The prevalence and risk factors of allergic rhinitis from a nationwide study of Korean elementary, middle, and high school students
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Childhood Asthma Atopy Center, Environmental Health Center, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. sjhong@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Korea Cancer Center Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 4Department of Pediatrics, Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Anyang, Korea.
- 5Department of Preventive Medicine, Dankook University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea.
- 6Department of Public Health, Graduate School of Dankook University, Cheonan, Korea.
- 7Department of Information Statistics, College of Natural Science, Korean National Open University, Seoul, Korea.
- 8Department of Occupational and Environmental Medicine, Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea.
- 9Department of Occupational and Environmental Medicine, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 10Department of Occupational and Environmental Medicine, Wonju Severance Christian's Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea.
- 11Department of Preventive Medicine, Kangwon National University School of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea.
- 12Department of Preventive Medicine, Eulji University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea.
- 13Department of Social and Preventive Medicine, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- 14Department of Preventive Medicine, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 15Department of Preventive Medicine, Wonkwang University School of Medicine, Iksan, Korea.
- 16Department of Preventive Medicine and Public Health, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 17Department of Occupational and Environmental Medicine, Chosun University School of Medicine, Gwangju, Korea.
- 18Division of Environmental Health, Department of Environmental Epidemiology, National Institute of Environment, Incheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2218657
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aard.2015.3.4.272
Abstract
- PURPOSE
We investigated the prevalence and risk factors of allergic rhinitis (AR), nationwide in random children and adolescents of Korea.
METHODS
A modified International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood (ISAAC) questionnaire survey was done in 1,820 children from elementary, middle, and high school nationwide in Korea. The subjects were selected by the stratifying sampling method by school grade and five regions. Current AR was defined as having AR symptoms during the last 12 months with a history of physician-diagnosed AR. Skin prick tests for 18 common allergens were performed.
RESULTS
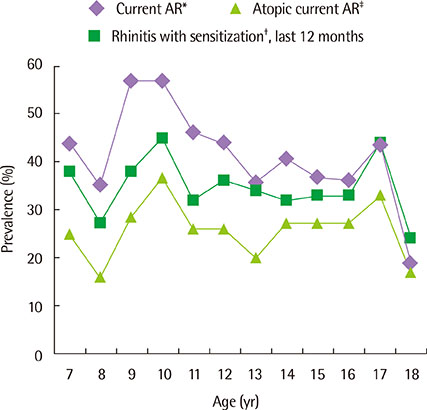
The number of males was 945, and that of females was 875. The mean age of the patients was 12.61+/-3.40 years. The prevalence of current AR and atopic current AR were 29.0% and 18.7%, respectively. Risk factors for current AR were male (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.486; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.189-1.856), family history of paternal AR (aOR, 3.208; 95% CI, 2.460-4.182), family history of maternal AR (aOR, 3.138; 95% CI, 2.446-4.025), antibiotic use in infancy (aOR, 1.547; 95% CI, 1.228-1.949), mold exposure during infancy (aOR, 1.416; 95% CI, 1.103-1.819), mold exposure during the last 12 months (aOR, 1.285; 95% CI, 1.012-1.630), and sensitization on skin prick tests (aOR, 2.596; 95% CI, 2.055-3.279). Risk factors for atopic current AR were the same as those of current AR, whereas breast-milk feeding (aOR, 0.720; 95% CI, 0.530-0.976) was a protective factor. Sensitized allergens as risk factors for current AR were Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus, Dermatophagoides farina, ragweed, mugwort, oak, alder, birch, Japanese hop, cat, and dog.
CONCLUSION
The prevalences of current AR and atopic current AR were 29.0% and 18.7%, respectively. Male, sex parental AR, antibiotic use in infancy, mold exposure during the last 12 months, mold exposure during infancy, and atopic sensitization were risk factors for current AR. Breast-milk feeding was a protective factor for atopic current AR. Aeroallergen sensitization was an important risk factor for AR.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 7 articles
-
Association between the serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D level and allergic rhinitis in Korean children
Seo Hee Yoon, Jung Yoon Kim, Yoon Hee Kim, Young A Park, In Suk Sol, Min Jung Kim, Kyung Won Kim, Myung Hyun Sohn, Kyu-Earn Kim
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2016;4(6):423-428. doi: 10.4168/aard.2016.4.6.423.Allergic sensitization and its association with air pollution in childhood allergic rhinitis
Hyo-Bin Kim
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2018;6(4):189-190. doi: 10.4168/aard.2018.6.4.189.Research on pediatric allergic rhinitis in Korea
Kyung Suk Lee, Yeong Ho Rha
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2018;6(Suppl 1):S58-S65. doi: 10.4168/aard.2018.6.S1.S58.Time trends of the prevalence of allergic diseases in Korea: A systematic literature review
Sung-Yoon Kang, Woo-Jung Song, Sang-Heon Cho, Yoon-Seok Chang
Asia Pac Allergy. 2018;8(1):. doi: 10.5415/apallergy.2018.8.e8.Linguistic adaptation of the rhinitis control assessment test in Korean
Mi-Ae Kim, Young-Min Ye, Ga Young Ban, Yoo Seob Shin, Dong-Ho Nahm, Hae-Sim Park
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2017;5(4):205-210. doi: 10.4168/aard.2017.5.4.205.Proper allergen selection for serum specific IgE test in children
Yong Ju Lee, Hyeon-Jong Yang, Jong-Seo Yoon, Man-Yong Han, Chang Keun Kim, Jin Tack Kim
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2018;6(5):237-240. doi: 10.4168/aard.2018.6.5.237.Relationship of serum vitamin D and interleukin-31 levels to allergic or nonallergic rhinitis in children
Seong Jun Park, Ji Eun Soh, Moon Soo Park, Hye Lim Jung, Jae Won Shim, Deok Soo Kim, Jung Yeon Shim
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2018;6(1):41-46. doi: 10.4168/aard.2018.6.1.41.
