J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2001 Sep;8(3):195-201. 10.4184/jkss.2001.8.3.195.
Responsiveness of Human Intervertebral Disc Cells in Matrix Synthesis To Adenovirus-Mediated Gene Transfer(IGF-1, TGF-beta1 Encoding Genes)
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. shmoon@yumc.yonsei.ac.kr
- KMID: 2209735
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2001.8.3.195
Abstract
-
BACKGROUND: Genetic modification of cells through gene transfer gains popularity as a sophisticated delivery system in the management of musculoskeletal disease. Anabolic growth factors like IGF-1 BMP-2 OP-1, and TGF-beta1 were candidate for therapeutic purposus for regenerating matrix of intervertebral disc. TGF-beta1, OP-1 and BMP-2 share same pathway i.e. Smad while IGF-1 utilize P13K pathway. Accordingly it is logical to use two cytokine encoding genes which using different signal transduction pathway to upregulate matrix synthesis.
PURPOSE: To elucidate the anabolic effect of the combination gene transfer(IGF-1 and TGF-beta1 encoding gene) to human disc cells, cultured in alginate beads.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
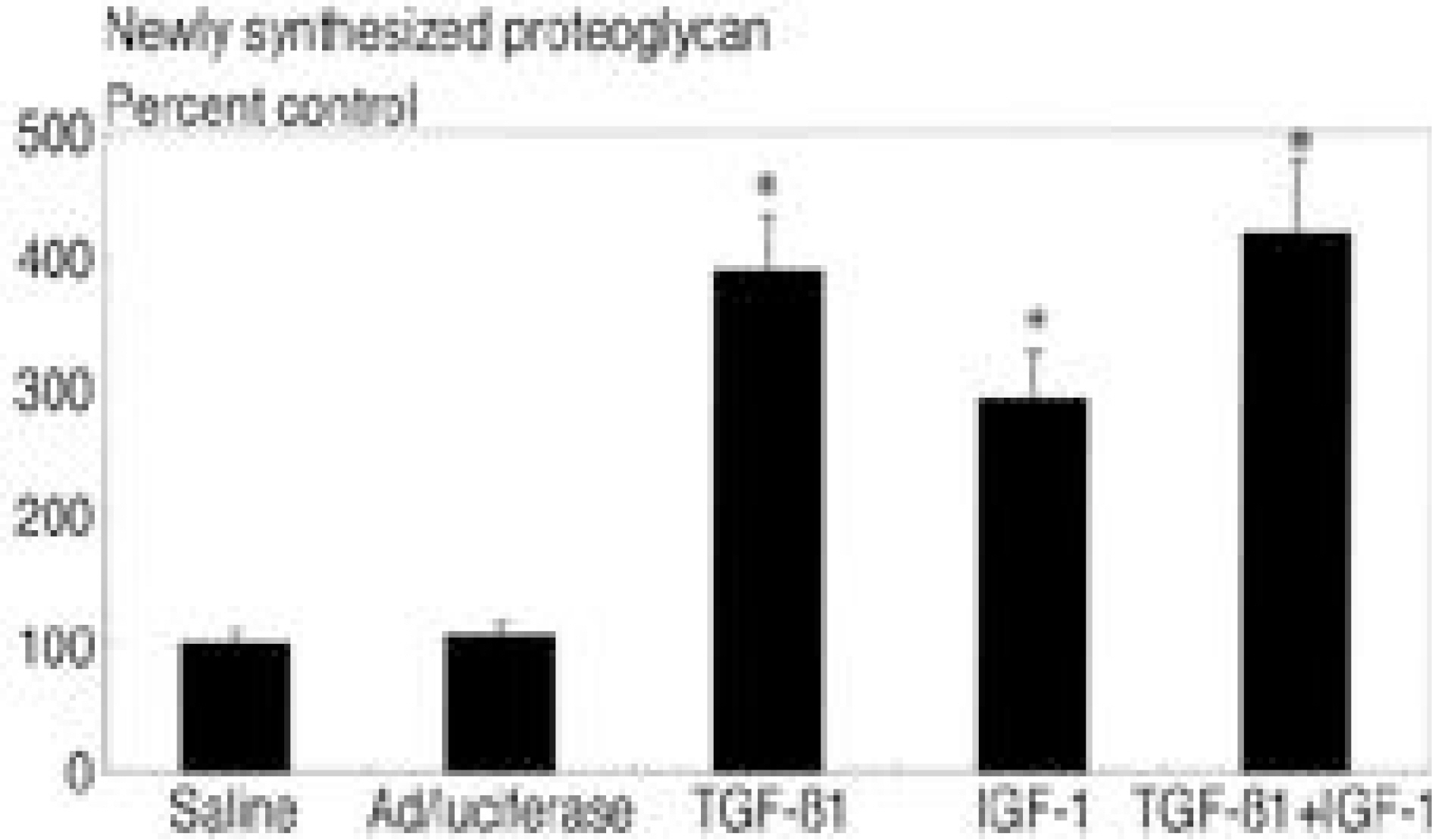
Lumbar and cervical intervertebral disc tissue was obtained from surgical disc procedure from fifteen patients. After isolation and culture of the cells, cultures were transduced with first, Adenovirus-TGFbeta1 construct(Ad/TGF-beta1) and Ad/IGF-1 respectively, second, with combination of two viral constructs(Ad/TGF-beta1+Ad/IGF-1). Cultures treated with saline and Ad/luciferase served as control. Then cultures were incorporated into alginate beads. Exogenous TGF-beta1(2ng/ml) and IGF-1(100ng/ml) were administered also. Newly synthesized proteoglycan was assessed using S35 incorporation using chromatography on Sephadex G-25 in PD-10 column.
RESULTS
In cultures transduced with single therapeutic gene construct, there were statistically significant 2.9 fold(Ad/TGF-beta1 and 1.8 fold(Ad/IGF-1) increase in newly synthesized proteoglycan comparing control(p<0.05). In culture transduced with double combination of therapeutic gene construct, there were 3.9 fold(Ad/TGF-beta1+Ad/IGF-1) increase in newly synthesized proteo-glycan comparing control(p<0.05). Culture treated with TGF-beta1(2ng/ml) showed 3.9 fold increase and IGF-1(100ng/ml) 2.9 fold increase, TGF-beta1+IGF-1 4.2 fold increase in proteoglycan synthesis compared to control.
