induction of inflammatory chemokines in vitro.
METHODS
A549 human airway epithelial cells were infected with either rhinovirus serotype 7, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)-A2 strain, or adenovirus serotype 3 and analyzed for interleukin (IL)-8 and regulated on activation, normal T-cell expressed and secreted (RANTES) release and mRNA expression. Additionally, activation of nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB and activator protein (AP)-1 were evaluated. The release of IL-8 and RANTES was also measured in cells stimulated simultaneously with a virus and the HDM allergen, Der f1.
RESULTS
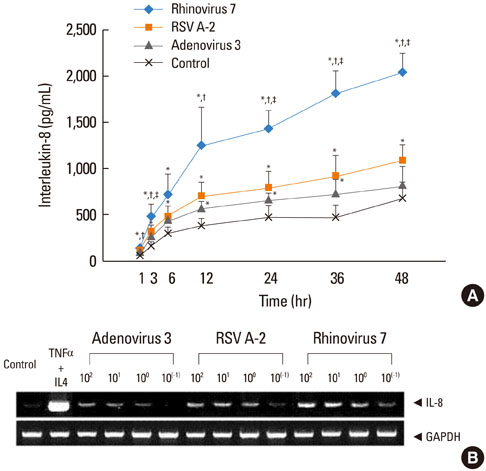
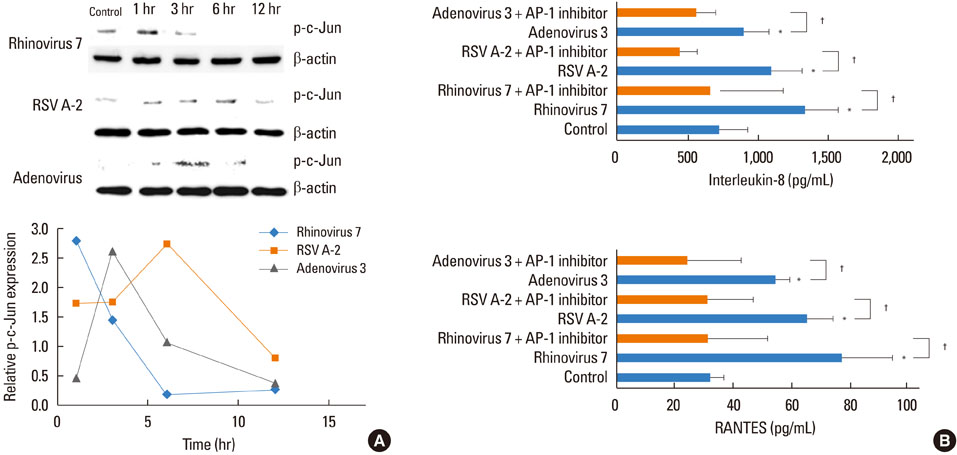
HRV caused greater IL-8 and RANTES release and mRNA expression compared with either RSV or adenovirus. NF-kappaB and AP-1 were activated in these processes. Cells incubated with a virus and Der f1 showed an increased IL-8 release. However, compared with cells incubated with virus alone as the stimulator, only HRV with Der f1 showed a statistically significant increase.