Reference
-
1. Bousquet J, Khaltaev N, Cruz AA, Denburg J, Fokkens WJ, Togias A, et al. Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma (ARIA) 2008 update (in collaboration with the World Health Organization, GA(2)LEN and AllerGen). Allergy. 2008; 63:Suppl 86. 8–160.2. Han DH, Ahn JC, Mun SJ, Park SK, Oh SY, Rhee CS. Novel risk factors for allergic rhinitis in Korean elementary school children: ARCO-kids phase II in a community. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2015; 7:234–240.
Article3. Hwang SH, Jung SY, Lim DH, Son BK, Kim JH, Yang JM, et al. Epidemiology of allergic rhinitis in Korean children. Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2013; 1:321–332.
Article4. Kim WK, Kwon JW, Seo JH, Kim HY, Yu J, Kim BJ, et al. Interaction between IL13 genotype and environmental factors in the risk for allergic rhinitis in Korean children. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012; 130:421–426.e5.
Article5. Hong SJ, Ahn KM, Lee SY, Kim KE. The prevalences of asthma and allergic diseases in Korean children. Korean J Pediatr. 2008; 51:343–350.
Article6. Kwon JW, Seo JH, Yu J, Kim BJ, Kim HB, Lee SY, et al. Relationship between the prevalence of allergic rhinitis and allergen sensitization in children of Songpa area, Seoul. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2011; 21:47–55.
Article7. Marogna M, Massolo A, Berra D, Zanon P, Chiodini E, Canonica GW, et al. The type of sensitizing allergen can affect the evolution of respiratory allergy. Allergy. 2006; 61:1209–1215.
Article8. Russell SL, Gold MJ, Hartmann M, Willing BP, Thorson L, Wlodarska M, et al. Early life antibiotic-driven changes in microbiota enhance susceptibility to allergic asthma. EMBO Rep. 2012; 13:440–447.
Article9. Katelaris CH, Lee BW, Potter PC, Maspero JF, Cingi C, Lopatin A, et al. Prevalence and diversity of allergic rhinitis in regions of the world beyond Europe and North America. Clin Exp Allergy. 2012; 42:186–207.
Article10. Seo JH, Kim HY, Jung YH, Lee E, Yang SI, Yu HS, et al. Interactions between innate immunity genes and early-life risk factors in allergic rhinitis. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2015; 7:241–248.
Article11. Jung YH, Hwang KH, Yang SI, Lee E, Kim KH, Kim MJ, et al. Changes of aeroallergen sensitization in children with asthma or allergic rhinitis from a tertiary referral hospital in Seoul over 10 years. Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2014; 2:97–102.
Article12. Kim DS, Park MR, Yu JS, Lee HS, Lee JH, Suh J, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of asthma and allergic rhinitis in elementary school children in Jinan-Gun. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2012; 22:374–382.
Article13. Yang SI, Lee E, Jung YH, Kim HY, Seo JH, Kwon JW, et al. Effect of antibiotic use and mold exposure in infancy on allergic rhinitis in susceptible adolescents. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2014; 113:160–165.e1.
Article14. Ha M, Kwon HJ, Leem JH, Kim HC, Lee KJ, Park I, et al. Korean Environmental Health Survey in Children and Adolescents (KorEHS-C): survey design and pilot study results on selected exposure biomarkers. Int J Hyg Environ Health. 2014; 217:260–270.
Article15. Kim HY, Seo JH, Jung YH, Lee E, Yang SI, Ha M, et al. Sensitization rates to inhalant allergens in children and adolescents of Incheon and Asan area and the relationship between polysensitization and prevalence of allergic diseases. Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2013; 1:41–49.
