J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2002 Sep;9(3):165-171. 10.4184/jkss.2002.9.3.165.
Transforming Growth Factor-beta1 and Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 Upregulates Matrix Synthesis and Chondrogenic Phenotype in Intervertebral Disc Cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Yonsei University, College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hwanlee@yumc.yonsei.ac.kr
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Ewha Women University, College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Aju University, College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2003220
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2002.9.3.165
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
To determine effect of transforming growth factor-beta1 and bone morphogenetic protein-2 in matrix synthesis and expression of chondrogenic phenotype in human intervertebral disc cells.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The intervertebral disc cells were harvested and cultured from the surgical patients for the degenerative disc disease. TGF-beta1 was purchased from R&D and BMP-2 was produced by transfection of pcDNA3.1/Hygro/BMP-2 to CHO cell using Lipofectamine 2000. rhBMP-2 was separated by Heparin-Sepharose A chromatography. TGF-bata1 and BMP-2 were administered to culture. Proteoglycan synthesis was assessed by 35S incorporation and expression of matrix mRNA was analyzed by RT-PCR for collagen I, collagen II, aggrecan, and osteocalcin.
RESULTS
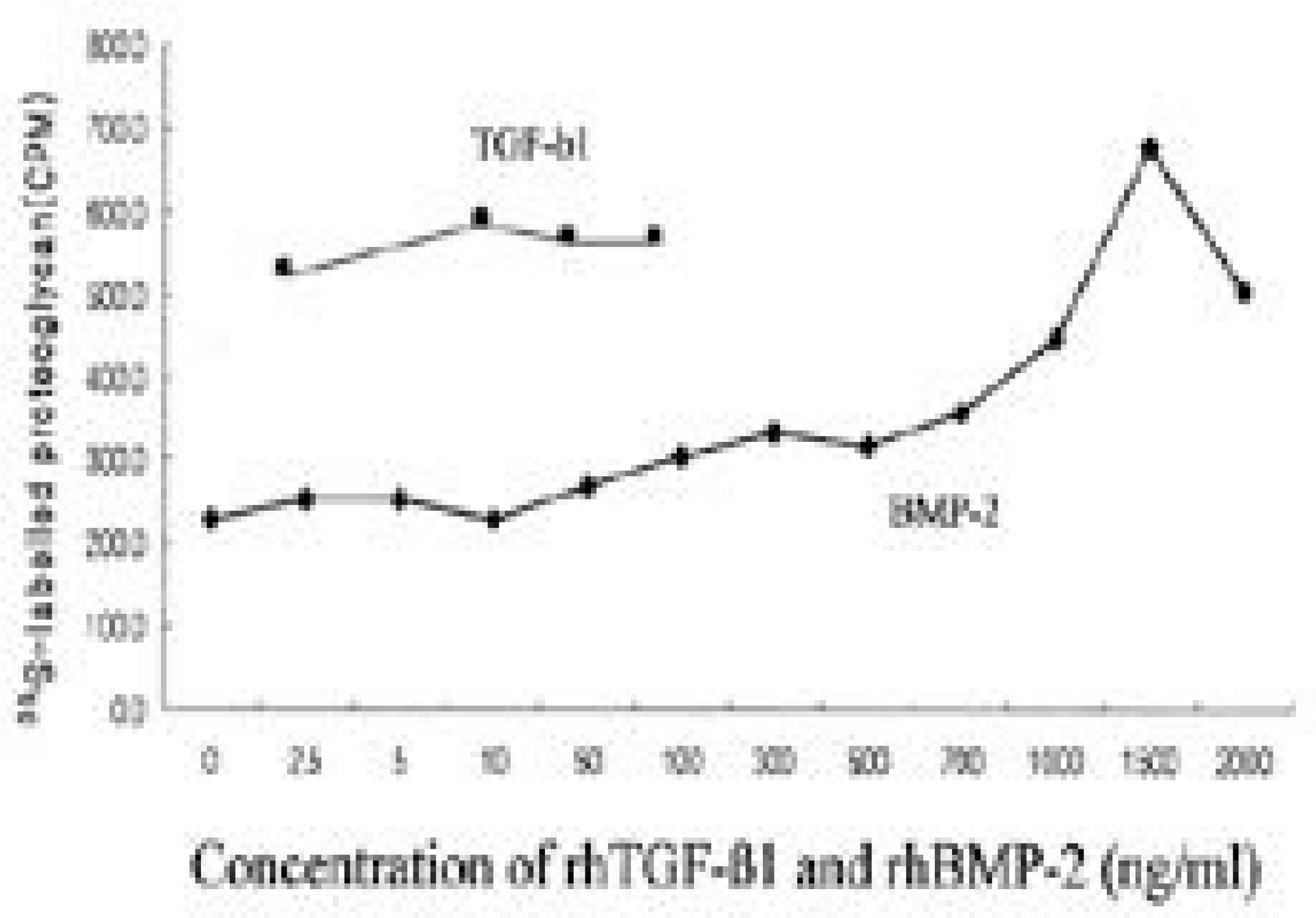
TGF-bata1 and BMP-2 showed increased proteoglycan synthesis and expression of collagen I, collagen II and aggrecan mRNA in dose dependent manner respectively. There was no recognizable synergistic effect in matrix synthesis and matrix mRNA expression. Throughout dosage, expression of osteogenic phenotype (osteocalcin mRNA) was not noted.