CONCLUSIONS
Combination gene therapy provided efficient mechanism of upregulating matrix regeneration of the human inter-vertebral disc cells.
MeSH Terms
-
Anabolic Agents
Cells, Cultured
Chromatography
Genetic Therapy
Humans*
Insulin-Like Growth Factor I
Intercellular Signaling Peptides and Proteins
Intervertebral Disc*
Logic
Musculoskeletal Diseases
Proteoglycans
Regeneration
Signal Transduction
Transforming Growth Factor beta1*
Anabolic Agents
Insulin-Like Growth Factor I
Intercellular Signaling Peptides and Proteins
Proteoglycans
Transforming Growth Factor beta1
Figure
Reference
-
1). Borenstein D. Epidemiology, etiology, diagnostic evaluation, and treatment of low back pain. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 4:226–32. 1992.
Article2). Buckwalter JA. Aging and degeneration of the human intervertebral disc. Spine. 20:1307–1314. 1995.
Article3). Butler D, Trafimow JH, Andersson GB, McNeill TW, Huckman MS. Discs degenerate before facets. Spine. 15:111–113. 1990.
Article4). Chelberg MK, Banks GM, Geiger DF, Oegema TR. Identification of heterogenous cell populations in normal human intervertebral disc. J Anat. 186:43–53. 1995.5). Crabb ID, O'Keefe RJ, Edward Puzas J, Rosier RN. Synergistic effect of transforming growth factor beta and fibroblast growth factor on DNA synthesis in chicken growth plate chondrocytes. J Bone Miner Res. 5:1105–1112. 1990.6). Evans CH, Robbins PD. Possible orthopaedic applications of gene therapy. J Bone Joint Surg. 77-A:1103–1114. 1995.
Article7). Evans CH, Robbins PD. Genetically augmented tissue engineering of the musculoskeletal system. Clin Orthop. 367:S410–8. 1999.
Article8). Evans CH, Robbins PD. Potential treatment of osteoarthritis by gene therapy. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 25:333–44. 1999.
Article9). Eyre D, Benya P, Buckwalter J, Frymoyer JW, Gordon SL. Intervertebral disc: Part B. Basic science perspective. New Perspectives in Low Back Pain. Park Ridge, IL: American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeon;p. 147–207. 1989.10). Gruber HE, Fisher EC, Desani B, Stasky AA, Hoelscher G, Hanley EN. Human intervertebral disc cells from the annulus: three dimensional culture in agarose or alginate and responsiveness to TGF-b1. Exp Cell Res. 235:13–21. 1997.11). Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. The Hallmarks of Cancer. Cell. 100:57–70. 2000.