CONCLUSIONS
IL-8 and RANTES were induced to a greater extent by HRV compared with other viruses, and only HRV with Der f1 acted synergistically to induce bronchial epithelial IL-8 release. These findings may correspond with the fact that rhinoviruses are identified more frequently than other viruses in cases of acute exacerbation of asthma.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adenoviridae
Antigens, Dermatophagoides
Arthropod Proteins
Asthma
Chemokine CCL5
Chemokines
Cysteine Endopeptidases
Epithelial Cells
Humans
Interleukin-8
Interleukins
NF-kappa B
Pyroglyphidae
Respiratory Syncytial Viruses
Rhinovirus
RNA, Messenger
Sprains and Strains
T-Lymphocytes
Transcription Factor AP-1
Viruses
Antigens, Dermatophagoides
Arthropod Proteins
Chemokine CCL5
Chemokines
Cysteine Endopeptidases
Interleukin-8
Interleukins
NF-kappa B
RNA, Messenger
Transcription Factor AP-1
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kim WK, Gern JE. Updates in the relationship between human rhinovirus and asthma. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2012; 4:116–121.2. Kotaniemi-Syrjänen A, Vainionpää R, Reijonen TM, Waris M, Korhonen K, Korppi M. Rhinovirus-induced wheezing in infancy--the first sign of childhood asthma? J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003; 111:66–71.3. Jackson DJ, Johnston SL. The role of viruses in acute exacerbations of asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 125:1178–1187. quiz 1188-9.4. Wark PA, Johnston SL, Moric I, Simpson JL, Hensley MJ, Gibson PG. Neutrophil degranulation and cell lysis is associated with clinical severity in virus-induced asthma. Eur Respir J. 2002; 19:68–75.5. Wenzel S. Mechanisms of severe asthma. Clin Exp Allergy. 2003; 33:1622–1628.6. Ammit AJ, Lazaar AL, Irani C, O'Neill GM, Gordon ND, Amrani Y, Penn RB, Panettieri RA Jr. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced secretion of RANTES and interleukin-6 from human airway smooth muscle cells: modulation by glucocorticoids and beta-agonists. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2002; 26:465–474.7. Terry CF, Loukaci V, Green FR. Cooperative influence of genetic polymorphisms on interleukin 6 transcriptional regulation. J Biol Chem. 2000; 275:18138–18144.8. Thomas LH, Wickremasinghe MI, Friedland JS. IL-1 beta stimulates divergent upper and lower airway epithelial cell CCL5 secretion. Clin Immunol. 2007; 122:229–238.9. Strieter RM. Interleukin-8: a very important chemokine of the human airway epithelium. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2002; 283:L688–L689.10. Sehmi R, Cromwell O, Wardlaw AJ, Moqbel R, Kay AB. Interleukin-8 is a chemo-attractant for eosinophils purified from subjects with a blood eosinophilia but not from normal healthy subjects. Clin Exp Allergy. 1993; 23:1027–1036.11. Krawiec ME, Westcott JY, Chu HW, Balzar S, Trudeau JB, Schwartz LB, Wenzel SE. Persistent wheezing in very young children is associated with lower respiratory inflammation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001; 163:1338–1343.12. Culley FJ, Pennycook AM, Tregoning JS, Dodd JS, Walzl G, Wells TN, Hussell T, Openshaw PJ. Role of CCL5 (RANTES) in viral lung disease. J Virol. 2006; 80:8151–8157.13. Sheeran P, Jafri H, Carubelli C, Saavedra J, Johnson C, Krisher K, Sánchez PJ, Ramilo O. Elevated cytokine concentrations in the nasopharyngeal and tracheal secretions of children with respiratory syncytial virus disease. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1999; 18:115–122.14. Konno S, Grindle KA, Lee WM, Schroth MK, Mosser AG, Brockman-Schneider RA, Busse WW, Gern JE. Interferon-gamma enhances rhinovirus-induced RANTES secretion by airway epithelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2002; 26:594–601.15. John AE, Berlin AA, Lukacs NW. Respiratory syncytial virus-induced CCL5/RANTES contributes to exacerbation of allergic airway inflammation. Eur J Immunol. 2003; 33:1677–1685.16. Zhang L, Peeples ME, Boucher RC, Collins PL, Pickles RJ. Respiratory syncytial virus infection of human airway epithelial cells is polarized, specific to ciliated cells, and without obvious cytopathology. J Virol. 