Elevated Levels of alpha-Synuclein Oligomer in the Cerebrospinal Fluid of Drug-Naive Patients with Parkinson's Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Bongseng Memorial Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- 2Department of Neurology, Dong-A University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea. smcheon@dau.ac.kr
- 3Department of Physiology, Dong-A University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2179007
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2011.7.4.215
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE
The detection of alpha-synuclein in the body fluids of patients with synucleinopathy has yielded promising but inconclusive results, in part because of conformational changes of alpha-synuclein in response to environmental conditions. The aim of this study was to determine the feasibility of using alpha-synuclein as a biological marker for Parkinson's disease (PD).
METHODS
Twenty-three drug-naive patients with PD (age 62.4+/-12.7 years, mean+/-SD; 11 males) and 29 age- and sex-matched neurologic control subjects (age 60.1+/-16.2 years; 16 males) were recruited. The levels of oligomeric and total alpha-synuclein in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and plasma were measured using two simultaneous enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays.
RESULTS
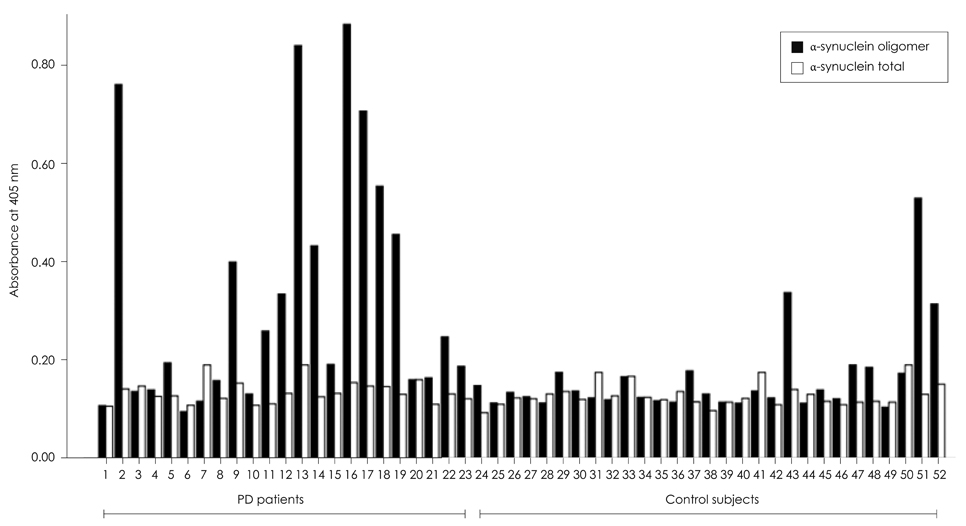
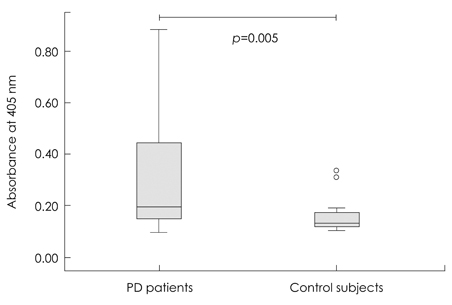
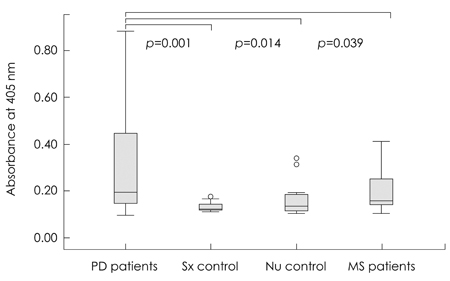
The level of alpha-synuclein oligomer in the CSF of PD patients was significantly higher in PD patients than in neurological controls, but other findings (plasma alpha-synuclein oligomer and total alpha-synuclein in CSF and plasma) did not differ significantly between the two groups. When the control subjects were divided into a symptomatic control group (11 patients who complained of parkinsonian symptoms and were diagnosed with hydrocephalus and drug-induced or vascular parkinsonism) and a neurologic control group (10 normal subjects and 8 patients with diabetic ophthalmoplegia), the level of alpha-synuclein oligomer in the CSF was still significantly higher in PD patients than in both of the control subgroups.
