Korean J Hematol.
2009 Dec;44(4):220-226. 10.5045/kjh.2009.44.4.220.
The Clinical Significance of Nasopharyngeal Carriages in Immunocompromised Children as Assessed
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, School of Medicine, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea. nel1205@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2252100
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/kjh.2009.44.4.220
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
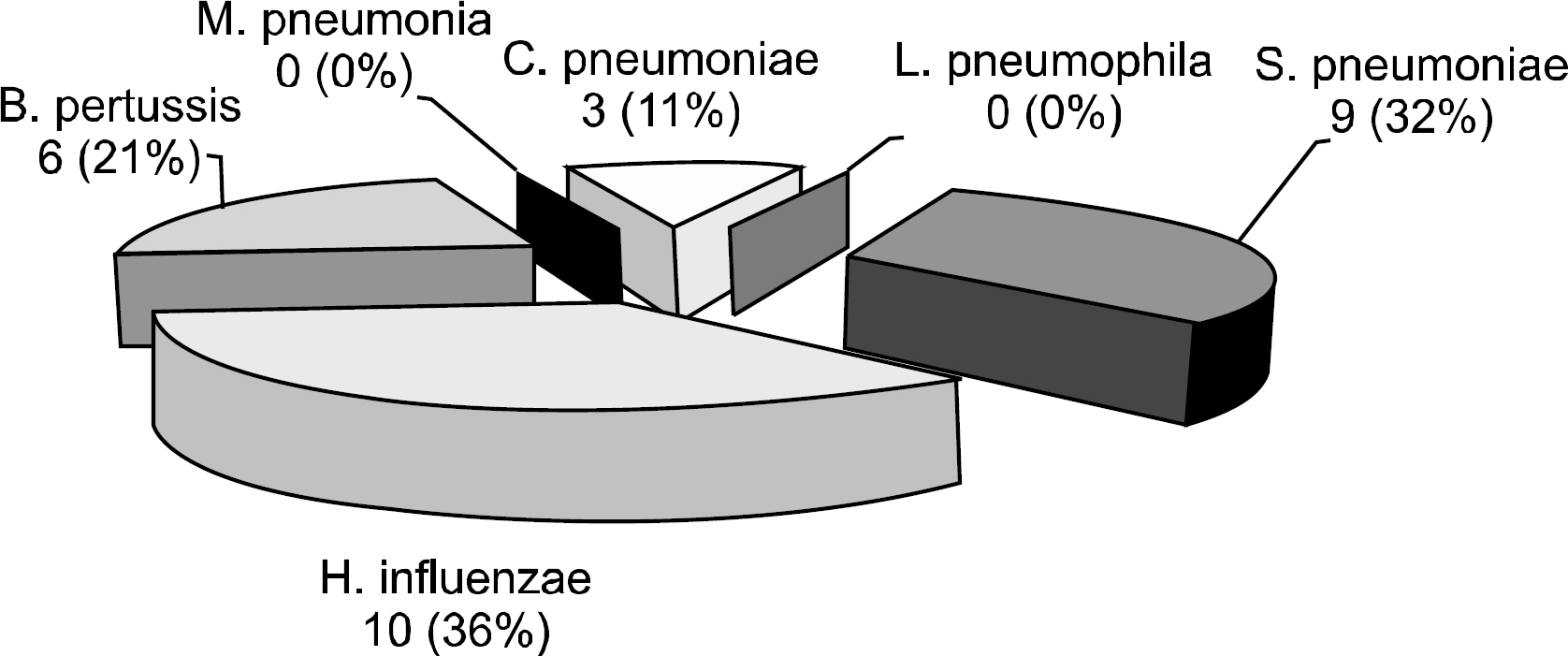
The aim of this study was to determine the prevalence of asymptomatic nasopharyngeal carriages in immunocompromized children by using a multiplex reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (mRT-PCR) assay kit. METHODS: We obtained clinical samples by nasopharyngeal swabs from 42 patients with underlying immune deficiency from May 20, 2008 to May 22, 2008. The children were free from signs of respiratory tract infections at the time of sampling. Isolated cDNA was extracted and after this the DNA was examined using a multiplex primer set for pneumonial bacteria detection (Seeplex(R) PneumoBacter ACE Detection, Seegene, Seoul, Korea). The amplified PCR products were separated on 2% agarose gels and stained with ethidium bromide and a screentape system (Lab901, Scottland, UK) and then they were compared. The nasopharyngeal swab culture was done simultaneously and this was compared with the results of mRT-PCR. RESULTS: A total of 42 patients (males: 24, females: 18) aged between 1.2 and 16.3 years (median: 9.2 years) were included in this study. The mRT-PCR detected bacteria (Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, Chlamydia pneumoniae, and Bordetella pertussis) in 28 patients (66.6%). Of these 28 patients, 4 patients (14.3%) showed more than 2 bacteria: 2 patients were positive for two bacteria (S. pneumoniae and H. influenzae, H.influenzae and B. pertussis) and 2 patients were positive for three bacteria (S. pneumoniae, B. pertussis and C. pneumoniae, C. Pneumoniae, H. influenzae and B. pertussis). S. pneumoniae was cultured in one patient (2.4%). Conclusions: The mRT-PCR is a sensitive tool for the detection of the asymptomatic nasopharyngeal carriages. The clinical significance of the bacteria detected in immunocompromized patients by mRT-PCR will need further evaluation.
MeSH Terms
-
Aged
Bacteria
Bordetella
Child
Chlamydophila pneumoniae
DNA
DNA, Complementary
Ethidium
Gels
Haemophilus influenzae
Humans
Influenza, Human
Nasopharynx
Pneumonia
Polymerase Chain Reaction
Prevalence
Respiratory Tract Infections
Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction
Sepharose
Whooping Cough
DNA
DNA, Complementary
Ethidium
Gels
Sepharose
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Neto AS, Lavado P, Flores P, et al. Risk factors for the nasopharyngeal carriage of respiratory pathogens by Portuguese children: phenotype and antimicrobial susceptibility of Haemophilus influenzae and Streptococcus pneumoniae. Microb Drug Resist. 2003; 9:99–108.2. Marchisio P, Esposito S, Schito GC, et al. Hercules Project Collaborative Group. Nasopharyngeal carriage of Streptococcus pneumoniae in healthy children: implications for the use of heptavalent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine. Emerg Infect Dis. 2002; 8:479–84.3. Ljungman P, Engelhard D, de la Cámara R, et al. Vaccination of stem cell transplant recipients: recommendations of the Infectious Diseases Working Party of the EBMT. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2005; 35:737–46.
Article4. Woolfson A, Huebner R, Wasas A, Chola S, Godfrey-Faussett P, Klugman K. Nasopharyngeal carriage of community-acquired, antibiotic-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae in a Zambian paediatric population. Bull World Health Organ. 1997; 75:453–62.5. Yagupsky P, Porat N, Fraser D, et al. Acquisition, carriage, and transmission of pneumococci with decreased antibiotic susceptibility in young children attending a day care facility in southern Israel. J Infect Dis. 1998; 177:1003–12.
Article6. Boken DJ, Chartrand SA, Goering RV, Kruger R, Harrison CJ. Colonization with penicillin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae in a childcare center. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1995; 14:879–84.
Article7. Sekhar S, Chakraborti A, Kumar R. Haemophilus influenzae colonization and its risk factors in children aged <2 years in northern India. Epidemiol Infect. 2009; 137:156–60.
Article8. Gómez E, Moore A, Sánchez J, et al. The epidemiology of Haemophilus influenzae type b carriage among infants and young children in Santo Domingo, Dominican Republic. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1998; 17:782–6.9. Gruteke P, Glas AS, Dierdorp M, Vreede WB, Pilon JW, Bruisten SM. Practical implementation of a multiplex PCR for acute respiratory tract infections in children. J Clin Microbiol. 2004; 42:5596–603.
Article10. Freymuth F, Vabret A, Cuvillon-Nimal D, et al. Comparison of multiplex PCR assays and conventional techniques for the diagnostic of respiratory virus infections in children admitted to hospital with an acute respiratory illness. J Med Virol. 2006; 78:1498–504.