CONCLUSION
TGF-beta1 and BMP-2 proved to be effective anabolic agent for maximizing matrix synthesis without evidence of osteogenesis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Barr E, Leiden JM. Systemic delivery of recombinant proteins by genetically modified myoblasts. Science. 254:1507–9. 1991.
Article2). Boden SD, Zdeblick TA, Sandhu HS, Heim SE. The use of rhBMP-2 in interbodyfusion cages. Definitive evidence of osteoinduction in humans: A preliminary report. Spine. 25:376–81. 2000.3). Brittberg M, Lindahl A, Nilsson A, Ohlsson C, Isaksson O, Peterson L. Treatment of deep cartilage defects in the knees with autologous chondrocyte transplantation. N Engl J Med. 331:889–95. 1994.4). Buckwalter JA. Aging and degeneration of the human intervertebral disc. Spine. 20:1307–1314. 1995.
Article5). Dhawan J, Pan LC, Pavlath GK, Travis MA, Lanctot AM, Blau HM. Systemic delivery of human growth hor -mone by injection of genetically engineered myoblasts. Science. 254:1509–12. 1991.6). Evans CH, Robbins PD. Possible orthopaedic applications of gene therapy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 77:1103–14. 1995.
Article7). Gruber HE, Fisher EC, Desani B, Stasky AA, Hoelscher G, Hanley EN. Human intervertebral disc cells from the annulus: three dimensional culture in agarose or alginate and responsiveness to TGF-b1. Exp Cell Res. 235:13–21. 1997.8). Hering TM, Kollar J, Huynh TD, Varelas JB, Sandell LJ. Modulation of extracellular matrix gene expression in bovine high-density chondrocyte cultures by ascorbic acid and enzymatic resuspension. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1994; 314:90–8.
Article9). Lipson SJ, Muir H. Proteoglycans in experimental intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine. 6:194–210. 1981.
Article10). Luyten FP, Chen P. Paralkar V, Reddi AH. Recombinant bone morphogenetic protein-4, transforming growth factor-β 1, and activin A enhance the cartilage phenotype of articular chondrocytes in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 1994; 210:224–9.11). Martin GJ Jr, Boden SD, Marone MA, Marone MA, Moskovitz PA. Posterolateral intertransverse process spinal arthrodesis with rhBMP-2 in a nonhuman primate: important lessons learned regarding dose, carrier, and safety. J Spinal Disord. 12:179–86. 1999.12). Minamide A, Tamaki T, Kawakami M, Hashizume H, Yoshida M, Sakata R. Experimental spinal fusion using sintered bovine bone coated with type I collagen and recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2. Spine. 24:1863–70. 1999.