CONCLUSIONS
These findings provide further evidence for a pathogenic role of the alpha-synuclein oligomer and suggest that CSF levels of alpha-synuclein oligomer can be a reliable marker for PD.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Parkinson's Disease with Fatigue: Clinical Characteristics and Potential Mechanisms Relevant to α-Synuclein Oligomer
Li-Jun Zuo, Shu-Yang Yu, Fang Wang, Yang Hu, Ying-Shan Piao, Yang Du, Teng-Hong Lian, Rui-Dan Wang, Qiu-Jin Yu, Ya-Jie Wang, Xiao-Min Wang, Piu Chan, Sheng-Di Chen, Yongjun Wang, Wei Zhang
J Clin Neurol. 2016;12(2):172-180. doi: 10.3988/jcn.2016.12.2.172.Parkinson's Disease with Fatigue: Clinical Characteristics and Potential Mechanisms Relevant to α-Synuclein Oligomer
Li-Jun Zuo, Shu-Yang Yu, Fang Wang, Yang Hu, Ying-Shan Piao, Yang Du, Teng-Hong Lian, Rui-Dan Wang, Qiu-Jin Yu, Ya-Jie Wang, Xiao-Min Wang, Piu Chan, Sheng-Di Chen, Yongjun Wang, Wei Zhang
J Clin Neurol. 2016;12(2):172-180. doi: 10.3988/jcn.2016.12.2.172.Combined Assessment of Serum Alpha-Synuclein and Rab35 is a Better Biomarker for Parkinson's Disease
Hung-Li Wang, Chin-Song Lu, Tu-Hsueh Yeh, Yu-Ming Shen, Yi-Hsin Weng, Ying-Zu Huang, Rou-Shayn Chen, Yu-Chuan Liu, Yi-Chuan Cheng, Hsiu-Chen Chang, Ying-Ling Chen, Yu-Jie Chen, Yan-Wei Lin, Chia-Chen Hsu, Huang-Li Lin, Chi-Han Chiu, Ching-Chi Chiu
J Clin Neurol. 2019;15(4):488-495. doi: 10.3988/jcn.2019.15.4.488.
Reference
-
1. Koh SB, Kwon DY, Lee JM, Han JK, Kim BJ, Park MK, et al. Prevalence of Parkinsonism in Ansan-city. J Korean Neurol Assoc. 2003. 21:498–501.2. Twelves D, Perkins KS, Counsell C. Systematic review of incidence studies of Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord. 2003. 18:19–31.
Article3. Gibb WR. Accuracy in the clinical diagnosis of parkinsonian syndromes. Postgrad Med J. 1988. 64:345–351.
Article4. Gelb DJ, Oliver E, Gilman S. Diagnostic criteria for Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol. 1999. 56:33–39.
Article5. Forno LS. Neuropathology of Parkinson's disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1996. 55:259–272.
Article6. Rajput AH, Rozdilsky B, Rajput A. Accuracy of clinical diagnosis in parkinsonism--a prospective study. Can J Neurol Sci. 1991. 18:275–278.7. Hughes AJ, Daniel SE, Blankson S, Lees AJ. A clinicopathologic study of 100 cases of Parkinson's disease. Arch Neurol. 1993. 50:140–148.
Article8. Tretiakoff K. Contribution a l'etudie de l'anatomie pathologique du locus niger de Soemmering avec quelques deductions relatives a la pathogenie des troubles du tonus musculaire et de la maladie de Parkinson [thesis]. 1919. Paris: University of Paris.9. Fukuda T, Tanaka J, Watabe K, Numoto RT, Minamitani M. Immunohistochemistry of neuronal inclusions in the cerebral cortex and brain-stem in Lewy body disease. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1993. 43:545–551.
Article10. Shults CW. Lewy bodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. 103:1661–1668.
Article11. Polymeropoulos MH, Lavedan C, Leroy E, Ide SE, Dehejia A, Dutra A, et al. Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson's disease. Science. 1997. 276:2045–2047.
Article12. Singleton AB, Farrer M, Johnson J, Singleton A, Hague S, Kachergus J, et al. alpha-Synuclein locus triplication causes Parkinson's disease. Science. 2003. 302:841.
