Allergy Asthma Respir Dis.
2015 Jul;3(4):307-309. 10.4168/aard.2015.3.4.307.
Immediate hypersensitivity reaction to polyethylene glycol 3350
- Affiliations
-
- 1Institute of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Seoul National University Medical Research Center, Seoul, Korea. helenmed@snu.ac.kr
- 2Respirology and Allergy Clinic, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea.
- 3Regional Pharmacovigilance Center, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym University Kangdong Sacred Heart Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Department of Internal Medicine, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 2218663
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aard.2015.3.4.307
Abstract
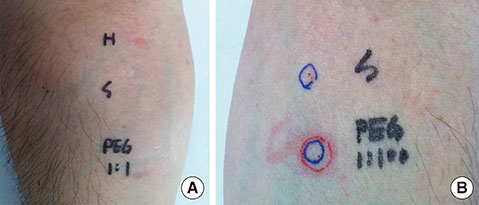
- Polyethylene glycol (PEG) 3350 is the main ingredient of oral solutions for bowel preparation prior to colonoscopy. This high-molecular-weight PEG has shown a low incidence of adverse reactions because of its low absorption via the intestine. Systemic allergic reactions to PEG solution are very rare, and only 10 cases have been reported in the literature worldwide. We experienced a case of immediate hypersensitivity reaction to PEG 3350. A 35-year-old male patient was prescribed PEG 3350 solution for colonoscopy. After ingestion of 2.5 pack (55 g of PEG 3350 powder), he began to show urticaria on both arms and trunk, and swelling in the lips. Symptoms resolved over the next few hours without any treatment. Skin prick and intradermal tests with PEG 3350 showed positive responses to both test. We also performed oral provocation tests with PEG 3350. Thirty minutes after ingestion of 2.5 g of PEG 3350 powder, the patient presented with mild urticaria and angioedema. Finally he was diagnosed with immediate hypersensitivity reaction by PEG 3350. The patient underwent colonoscopy after preparation with sodium phosphate solution without any adverse reactions. We herein report the first case of PEG 3350-induced immediate hypersensitivity reaction confirmed by skin and oral provocation tests in Korea.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Marshall JB, Pineda JJ, Barthel JS, King PD. Prospective, randomized trial comparing sodium phosphate solution with polyethylene glycol-electrolyte lavage for colonoscopy preparation. Gastrointest Endosc. 1993; 39:631–634.
Article2. Brady CE 3rd, DiPalma JA, Morawski SG, Santa Ana CA, Fordtran JS. Urinary excretion of polyethylene glycol 3350 and sulfate after gut lavage with a polyethylene glycol electrolyte lavage solution. Gastroenterology. 1986; 90:1914–1918.
Article3. Schuman E, Balsam PE. Probable anaphylactic reaction to polyethylene glycol electrolyte lavage solution. Gastrointest Endosc. 1991; 37:411.
Article4. Brullet E, Moron A, Calvet X, Frias C, Sola J. Urticarial reaction to oral polyethylene glycol electrolyte lavage solution. Gastrointest Endosc. 1992; 38:400–401.
Article5. Stollman N, Manten HD. Angioedema from oral polyethylene glycol electrolyte lavage solution. Gastrointest Endosc. 1996; 44:209–210.
Article6. Lee JS, Chae HS, Chung WC, Kim SS, Song HJ, Lee KM, et al. Urticaria reaction by oral polyethylene glycol ingestion. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 2002; 24:299–301.7. Assal C, Watson PY. Angioedema as a hypersensitivity reaction to polyethylene glycol oral electrolyte solution. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006; 64:294–295.
Article8. Anton Girones M, Roan Roan J, de la Hoz B, Sanchez Cano M. Immediate allergic reactions by polyethylene glycol 4000: two cases. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2008; 36:110–112.
Article9. Savitz JA, Durning SJ. A rare case of anaphylaxis to bowel prep: a case report and review of the literature. Mil Med. 2011; 176:944–945.
Article10. Shah S, Prematta T, Adkinson NF, Ishmael FT. Hypersensitivity to polyethylene glycols. J Clin Pharmacol. 2013; 53:352–355.
Article11. Co-Minh HB, Demoly P, Guillot B, Raison-Peyron N. Anaphylactic shock after oral intake and contact urticaria due to polyethylene glycols. Allergy. 2007; 62:92–93.
Article12. Knop K, Hoogenboom R, Fischer D, Schubert US. Poly(ethylene glycol) in drug delivery: pros and cons as well as potential alternatives. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2010; 49:6288–6308.
Article13. Wenande EC, Skov PS, Mosbech H, Poulsen LK, Garvey LH. Inhibition of polyethylene glycol-induced histamine release by monomeric ethylene and diethylene glycol: a case of probable polyethylene glycol allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013; 131:1425–1427.
Article14. Bommarito L, Mietta S, Nebiolo F, Geuna M, Rolla G. Macrogol hypersensitivity in multiple drug allergy. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2011; 107:542–543.
Article15. Zhang H, Henry WA, Chen LA, Khashab MA. Urticaria due to polyethylene glycol-3350 and electrolytes for oral solution in a patient with jejunal nodular lymphoid hyperplasia. Ann Gastroenterol. 2015; 28:148–150.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Efficacy and Safety of Combined Oral and Enema Therapy Using Polyethylene Glycol 3350-Electrolyte for Disimpaction in Pediatric Constipation
- Polyethylene Glycol (PEG-3350, Colyte) Poisoning due to Intra-Peritoneal Leakage in an Elderly Patient
- A Randomized Prospective Trial Comparing a New Polyethylene Glycol Based Lavage Solution with the Standard Polyethylene Glycol Solution in the Preparation of Patients Undergoing Colonoscopy (Clinical trial of new PEG solution in bowel preparation)
- Anaphylaxis to Polyethylene Glycol (Colyte®) in a Patient with Diverticulitis
- Assessment of Intestinal Permeability Using Polyethylene Glycol in Liver Cirrhosis with Ascites