J Rheum Dis.
2015 Apr;22(2):93-101. 10.4078/jrd.2015.22.2.93.
Inhibitory Effects for Rheumatoid Arthritis of Dietary Supplementation with Resveratrol in Collagen-induced Arthritis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine and Institute of Health Science, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Jinju, Korea. golgu@gnu.ac.kr
- 2Clinical Research Institute, Gyeongsang National University Hospital, Jinju, Korea.
- 3Research Division for Emerging Innovative Technology, Korea Food Research Institute, Seongnam, Korea.
- KMID: 2222911
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2015.22.2.93
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
Resveratrol is well-known for its anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant effects on several diseases. We investigated whether dietary supplementation with resveratrol may suppress joint inflammation and destruction in a mouse model of collagen-induced arthritis (CIA).
METHODS
Mice were randomly divided into two groups; CIA mice with normal diet-fed and CIA mice fed a 0.05% resveratrol diet. The effect of resveratrol on arthritis was assessed by clinical scoring system. The plain radiographs of paws were obtained to evaluate the effects on preventing bone destruction. Joint inflammation, cartilage damage, and osteoclastic bone resorption were checked by staining with H&E, Safranin-O, and tartrate resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP). Levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines were checked by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The level of expression of nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB was measured by electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA).
RESULTS
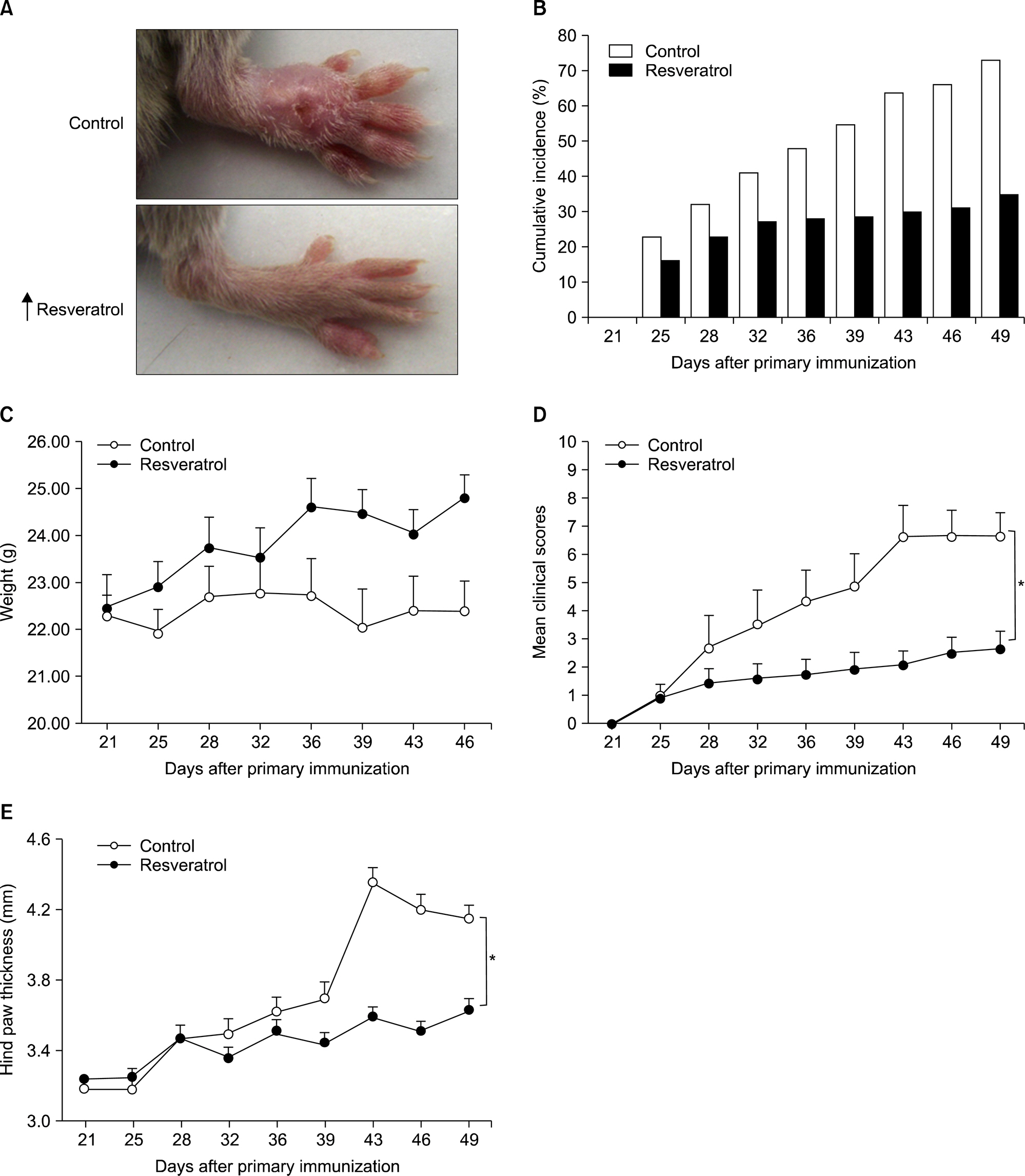
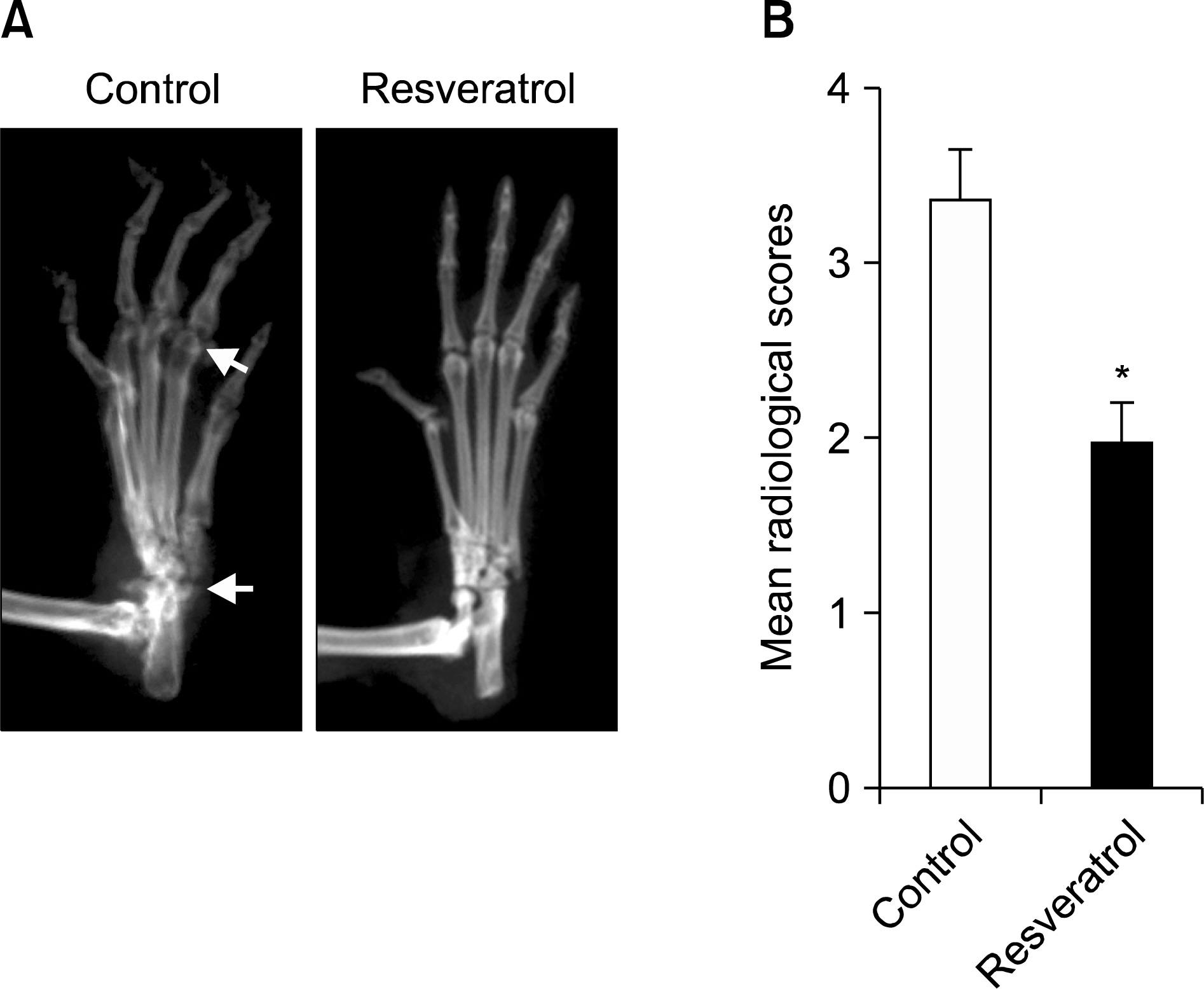
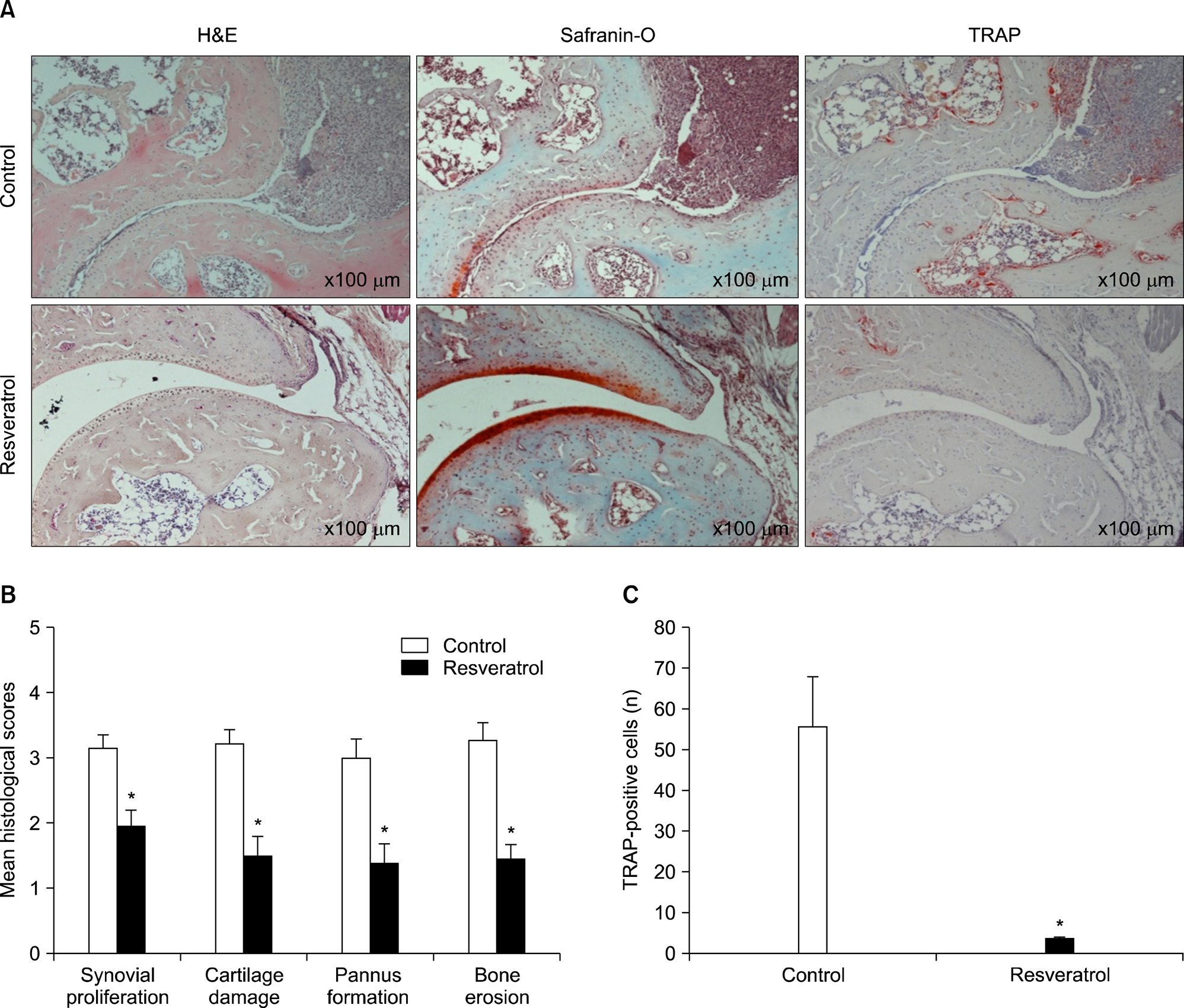
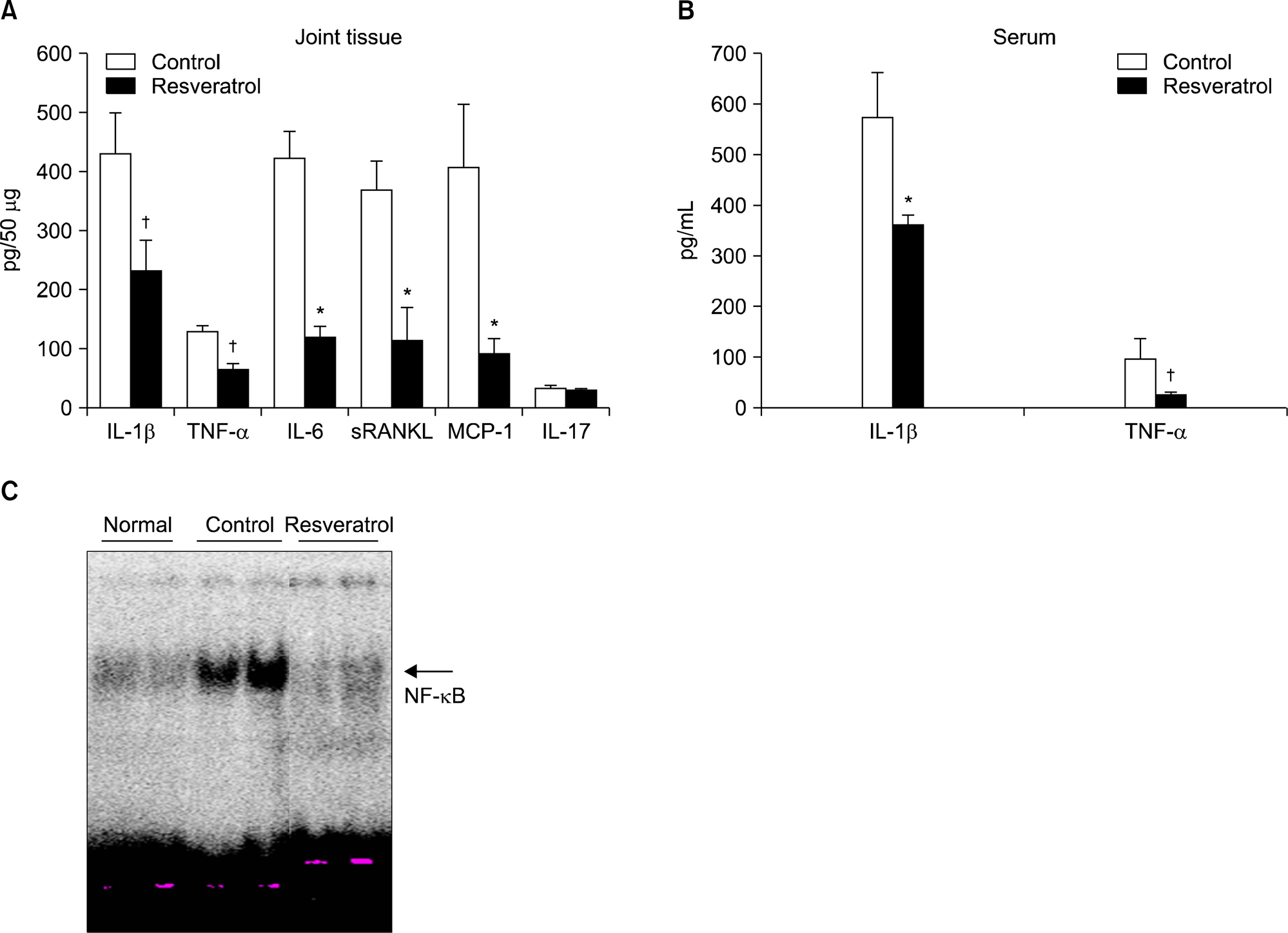
Dietary supplementation with resveratrol led to mitigated severity of arthritis compared to the normal diet group (6.7+/-0.8 vs. 2.7+/-0.6, p<0.01). Resveratrol-fed mice showed decreased bone destruction on radiograph (3.4+/-0.3 vs. 2.0+/-0.2, p<0.01), and showed significantly inhibited pathological changes (inflammation 2.0+/-0.3 vs.3.2+/-0.2, p<0.01; cartilage damage 1.5+/-0.3 vs. 3.2+/-0.2, p<0.01; pannus formation 1.4+/-0.3 vs. 3.0+/-0.3, p<0.01; erosion; 1.4+/-0.2 vs. 3.3+/-0.3, p<0.01). Generation of TRAP-positive osteoclasts was inhibited in the resveratrol-fed mice (55.3+/-12.7 vs. 3.27+/-0.8, p<0.01). Resveratrol-fed mice showed decreased levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin (IL)-1beta, IL-6,monocyte chemoattractant protein 1, and the soluble receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand in joint tissues and sera. Expression of NF-kappaB, measured by EMSA, was decreased in resveratrol-fed mice.