Article16. Lee Y, Choi J, Park MR, Kim J, Kim WK, Park YM, et al. Analysis of regional prevalence of allergic diseases in Korean school children. Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2015; 3:62–69.
Article17. Luft P, Oostingh GJ, Gruijthuijsen Y, Horejs-Hoeck J, Lehmann I, Duschl A. Patulin influences the expression of Th1/Th2 cytokines by activated peripheral blood mononuclear cells and T cells through depletion of intracellular glutathione. Environ Toxicol. 2008; 23:84–95.
Article18. Foliaki S, Pearce N, Bjorksten B, Mallol J, Montefort S, von Mutius E, et al. Antibiotic use in infancy and symptoms of asthma, rhinoconjunctivitis, and eczema in children 6 and 7 years old: international study of asthma and allergies in childhood phase III. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 124:982–989.
Article19. Hoskin-Parr L, Teyhan A, Blocker A, Henderson AJ. Antibiotic exposure in the first two years of life and development of asthma and other allergic diseases by 7.5 yr: a dose-dependent relationship. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2013; 24:762–771.
Article20. Björkstén B, Naaber P, Sepp E, Mikelsaar M. The intestinal microflora in allergic Estonian and Swedish 2-year-old children. Clin Exp Allergy. 1999. 29:p. 342–346.
Article21. Kalliomaki M, Salminen S, Poussa T, Arvilommi H, Isolauri E. Probiotics and prevention of atopic disease: 4-year follow-up of a randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2003; 361:1869–1871.
Article22. Legatzki A, Rosler B, von Mutius E. Microbiome diversity and asthma and allergy risk. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2014; 14:466.
Article23. Oyama N, Sudo N, Sogawa H, Kubo C. Antibiotic use during infancy promotes a shift in the T(H)1/T(H)2 balance toward T(H)2-dominant immunity in mice. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001; 107:153–159.
Article24. Russell SL, Gold MJ, Willing BP, Thorson L, McNagny KM, Finlay BB. Perinatal antibiotic treatment affects murine microbiota, immune responses and allergic asthma. Gut Microbes. 2013; 4:158–164.
Article25. Jaakkola JJ, Hwang BF, Jaakkola MS. Home dampness and molds as determinants of allergic rhinitis in childhood: a 6-year, population-based cohort study. Am J Epidemiol. 2010; 172:451–459.
Article26. Tischer CG, Hohmann C, Thiering E, Herbarth O, Muller A, Henderson J, et al. Meta-analysis of mould and dampness exposure on asthma and allergy in eight European birth cohorts: an ENRIECO initiative. Allergy. 2011; 66:1570–1579.
Article27. Weinmayr G, Gehring U, Genuneit J, Buchele G, Kleiner A, Siebers R, et al. Dampness and moulds in relation to respiratory and allergic symptoms in children: results from Phase Two of the International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood (ISAAC Phase Two). Clin Exp Allergy. 2013; 43:762–774.
Article28. Kusunoki T, Morimoto T, Nishikomori R, Yasumi T, Heike T, Mukaida K, et al. Breastfeeding and the prevalence of allergic diseases in schoolchildren: does reverse causation matter? Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2010; 21(1 Pt 1):60–66.
Article29. Van Odijk J, Kull I, Borres MP, Brandtzaeg P, Edberg U, Hanson LA, et al. Breastfeeding and allergic disease: a multidisciplinary review of the literature (1966-2001) on the mode of early feeding in infancy and its impact on later atopic manifestations. Allergy. 2003; 58:833–843.
Article30. Rautava S, Luoto R, Salminen S, Isolauri E. Microbial contact during pregnancy, intestinal colonization and human disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012; 9:565–576.
Article31. Duncan JM, Sears MR. Breastfeeding and allergies: time for a change in paradigm? Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008; 8:398–405.
Article32. Matheson MC, Allen KJ, Tang ML. Understanding the evidence for and against the role of breastfeeding in allergy prevention. Clin Exp Allergy. 2012; 42:827–851.
Article33. Kramer MS. Breastfeeding and allergy: the evidence. Ann Nutr Metab. 2011; 59:Suppl 1. 20–26.
Article34. Lee JW, Choi GS, Kim JE, Jin HJ, Kim JH, Ye YM, et al. Changes in sensitization rates to pollen allergens in allergic patients in the Southern part of Gyeonggi province over the last 10 years. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 31:33–40.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Comparative Study of the Prevalence of Allergic Disease between Rural and Urban Elementary School Students
- The Prevalence of Allergic Diseases in Children Living In Jeju
- A Survey of Allergic Diseases in University Students of Bangkok, Thailand
- The Prevalence of Asthma, Allergic Rhinitis, and Atopic Dermatitis in Elementary School Students according to the Body Mass Index
- Survey of food allergy in elementary school children in Bucheon-city and relationship between food allergy and other allergic diseases