Korean J Crit Care Med.
2015 Feb;30(1):56-60. 10.4266/kjccm.2015.30.1.56.
Polyethylene Glycol (PEG-3350, Colyte) Poisoning due to Intra-Peritoneal Leakage in an Elderly Patient
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. jhjung@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2227704
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4266/kjccm.2015.30.1.56
Abstract
- Polyethylene glycol (PEG)-3350 is the most frequently used lavage solution for bowel cleansing prior to colonoscopy or elective surgery because its large molecular weight means that it is poorly absorbed. However, if it leaks into the peritoneal cavity, complications may arise. Few published studies have assessed the absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion of PEG. Moreover, no published clinical data regarding complications due to the intra-peritoneal leakage of PEG-3350 could be found. We report on an elderly patient who developed the poisoning caused by leaking of PEG-3350 during bowel preparation. It resulted in severe metabolic acidosis, hypernatremia, hyperosmolality and a high anion gap, but it was effectively treated with early continuous renal replacement therapy after surgery.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
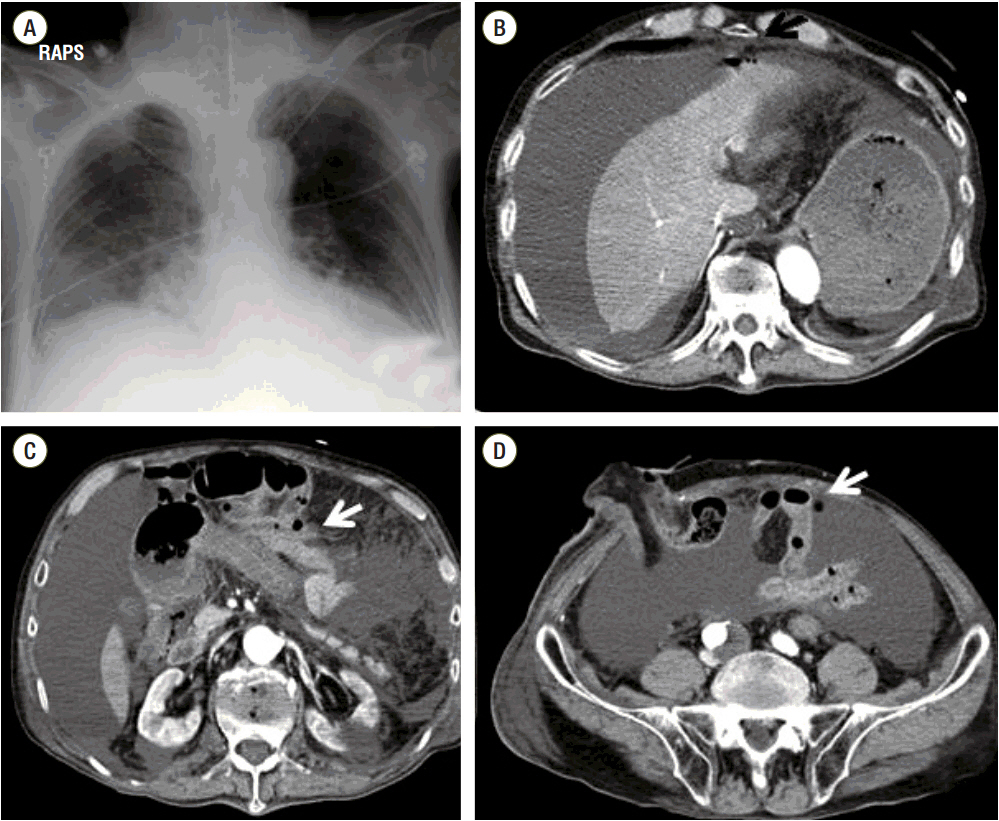
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Davis GR, Santa Ana CA, Morawski SG, Fordtran JS. Development of a lavage solution associated with minimal water and electrolyte absorption or secretion. Gastroenterology. 1980; 78(5 Pt 1):991–5.
Article2. Pelham RW, Nix LC, Chavira RE, Cleveland MV, Stetson P. Clinical trial: single-and multiple-dose pharmacokinetics of polyethylene glycol (PEG-3350) in healthy young and elderly subjects. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2008; 28:256–65.3. Winne D, Görig H. Appearance of 14C-polyethylene glycol 4000 in intestinal venous blood: influence of osmolarity and laxatives, effect on net water flux determination. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1982; 321:149–56.
Article4. Schiller LR, Emmett M, Santa Ana CA, Fordtran JS. Osmotic effects of polyethylene glycol. Gastroenterology. 1988; 94:933–41.
Article5. Pellegrini G, Starkey Lewis PJ, Palmer L, Hetzel U, Goldring CE, Park BK, et al. Intraperitoneal administration of high doses of polyethylene glycol (PEG) causes hepatic subcapsular necrosis and low-grade peritonitis with a rise in hepatic biomarkers. Toxicology. 2013; 314:262–6.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Immediate hypersensitivity reaction to polyethylene glycol 3350
- Efficacy and Safety of Combined Oral and Enema Therapy Using Polyethylene Glycol 3350-Electrolyte for Disimpaction in Pediatric Constipation
- Anaphylaxis to Polyethylene Glycol (Colyte®) in a Patient with Diverticulitis
- A Case of Boerhaave's Syndrome after Bowel Preparation with Polyethylene Glycol
- Polyethylene Glycol Plus Electrolytes with Stimulant Laxative in Paediatric Faecal Disimpaction: A Randomised Controlled Study