Chonnam Med J.
2008 Dec;44(3):184-187. 10.4068/cmj.2008.44.3.184.
Steroid-refractory Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia Following Unrelated Allogeneic Peripheral Blood Stem Cell Transplantation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea.
- 2Genome Research Center for Hematopoietic Diseases, Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital, Hwasun, Korea. hjoonk@jnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2172300
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4068/cmj.2008.44.3.184
Abstract
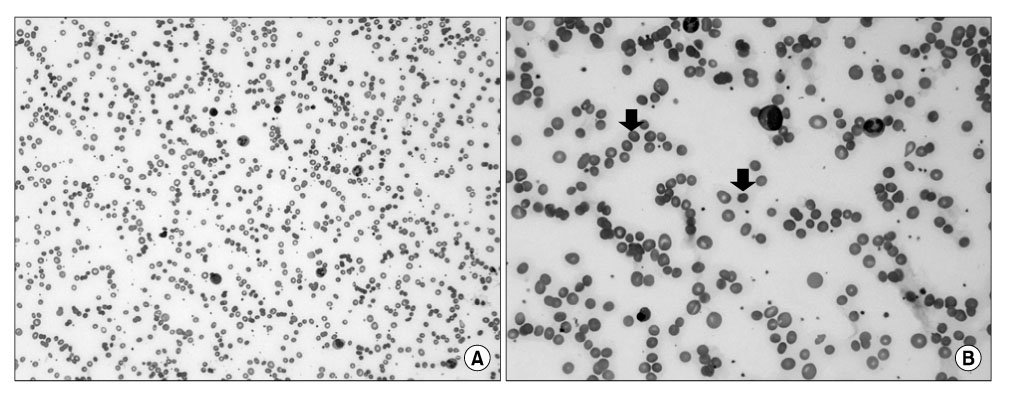
- A 29 years old female with chronic myelogenous leukemia underwent an unmanipulated, unrelated, HLA- matched peripheral blood stem cell transplantation (PBSCT) after imatinib mesylate treatment. The patient and donor had different ABO blood types and at 1 year later after PBSCT, the patient showed severe autoimmune hemolytic anemia (AIHA). She was treated with several immunosuppressive agents including high-dose steroid, cyclophosphamide, intravenous immunoglobulin and rituximab and underwent multiple sessions of plasma exchange. As her AIHA showed no response to these multiple therapies, she underwent splenic artery embolization and splenectomy. After then her AIHA was resolved with low dose oral steroid maintenance. Although the incidence of AIHA is known to be increased after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT), it has been rarely reported in Korea. Since AIHA in the setting of post-allogeneic HSCT is often difficult to treat and the prognosis is very poor, the accurate and early diagnosis is needed.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Anemia, Hemolytic, Autoimmune
Antibodies, Monoclonal, Murine-Derived
Benzamides
Cyclophosphamide
Early Diagnosis
Female
Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
Humans
Immunoglobulins
Immunosuppressive Agents
Incidence
Korea
Leukemia, Myelogenous, Chronic, BCR-ABL Positive
Mesylates
Peripheral Blood Stem Cell Transplantation
Piperazines
Plasma Exchange
Prognosis
Pyrimidines
Splenectomy
Splenic Artery
Tissue Donors
Imatinib Mesylate
Rituximab
Antibodies, Monoclonal, Murine-Derived
Benzamides
Cyclophosphamide
Immunoglobulins
Immunosuppressive Agents
Mesylates
Piperazines
Pyrimidines
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sanz J, Arriaga F, Montesinos P, Ortí G, Lorenzo I, Cantero S, et al. Autoimmune hemolytic anemia following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in adult patients. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2007. 39:555–561.
Article2. Hongeng S, Tardtong P, Worapongpaiboon S, Ungkanont A, Jootar S. Successful treatment of refractory autoimmune haemolytic anaemia in a post-unrelated bone marrow transplant paediatric patient with rituximab. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2002. 29:871–872.
Article3. Chae H, Kim Y, Kim M, Lim J, Han K, Cho SG, et al. A case of autoimmune hemolytic anemia complicating hematopoietic cell transplantation. Korean J Lab Med. 2008. 28:64–69.
Article4. Drobyski WR, Potluri J, Sauer D, Gottschall JL. Autoimmune hemolytic anemia following T cell-depleted allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1996. 17:1093–1099.5. Sevilla J, González-Vicent M, Madero L, Díaz MA. Acute autoimmune hemolytic anemia following unrelated cord blood transplantation as an early manifestation of chronic graft-versus-host disease. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2001. 28:89–92.
Article6. Baek JH, Sohn SK, Ahn BM, Moon JH, Jeon SB, Sung WJ, et al. Uncommon hematologic manifestations of GVHD after allogeneic stem cell transplantation: two cases with hypereosinophilia or autoimmune hemolytic anemia. Korean J Hemato Stem Cell Trans. 2004. 9:34–37.7. Park HK, Oh SH, Choi KM, Lee HK, Kim DW. Cold agglutinin disease due to Anti-Pr cold antibody in a patient with bone marrow transplantation. Korean J Blood Transfus. 2003. 14:229–233.8. Chen FE, Owen I, Savage D, Roberts I, Apperley J, Goldman JM, et al. Late onset haemolysis and red cell autoimmunisation after allogeneic bone marrow transplant. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1997. 19:491–495.
Article9. O'Brien TA, Eastlund T, Peters C, Neglia JP, Defor T, Ramsay NK, et al. Autoimmune haemolytic anaemia complicating haematopoietic cell transplantation in paediatric patients: high incidence and significant mortality in unrelated donor transplants for non-malignant diseases. Br J Haematol. 2004. 127:67–75.10. Lee JH, Lee KS. A case of autoimmune hemolytic anemia treated with rituximab in a child. Korean J Hematol. 2006. 41:321–325.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Successful Treatment of Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia with Sirolimus after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: A Case Report
- A Case of Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia Complicating Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation
- Two Cases of Generalized Vitiligo after Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation
- A Case of Scleroderma following Autologous Peripheral Stem Cell Transplantation
- Mycophenolate Mofetil for Treatment of Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia and Nephrotic Syndrome after Cord Blood Transplantation