CONCLUSION
Dietary supplementation with resveratrol mitigates inflammation and bone destruction in CIA mice.
MeSH Terms
-
Acid Phosphatase
Animals
Antioxidants
Arthritis
Arthritis, Experimental*
Arthritis, Rheumatoid*
Bone Resorption
Cartilage
Cytokines
Diet
Dietary Supplements*
Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Inflammation
Interleukins
Joints
Mice
NF-kappa B
Osteoclasts
Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor-kappa B
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
Acid Phosphatase
Antioxidants
Cytokines
Interleukins
NF-kappa B
Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor-kappa B
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
Figure
Reference
-
1. O'Dell JR. Therapeutic strategies for rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2004; 350:2591–602.2. McInnes IB, Schett G. The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2011; 365:2205–19.
Article3. Smolen JS, Landewé R, Breedveld FC, Dougados M, Emery P, Gaujoux-Viala C, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010; 69:964–75.4. Singh JA, Furst DE, Bharat A, Curtis JR, Kavanaugh AF, Kremer JM, et al. 2012 update of the 2008 American College of Rheumatology recommendations for the use of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs and biologic agents in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2012; 64:625–39.
Article5. Kim YR, Yoo TS, Park HK, Kim TH, Jun JB, Jung SS, et al. Complementary and alternative medicine use and its usefulness in patients with RA. J Korean Rheum Assoc. 2002; 9:173–83.6. Lee MS, Lee MS, Yang CY, Lee SI, Joo MC, Shin BC, et al. Use of complementary and alternative medicine by rheumatoid arthritis patients in Korea. Clin Rheumatol. 2008; 27:29–33.
Article7. Olsen NJ, Stein CM. New drugs for rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2004; 350:2167–79.
Article8. Smolen JS, Steiner G. Therapeutic strategies for rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2003; 2:473–88.
Article9. Bertelli AA, Das DK. Grapes, wines, resveratrol, and heart health. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2009; 54:468–76.
Article10. Olas B, Wachowicz B, Majsterek I, Blasiak J. Resveratrol may reduce oxidative stress induced by platinum compounds in human plasma, blood platelets and lymphocytes. Anticancer Drugs. 2005; 16:659–65.
Article11. Pervaiz S. Resveratrol: from grapevines to mammalian biology. FASEB J. 2003; 17:1975–85.
Article12. Howitz KT, Bitterman KJ, Cohen HY, Lamming DW, Lavu S, Wood JG, et al. Small molecule activators of sirtuins extend Saccharomyces cerevisiae lifespan. Nature. 2003; 425:191–6.
Article13. Bhardwaj A, Sethi G, Vadhan-Raj S, Bueso-Ramos C, Takada Y, Gaur U, et al. Resveratrol inhibits proliferation, induces apoptosis, and overcomes chemoresistance through downregulation of STAT3 and nuclear factor-kappaB-regu-lated antiapoptotic and cell survival gene products in human multiple myeloma cells. Blood. 2007; 109:2293–302.14. Lei M, Wang JG, Xiao DM, Fan M, Wang DP, Xiong JY, et al. Resveratrol inhibits interleukin 1β-mediated inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in articular chondrocytes by activating SIRT1 and thereby suppressing nuclear factor-κ B activity. Eur J Pharmacol. 2012; 674:73–9.15. Xuzhu G, Komai-Koma M, Leung BP, Howe HS, McSharry C, McInnes IB, et al. Resveratrol modulates murine collagen-induced arthritis by inhibiting Th17 and B-cell function. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012; 71:129–35.