Article11. Mahony J, Chong S, Merante F, et al. Development of a respiratory virus panel test for detection of twenty human respiratory viruses by use of multiplex PCR and a fluid microbead-based assay. J Clin Microbiol. 2007; 45:2965–70.
Article12. Obaro S, Adegbola R. The pneumococcus: carriage, disease and conjugate vaccines. J Med Microbiol. 2002; 51:98–104.
Article13. Bruyn GA, Zegers BJ, van Furth R. Mechanisms of host defense against infection with Streptococcus pneumoniae. Clin Infect Dis. 1992; 14:251–62.
Article14. Kim KH, Lee JE, Whang IT, et al. Serogroup and antimicrobial resistance of Streptococcus pneumoniae isolated from oropharynx in children attending day care center. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 2002; 45:346–53.15. Chou MY, Brown AE, Blevins A, Armstrong D. Severe pneumococcal infection in patients with neoplastic disease. Cancer. 1983; 51:1546–50.
Article16. Youssef S, Rodriguez G, Rolston KV, Champlin RE, Raad II, Safdar A. Streptococcus pneumoniae infections in 47 hematopoietic stem cell transplantation recipients: clinical characteristics of infections and vaccine-breakthrough infections, 1989–2005. Medicine (Baltimore). 2007; 86:69–77.17. Kim BN, Bae LG, Kim MN, et al. Risk factors for penicillin resistance and mortality in Korean adults with Streptococcus pneumoniae bacteremia. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2002; 21:35–42.
Article18. Watanabe H, Sato S, Kawakami K, et al. A comparative clinical study of pneumonia by penicillin-resistant and -sensitive Streptococcus pneumoniae in a community hospital. Respirology. 2000; 5:59–64.
Article19. Kumashi P, Girgawy E, Tarrand JJ, Rolston KV, Raad II, Safdar A. Streptococcus pneumoniae bacteremia in patients with cancer: disease characteristics and outcomes in the era of escalating drug resistance (1998–2002). Medicine (Baltimore). 2005; 84:303–12.20. Torun MM, Namal N, Demirci M, Bahar H. Nasopharyngeal carriage and antibiotic resistance of Haemophilus influenzae, Streptococcus pneumoniae and Moraxella catarrhalis in healthy school children in Turkey. Indian J Med Microbiol. 2009; 27:86–8.
Article21. Kim KW, Kim KE. Mycoplasma and chlamydia infection in Korea. Korean J Pediatr. 2009; 52:277–82.
Article22. Cagney M, MacIntyre CR, McIntyre P, Torvaldsen S, Melot V. Cough symptoms in children aged 5–14 years in Sydney, Australia: non-specific cough or unrecognized pertussis? Respirology. 2005; 10:359–64.
Article23. Dragsted DM, Dohn B, Madsen J, Jensen JS. Comparison of culture and PCR for detection of Bordetella pertussis and Bordetella parapertussis under routine laboratory conditions. J Med Microbiol. 2004; 53:749–54.
Article24. AndréP. Caro V, Njamkepo E, Wendelboe AM, Van Rie A, Guiso N. Comparison of serological and real-time PCR assays to diagnose Bordetella pertussis infection in 2007. J Clin Microbiol. 2008; 46:1672–7.25. Saukkoriipi A, LeskeläK , Herva E, Leinonen M. Streptococcus pneumoniae in nasopharyngeal secretions of healthy children: comparison of real-time PCR and culture from STGG-transport medium. Mol Cell Probes. 2004; 18:147–53.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Detection of nasopharyngeal carriages in children by multiplex reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction
- COVID-19 in immunocompromised children and adolescents
- Three-dimensional evaluation of the relationship between nasopharyngeal airway shape and adenoid size in children
- Surveillance for antimicrobial resistance of Streptococcus pneumoniae among children attending day care center in Seoul, Korea
- A Case of Nasopharyngeal Tuberculosis Which Was Difficult to Differentiate From Sarcoidosis