Diabetes Metab J.
2011 Jun;35(3):219-225. 10.4093/dmj.2011.35.3.219.
ATP-Sensitive Potassium Channel-Deficient Mice Show Hyperphagia but Are Resistant to Obesity
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. ywkim@med.yu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Physiology, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 3Department of Physiology, Keimyung University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 2175420
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2011.35.3.219
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
The hypothalamus, the center for body weight regulation, can sense changes in blood glucose level based on ATP-sensitive potassium (KATP) channels in the hypothalamic neurons. We hypothesized that a lack of glucose sensing in the hypothalamus affects the regulations of appetite and body weight.
METHODS
To evaluate this hypothesis, the responses to glucose loading and high fat feeding for eight weeks were compared in Kir6.2 knock-out (KO) mice and control C57BL/6 mice, because Kir6.2 is a key component of the KATP channel.
RESULTS
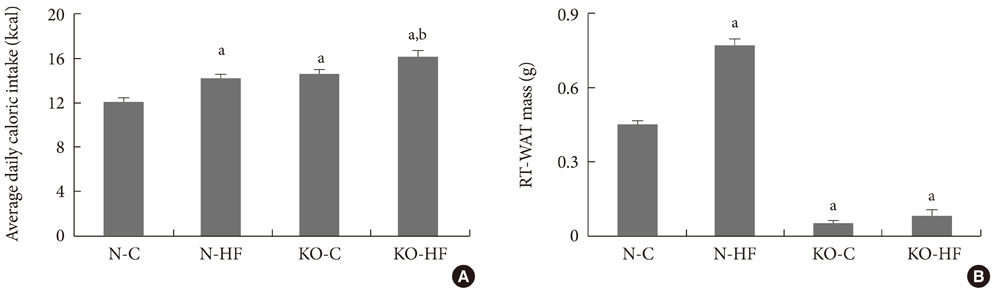
The hypothalamic neuropeptide Y (NPY) analyzed one hour after glucose injection was suppressed in C57BL/6 mice, but not in Kir6.2 KO mice, suggesting a blunted hypothalamic response to glucose in Kir6.2 KO mice. The hypothalamic NPY expression at a fed state was elevated in Kir6.2 KO mice and was accompanied with hyperphagia. However, the retroperitoneal fat mass was markedly decreased in Kir6.2 KO mice compared to that in C57BL/6 mice. Moreover, the body weight and visceral fat following eight weeks of high fat feeding in Kir6.2 KO mice were not significantly different from those in control diet-fed Kir6.2 KO mice, while body weight and visceral fat mass were elevated due to high fat feeding in C57BL/6 mice.
CONCLUSION
These results suggested that Kir6.2 KO mice showed a blunted hypothalamic response to glucose loading and elevated hypothalamic NPY expression accompanied with hyperphagia, while visceral fat mass was decreased, suggesting resistance to diet-induced obesity. Further study is needed to explain this phenomenon.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Wang Y, Beydoun MA. The obesity epidemic in the United States--gender, age, socioeconomic, racial/ethnic, and geographic characteristics: a systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Epidemiol Rev. 2007. 29:6–28.2. Schwartz MW, Woods SC, Porte D Jr, Seeley RJ, Baskin DG. Central nervous system control of food intake. Nature. 2000. 404:661–671.3. Flier JS. Obesity wars: molecular progress confronts an expanding epidemic. Cell. 2004. 116:337–350.4. Harrold JA. Hypothalamic control of energy balance. Curr Drug Targets. 2004. 5:207–219.5. Scarpace PJ, Matheny M, Tumer N. Hypothalamic leptin resistance is associated with impaired leptin signal transduction in aged obese rats. Neuroscience. 2001. 104:1111–1117.6. Obici S, Rossetti L. Minireview: nutrient sensing and the regulation of insulin action and energy balance. Endocrinology. 2003. 144:5172–5178.7. Levin BE, Routh VH, Kang L, Sanders NM, Dunn-Meynell AA. Neuronal glucosensing: what do we know after 50 years? Diabetes. 2004. 53:2521–2528.8. Burdakov D, Luckman SM, Verkhratsky A. Glucose-sensing neurons of the hypothalamus. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2005. 360:2227–2235.9. Schuit FC, Huypens P, Heimberg H, Pipeleers DG. Glucose sensing in pancreatic beta-cells: a model for the study of other glucose-regulated cells in gut, pancreas, and hypothalamus. Diabetes. 2001. 50:1–11.10. Miki T, Liss B, Minami K, Shiuchi T, Saraya A, Kashima Y, Horiuchi M, Ashcroft F, Minokoshi Y, Roeper J, Seino S. ATP-sensitive K+ channels in the hypothalamus are essential for the maintenance of glucose homeostasis. Nat Neurosci. 2001. 4:507–512.11. Minami K, Miki T, Kadowaki T, Seino S. Roles of ATP-sensitive K+ channels as metabolic sensors: studies of Kir6.x null mice. Diabetes. 2004. 53:Suppl 3. S176–S180.12. Parton LE, Ye CP, Coppari R, Enriori PJ, Choi B, Zhang CY, Xu C, Vianna CR, Balthasar N, Lee CE, Elmquist JK, Cowley MA, Lowell BB. Glucose sensing by POMC neurons regulates glucose homeostasis and is impaired in obesity. Nature. 