Article16. Chen XY, Wang ZC, Li J, Liu XL, Sun YH. Regulation of synoviocyte activity by resveratrol in rats with adjuvant arthritis. Exp Ther Med. 2013; 6:172–6.
Article17. Glehr M, Breisach M, Walzer S, Lohberger B, Fürst F, Friesenbichler J, et al. The influence of resveratrol on the synovial expression of matrix metalloproteinases and receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Z Naturforsch C. 2013; 68:336–42.
Article18. Tian J, Chen JW, Gao JS, Li L, Xie X. Resveratrol inhibits TNF-α-induced IL-1β, MMP-3 production in human rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes via modulation of PI3kinase/Akt pathway. Rheumatol Int. 2013; 33:1829–35.
Article19. Manna SK, Mukhopadhyay A, Aggarwal BB. Resveratrol suppresses TNF-induced activation of nuclear transcription factors NF-kappa B, activator protein-1, and apoptosis: potential role of reactive oxygen intermediates and lipid peroxidation. J Immunol. 2000; 164:6509–19.20. Csaki C, Keshishzadeh N, Fischer K, Shakibaei M. Regulation of inflammation signalling by resveratrol in human chondrocytes in vitro. Biochem Pharmacol. 2008; 75:677–87.
Article21. Kim HO, Lee SI. Experimental Animal models for rheumatoid arthritis: methods and applications. J Rheum Dis. 2012; 19:189–95.
Article22. Jeong YG, Kim HO, Lim HS, Hah YS, Cho HY, Yu J, et al. COMP-angiopoietin-1 stimulates synovial proliferation but suppresses osteoclast by enhancing angiogenesis and osteoblast maturation in collagen-induced arthritis. J Rheum Dis. 2012; 19:82–90.
Article23. Hah YS, Lee YR, Jun JS, Lim HS, Kim HO, Jeong YG, et al. A20 suppresses inflammatory responses and bone destruction in human fibroblast-like synoviocytes and in mice with collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2010; 62:2313–21.
Article24. Filipovic I, Walker D, Forster F, Curry AS. Quantifying the economic burden of productivity loss in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2011; 50:1083–90.
Article25. Son KM, Jung YO, Kim IJ, Kim BJ, Lee SY, Mun SY, et al. Clinical characteristics of Korean rheumatoid arthritis patients with indications for TNF-α blocker. J Rheum Dis. 2013; 20:356–60.
Article26. Di Giuseppe D, Wallin A, Bottai M, Askling J, Wolk A. Long-term intake of dietary long-chain n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and risk of rheumatoid arthritis: a prospective cohort study of women. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013; Aug 12 [Epub].DOI: DOI:10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-203338.
Article27. Kopp P. Resveratrol, a phytoestrogen found in red wine. A possible explanation for the conundrum of the ‘French paradox’? Eur J Endocrinol. 1998; 138:619–20.28. Boyle WJ, Simonet WS, Lacey DL. Osteoclast differentiation and activation. Nature. 2003; 423:337–42.
Article29. Shakibaei M, Buhrmann C, Mobasheri A. Resveratrol-mediated SIRT-1 interactions with p300 modulate receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand (RANKL) activation of NF-kappaB signaling and inhibit osteoclastogenesis in bone-derived cells. J Biol Chem. 2011; 286:11492–505.30. Amri A, Chaumeil JC, Sfar S, Charrueau C. Administration of resveratrol: What formulation solutions to bioavailability limitations? J Control Release. 2012; 158:182–93.
Article31. Rotches-Ribalta M, Andres-Lacueva C, Estruch R, Escribano E, Urpi-Sarda M. Pharmacokinetics of resveratrol metabolic profile in healthy humans after moderate consumption of red wine and grape extract tablets. Pharmacol Res. 2012; 66:375–82.
Article