2002; 76:5654–5666.17. Schroth MK, Grimm E, Frindt P, Galagan DM, Konno SI, Love R, Gern JE. Rhinovirus replication causes RANTES production in primary bronchial epithelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1999; 20:1220–1228.18. Bartlett NW, Walton RP, Edwards MR, Aniscenko J, Caramori G, Zhu J, Glanville N, Choy KJ, Jourdan P, Burnet J, Tuthill TJ, Pedrick MS, Hurle MJ, Plumpton C, Sharp NA, Bussell JN, Swallow DM, Schwarze J, Guy B, Almond JW, Jeffery PK, Lloyd CM, Papi A, Killington RA, Rowlands DJ, Blair ED, Clarke NJ, Johnston SL. Mouse models of rhinovirus-induced disease and exacerbation of allergic airway inflammation. Nat Med. 2008; 14:199–204.19. Gern JE, Vrtis R, Grindle KA, Swenson C, Busse WW. Relationship of upper and lower airway cytokines to outcome of experimental rhinovirus infection. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000; 162:2226–2231.20. Gern JE. Rhinovirus and the initiation of asthma. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 9:73–78.21. Miller AL, Bowlin TL, Lukacs NW. Respiratory syncytial virus-induced chemokine production: linking viral replication to chemokine production in vitro and in vivo. J Infect Dis. 2004; 189:1419–1430.22. Wong T, Hellermann G, Mohapatra S. The infectious march: the complex interaction between microbes and the immune system in asthma. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2010; 30:453–480.23. Van Ly D, King NJ, Moir LM, Burgess JK, Black JL, Oliver BG. Effects of beta(2) Agonists, Corticosteroids, and Novel Therapies on Rhinovirus-Induced Cytokine Release and Rhinovirus Replication in Primary Airway Fibroblasts. J Allergy (Cairo). 2011; 2011:457169.24. Edwards MR, Hewson CA, Laza-Stanca V, Lau HT, Mukaida N, Hershenson MB, Johnston SL. Protein kinase R, IkappaB kinase-beta and NF-kappaB are required for human rhinovirus induced pro-inflammatory cytokine production in bronchial epithelial cells. Mol Immunol. 2007; 44:1587–1597.25. Bossios A, Gourgiotis D, Skevaki CL, Saxoni-Papageorgiou P, Lötvall J, Psarras S, Karpathios T, Constandopoulos AG, Johnston SL, Papadopoulos NG. Rhinovirus infection and house dust mite exposure synergize in inducing bronchial epithelial cell interleukin-8 release. Clin Exp Allergy. 2008; 38:1615–1626.26. Jackson DJ, Evans MD, Gangnon RE, Tisler CJ, Pappas TE, Lee WM, Gern JE, Lemanske RF Jr. Evidence for a causal relationship between allergic sensitization and rhinovirus wheezing in early life. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012; 185:281–285.27. Foster S, Bedford KJ, Gould ME, Coward WR, Hewitt CR. Respiratory syncytial virus infection and virus-induced inflammation are modified by contaminants of indoor air. Immunology. 2003; 108:109–115.28. Grunstein MM, Veler H, Shan X, Larson J, Grunstein JS, Chuang S. Proasthmatic effects and mechanisms of action of the dust mite allergen, Der p 1, in airway smooth muscle. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005; 116:94–101.29. Xatzipsalti M, Papadopoulos NG. Cellular and animals models for rhinovirus infection in asthma. Contrib Microbiol. 2007; 14:33–41.30. Thomas LH, Friedland JS, Sharland M, Becker S. Respiratory syncytial virus-induced RANTES production from human bronchial epithelial cells is dependent on nuclear factor-kappa B nuclear binding and is inhibited by adenovirus-mediated expression of inhibitor of kappa B alpha. J Immunol. 1998; 161:1007–1016.31. Yoon JS, Kim HH, Lee Y, Lee JS. Cytokine induction by respiratory syncytial virus and adenovirus in bronchial epithelial cells. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2007; 42:277–282.32. Adam E, Hansen KK, Astudillo Fernandez O, Coulon L, Bex F, Duhant X, Jaumotte E, Hollenberg MD, Jacquet A. The house dust mite allergen Der p 1, unlike Der p 3, stimulates the expression of interleukin-8 in human airway epithelial cells via a proteinase-activated receptor-2-independent mechanism. J Biol Chem. 2006; 281:6910–6923.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Cytokine and Chemokine Production and Activation of NF-kappaB in RSV- and Adenovirus-infected Bronchial Epithelial Cells
- The Effect of Dexamethasone on Respiratory Syncytial Virus Induced RANTES and IL-8 Production of a Human Bronchial Epithelial Cell Line
- The Effects of Corticosteroids on IL-6, IL-8 and RANTES Production from RSV-infected Epithelial Cells
- Effect of Clarithromycin on Rhinovirus-16 Infection in A549 Cells
- The effect of corticosteroid on RANTES and IL-8 mRNA expression in human bronchial epithelial cell line infected with respiratory syncytial virus