2007. 449:228–232.13. Gyte A, Pritchard LE, Jones HB, Brennand JC, White A. Reduced expression of the KATP channel subunit, Kir6.2, is associated with decreased expression of neuropeptide Y and agouti-related protein in the hypothalami of Zucker diabetic fatty rats. J Neuroendocrinol. 2007. 19:941–951.14. Polakof S, Panserat S, Plagnes-Juan E, Soengas JL. Altered dietary carbohydrates significantly affect gene expression of the major glucosensing components in Brockmann bodies and hypothalamus of rainbow trout. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2008. 295:R1077–R1088.15. Jo YH, Su Y, Gutierrez-Juarez R, Chua S Jr. Oleic acid directly regulates POMC neuron excitability in the hypothalamus. J Neurophysiol. 2009. 101:2305–2316.16. Noma A. ATP-regulated K+ channels in cardiac muscle. Nature. 1983. 305:147–148.17. Cook DL, Hales CN. Intracellular ATP directly blocks K+ channels in pancreatic B-cells. Nature. 1984. 311:271–273.18. Ashcroft FM. Adenosine 5'-triphosphate-sensitive potassium channels. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1988. 11:97–118.19. Miki T, Nagashima K, Tashiro F, Kotake K, Yoshitomi H, Tamamoto A, Gonoi T, Iwanaga T, Miyazaki J, Seino S. Defective insulin secretion and enhanced insulin action in KATP channel-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998. 95:10402–10406.20. Plum L, Ma X, Hampel B, Balthasar N, Coppari R, Munzberg H, Shanabrough M, Burdakov D, Rother E, Janoschek R, Alber J, Belgardt BF, Koch L, Seibler J, Schwenk F, Fekete C, Suzuki A, Mak TW, Krone W, Horvath TL, Ashcroft FM, Bruning JC. Enhanced PIP3 signaling in POMC neurons causes KATP channel activation and leads to diet-sensitive obesity. J Clin Invest. 2006. 116:1886–1901.21. Fioramonti X, Contie S, Song Z, Routh VH, Lorsignol A, Penicaud L. Characterization of glucosensing neuron subpopulations in the arcuate nucleus: integration in neuropeptide Y and pro-opio melanocortin networks. Diabetes. 2007. 56:1219–1227.22. Mountjoy PD, Bailey SJ, Rutter GA. Inhibition by glucose or leptin of hypothalamic neurons expressing neuropeptide Y requires changes in AMP-activated protein kinase activity. Diabetologia. 2007. 50:168–177.23. Gonzalez JA, Reimann F, Burdakov D. Dissociation between sensing and metabolism of glucose in sugar sensing neurones. J Physiol. 2009. 587(Pt 1):41–48.24. Burdakov D, Gerasimenko O, Verkhratsky A. Physiological changes in glucose differentially modulate the excitability of hypothalamic melanin-concentrating hormone and orexin neurons in situ. J Neurosci. 2005. 25:2429–2433.25. Miki T, Minami K, Zhang L, Morita M, Gonoi T, Shiuchi T, Minokoshi Y, Renaud JM, Seino S. ATP-sensitive potassium channels participate in glucose uptake in skeletal muscle and adipose tissue. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2002. 283:E1178–E1184.26. Chutkow WA, Samuel V, Hansen PA, Pu J, Valdivia CR, Makielski JC, Burant CF. Disruption of Sur2-containing K(ATP) channels enhances insulin-stimulated glucose uptake in skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. 98:11760–11764.27. Alekseev AE, Reyes S, Yamada S, Hodgson-Zingman DM, Sattiraju S, Zhu Z, Sierra A, Gerbin M, Coetzee WA, Goldhamer DJ, Terzic A, Zingman LV. Sarcolemmal ATP-sensitive K(+) channels control energy expenditure determining body weight. Cell Metab. 2010. 11:58–69.28. Himms-Hagen J. Exercise in a pill: feasibility of energy expenditure targets. Curr Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord. 2004. 3:389–409.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Activation of the Cardiac ATP-Sensitive K+Channel by KR-30816,Newly Synthesized Potassium Channel Opener
- Effects of micron-Opioid Agonist on ATP-sensitive Potassium Channel Activity in Isolated Ventricular Cardiomyocytes
- Role of Plasmalogen-derived Lysolipids onthe Pathophysiology of Myocardial Ischemia
- Effects of Endothelium-derived Relaxing Factors on the Regulation of ATP-sensitive Potassium Channel Activity in Cardiac Myocytes
- Characteristics of Potassium Channel in the Isolated Rat Detrusor Muscle