Article13. Miller DW, Hague SM, Clarimon J, Baptista M, Gwinn-Hardy K, Cookson MR, et al. Alpha-synuclein in blood and brain from familial Parkinson disease with SNCA locus triplication. Neurology. 2004. 62:1835–1838.
Article14. Ross OA, Braithwaite AT, Skipper LM, Kachergus J, Hulihan MM, Middleton FA, et al. Genomic investigation of alpha-synuclein multiplication and parkinsonism. Ann Neurol. 2008. 63:743–750.15. Wood SJ, Wypych J, Steavenson S, Louis JC, Citron M, Biere AL. Alpha-synuclein fibrillogenesis is nucleation-dependent. Implications for the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease. J Biol Chem. 1999. 274:19509–19512.16. Conway KA, Lee SJ, Rochet JC, Ding TT, Williamson RE, Lansbury PT Jr. Acceleration of oligomerization, not fibrillization, is a shared property of both alpha-synuclein mutations linked to early-onset Parkinson's disease: implications for pathogenesis and therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. 97:571–576.
Article17. Uversky VN, Lee HJ, Li J, Fink AL, Lee SJ. Stabilization of partially folded conformation during alpha-synuclein oligomerization in both purified and cytosolic preparations. J Biol Chem. 2001. 276:43495–43498.
Article18. Galvin JE. Interaction of alpha-synuclein and dopamine metabolites in the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease: a case for the selective vulnerability of the substantia nigra. Acta Neuropathol. 2006. 112:115–126.
Article19. Soto C, Estrada LD. Protein misfolding and neurodegeneration. Arch Neurol. 2008. 65:184–189.
Article20. Braak H, Rüb U, Gai WP, Del Tredici K. Idiopathic Parkinson's disease: possible routes by which vulnerable neuronal types may be subject to neuroinvasion by an unknown pathogen. J Neural Transm. 2003. 110:517–536.
Article21. Lee SJ. Origins and effects of extracellular alpha-synuclein: implications in Parkinson's disease. J Mol Neurosci. 2008. 34:17–22.
Article22. Danzer KM, Krebs SK, Wolff M, Birk G, Hengerer B. Seeding induced by alpha-synuclein oligomers provides evidence for spreading of alpha-synuclein pathology. J Neurochem. 2009. 111:192–203.
Article23. Lee HJ, Patel S, Lee SJ. Intravesicular localization and exocytosis of alpha-synuclein and its aggregates. J Neurosci. 2005. 25:6016–6024.
Article24. Lee HJ, Suk JE, Bae EJ, Lee JH, Paik SR, Lee SJ. Assembly-dependent endocytosis and clearance of extracellular alpha-synuclein. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2008. 40:1835–1849.
Article25. Kim C, Lee SJ. Controlling the mass action of alpha-synuclein in Parkinson's disease. J Neurochem. 2008. 107:303–316.26. Lee PH, Lee G, Park HJ, Bang OY, Joo IS, Huh K. The plasma alpha-synuclein levels in patients with Parkinson's disease and multiple system atrophy. J Neural Transm. 2006. 113:1435–1439.
Article27. Li QX, Mok SS, Laughton KM, McLean CA, Cappai R, Masters CL, et al. Plasma alpha-synuclein is decreased in subjects with Parkinson's disease. Exp Neurol. 2007. 204:583–588.28. Mollenhauer B, Cullen V, Kahn I, Krastins B, Outeiro TF, Pepivani I, et al. Direct quantification of CSF alpha-synuclein by ELISA and first cross-sectional study in patients with neurodegeneration. Exp Neurol. 2008. 213:315–325.
Article29. Ohrfelt A, Grognet P, Andreasen N, Wallin A, Vanmechelen E, Blennow K, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid alpha-synuclein in neurodegenerative disorders-a marker of synapse loss? Neurosci Lett. 2009. 450:332–335.30. El-Agnaf OM, Salem SA, Paleologou KE, Curran MD, Gibson MJ, Court JA, et al. Detection of oligomeric forms of alpha-synuclein protein in human plasma as a potential biomarker for Parkinson's disease. FASEB J. 2006. 20:419–425.31. Paleologou KE, Kragh CL, Mann DM, Salem SA, Al-Shami R, Allsop D, et al. Detection of elevated levels of soluble alpha-synuclein oligomers in post-mortem brain extracts from patients with dementia with Lewy bodies. Brain. 2009. 132:1093–1101.