Article12). Itoh S, Itoh F, Goumans M-J, Dijke PT. Signalling of transforming growth factor-ß family members through Smad protein. Eur J Biochem. 267:6954–6967. 2000.13). Lipson SJ, Muir H. Proteoglycans in experimental intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine. 6:194–210. 1981.
Article14). Maldonado BA, Oegema TR. Initial characterization of the metabolism of intervertebral disc cells encapsulated in microspheres. J Orthop Res. 10:677–690. 1992.
Article15). Melrose J, Ghosh P, Taylor TK, Hall A, Osti OL, Ver-non-Roberts B, Fraser RD. A longitudinal study of the matrix changes induced in the intervertebral disc by surgical damage to the annulus fibosus. J Orthop Res. 10:665–676. 1992.16). Moon SH, Kang JD, Nishida K, Gilbertson LG, Niyibizi C, Smith PN, Knaub MA, Robbins PD, Evans CH. Human cervical intervertebral disc cells are susceptible to adenovirus-mediated gene therapy. Proceedings of Cervical Spine Research Society, p150-153. 1999.17). Moon SH, Nishida K, Kang JD, Gilbertson LG, Muz-zonigro TS, Knaub MA, Robbins PD, Evans CH. Human intervertebral disc cells are genetically modifiable in-vitro by adenovirus-meidated gene transfer: Implications for the clinical management of intervertebral disc dis -order. Spine. 25:2573–2579. 2000.18). Nishida K, Kang JD, Gilbertson LG, Moon S-H, Suh J-K, Vogt MT, Robbins PD, Evans CH. Modulation of the biologic activity of the rabbit intervertebral disc by gene therapy: An in vivo study of adenovirus-mediated transfer of the human transforming growth factor ß 1 encoding gene. Spine. 24:2419–2425. 1999.19). Nishida K, Kang JD, Suh J-K, Robbins PD, Evans CH, Gilbertson LG. Adenovirus-mediated gene transfer to nucleus pulposus cells: Implication for the treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine. 23:2437–2443. 1998.20). Osada R, Ohshima H, Ishihara H, Yudoh K, Sakai K, Matsui H, Tsuji H. Atocrine/paracrine mechanism of insulin-like growth factor-1 secretion, and the effect of insuline-like growth factors-1 on proteoglycan synthesis in bovine intervertebral discs. J Orhtop Res. 14:690–699. 1996.21). Reinecke JA, Wehling P, Robbins P, Evans CH, Sager M, Schulze-Allen G, Koch H. In vitro transfer of genes in spinal tissue. Zeitschrift fur Orthopadie und Ihre Grenzgebiete. 135:412–416. 1997.22). Takegami K, Matuda K, Kumano F, An H, Chiba K, Pankaj D, Sampath TK, Thonar EJ-MA. O steo-genic protein-1 is most effective in stimulating nucleus pulposus and annulus fibrosus cells to repair their matrix after chondroitinase ABC-induced chemonucleolysis. 45th Annual Meeting Trans Orthop Res Soc, 201. 1999.23). Thompson JP, Oegema TR, Bradford DS. Stimulation of mature canine intervertebral disc by growth facors. Spine. 16:253–260. 1991.24). Wehling P, Schulitz KP, Robbins PD, Evans CH, Reinecke JA. Transfer of genes to chondrocytic cells of the lumbar spine. Proposal for a treatment strategy of spinal disorders by local gene therapy. Spine. 22:1092–1097. 1997.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Adenovirus-Mediated Therapeutic Gene Transfer: Matrix Synthesis of Human Intervertebral Disc Cells
- Matrix Synthesis of Human Intervertebral Disc Cells: Effect of Gene Transfer, Exogenous Growth Factor, Incubation Period, and Culture Methods
- Intradiscal Gene Therapy: Therapeutic Implications in Degenerative Disc Disease
- Tissue Engineering of the Intervertebral Disc with Cultured Nucleus Pulposus Cells Using Atelocollagen Scaffold and Gene Therapy
- Transforming Growth Factor-beta1 and Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 Upregulates Matrix Synthesis and Chondrogenic Phenotype in Intervertebral Disc Cells