Article13). Moon SH, Gilbertson LG, Nishida K, Knaub MA, Muz-zonigro T, Robbins PD, CH Evans and JD Kang. Human intervertebral disc cells are genetically modifiable by ade -novirus-mediated gene transfer. Spine. 25:2573–79. 2000.14). Moon SH, Kang JD, Nishida K, Gilbertson LG, Niyibizi C, Smith PN, Knaub MA, Robbins PD, Evan CH. Human cervical intervertebral disc cell are susceptible to adenovirus-mediated gene therapy: Therapeutic gene transfer. Proceedings of Cervical Spine Research Society, Seattle WA. 1999.15). Moon SH, Nishida K, Gilbertson LG, Hall RA, Robbins PD, Kang JD. Biologic response of human intervertebral disc cells to gene therapy cocktail. Proceedings of Orthopaedic Research Society, SanFrancisco. 2001.
Article16). Moon SH, Nishida K, Gilbertson LG, Hall RA, Robbins PD, Kang JD. Cocktail therapeutic gene transfer to human intervertebral disc cells cultured in three-dimension -al alginate beads. Proceedings of North American Spine Society, New Orleans. 2000.17). Moullier P, Bohl D, Heard JM, Danos O. Correction of lysosomal storage in the liver and spleen of MPS VII mice by implantation of genetically modified skin fibrob -lasts. Nat Genet. 4:154–9. 1993.18). Nishida K, Kang JD, Gilbertson LG, Moon S-H, Suh J-K, Vogt MT, Robbins PD, Evans CH. Modulation of the biologic activity of the rabbit intervertebral disc by gene therapy: An in vivo study of adenovirus-mediated transfer of the human transforming growth factor β 1 encoding gene. Spine. 24:2419–25. 1999.19). Nishida K, Kang JD, Suh J-K, Robbins PD, Evans CH, Gilbertson LG. Adenovirus-mediated gene transfer to nucleus pulposus cells: Implication for the treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine. 23:2437–43. 1998.20). Osada R, Oshima H, Ishihara H, Yudoh K, Sakai K, Matsui H, Tsuji H. Autocrine/paracrine mechanism of insulin-like growth factor-1 secretion, and the effect of insuline-like growth factors-1 on proteoglycan synthesis in bovine intervertebral discs. J Orthop Res. 14:690–9. 1996.21). Pearce RH, Grimmer BJ, Adams ME. Degeneration and the chemical composition of the human lumbar intervertebral disc. J Orthop Res. 5:198–205. 1987.
Article22). Robbins PD, Ghivizzani SC. Viral vectors for gene therapy. Pharmacol Ther. 80:35–47. 1998.
Article23). Smith P, Shuler FD, Georgescu HI, Ghivizzani SC, Johnstone B, Ninibizi C, Robbins PD, Evans CH. Genetic enhancement of matrix synthesis by articular chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 2000; 43:1156–64.24). Stewart MC, Saunders KM, Burton-Wurster N, Macleod JN. Phenotypic stability of articular chondrocytes in vitro. J Bone Miner Res. 15:166–174. 2000.25). Takegami K, Matuda K, Kumano F, An H, Chiba K, Pankaj D. Osteogenic protein-1 is most effective in stimu -lating nucleus pulposus and annulus fibrosus cells to repair their matrix after chondroitinase ABC-induced chemonucleolysis. 45th Annual Meeting, Trans Orthop Res Soc, 201. 1999.26). Thompson JP, Oegema TR, Bradford DS. Stimulation of mature canine intervertebral disc by growth facors. Spine. 16:253–60. 1991.27). Vacanti CA, Kim W, Schloo B, Upton J, Vacanti W. Joint resurfacing with cartilage grown in situ from cell-polymer structures. Am J Sports Med. 22:485–8. 1994.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Biological Effect of TGF - B 1 on Human Intervertebral Disc by Cell Culture System
- Tissue Engineering of the Intervertebral Disc with Cultured Nucleus Pulposus Cells Using Atelocollagen Scaffold and Gene Therapy
- Phenotypical Stability and Matrix Synthesis of Human Intervertebral Disc Cells in Response to Dexamethasone and Transforming Growth Factor-beta1
- Matrix Synthesis of Human Intervertebral Disc Cells: Effect of Gene Transfer, Exogenous Growth Factor, Incubation Period, and Culture Methods
- The Relation Between Sox9, TGF-beta1, and Proteoglycan in Human Intervertebral Disc Cells