Article32. Outeiro TF, Kazantsev A. Drug Targeting of alpha-Synuclein Oligomerization in Synucleinopathies. Perspect Medicin Chem. 2008. 2:41–49.33. Yuan B, Sierks MR. Intracellular targeting and clearance of oligomeric alpha-synuclein alleviates toxicity in mammalian cells. Neurosci Lett. 2009. 459:16–18.
Article34. Pandey AP, Haque F, Rochet JC, Hovis JS. Clustering of alpha-synuclein on supported lipid bilayers: role of anionic lipid, protein, and divalent ion concentration. Biophys J. 2009. 96:540–551.
Article35. Brown DR. Metal binding to alpha-synuclein peptides and its contribution to toxicity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009. 380:377–381.
Article36. Outeiro TF, Klucken J, Bercury K, Tetzlaff J, Putcha P, Oliveira LM, et al. Dopamine-induced conformational changes in alpha-synuclein. PLoS One. 2009. 4:e6906.
Article37. Uversky VN, Li J, Fink AL. Evidence for a partially folded intermediate in alpha-synuclein fibril formation. J Biol Chem. 2001. 276:10737–10744.
Article38. Uversky VN. A protein-chameleon: conformational plasticity of alpha-synuclein, a disordered protein involved in neurodegenerative disorders. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2003. 21:211–234.
Article39. Iwai A, Masliah E, Yoshimoto M, Ge N, Flanagan L, de Silva HA, et al. The precursor protein of non-A beta component of Alzheimer's disease amyloid is a presynaptic protein of the central nervous system. Neuron. 1995. 14:467–475.
Article40. Davidson WS, Jonas A, Clayton DF, George JM. Stabilization of alpha-synuclein secondary structure upon binding to synthetic membranes. J Biol Chem. 1998. 273:9443–9449.
Article41. Li JY, Englund E, Holton JL, Soulet D, Hagell P, Lees AJ, et al. Lewy bodies in grafted neurons in subjects with Parkinson's disease suggest host-to-graft disease propagation. Nat Med. 2008. 14:501–503.
Article42. Kordower JH, Chu Y, Hauser RA, Freeman TB, Olanow CW. Lewy body-like pathology in long-term embryonic nigral transplants in Parkinson's disease. Nat Med. 2008. 14:504–506.
Article43. Tokuda T, Salem SA, Allsop D, Mizuno T, Nakagawa M, Qureshi MM, et al. Decreased alpha-synuclein in cerebrospinal fluid of aged individuals and subjects with Parkinson's disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006. 349:162–166.
Article44. Yamakawa K, Izumi Y, Takeuchi H, Yamamoto N, Kume T, Akaike A, et al. Dopamine facilitates alpha-synuclein oligomerization in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010. 391:129–134.
Article45. Du HN, Tang L, Luo XY, Li HT, Hu J, Zhou JW, et al. A peptide motif consisting of glycine, alanine, and valine is required for the fibrillization and cytotoxicity of human alpha-synuclein. Biochemistry. 2003. 42:8870–8878.
Article46. Volles MJ, Lansbury PT Jr. Zeroing in on the pathogenic form of alpha-synuclein and its mechanism of neurotoxicity in Parkinson's disease. Biochemistry. 2003. 42:7871–7878.
Article47. Zhang W, Wang T, Pei Z, Miller DS, Wu X, Block ML, et al. Aggregated alpha-synuclein activates microglia: a process leading to disease progression in Parkinson's disease. FASEB J. 2005. 19:533–542.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Parkinson's Disease with Fatigue: Clinical Characteristics and Potential Mechanisms Relevant to α-Synuclein Oligomer
- Alpha-Synuclein Function and Dysfunction on Cellular Membranes
- Cerebrospinal Fluid Amyloid β1-42, Tau, and Alpha-Synuclein Predict the Heterogeneous Progression of Cognitive Dysfunction in Parkinson's Disease
- Accumulation of Alpha-synuclein Causes Colonic Dysmotility Independently of Enteric Nervous Damage in the Early Stage of Parkinson's Disease (Neurogastroenterol Motil 2012;24:e425-e436)
- Structure, Distribution, and Genetic Profile of α-Synuclein and Their Potential Clinical Application in Parkinson's Disease