Chonnam Med J.
2011 Dec;47(3):144-149. 10.4068/cmj.2011.47.3.144.
Time Point Expression of Apoptosis Regulatory Proteins in a Photochemically-Induced Focal Cerebral Ischemic Rat Brain
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Forensic Medicine, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea.
- 2Department of Neurology, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea.
- 3Department of Neurosurgery, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea.
- 4Department of Pathology, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea. mclee@jnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2172222
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4068/cmj.2011.47.3.144
Abstract
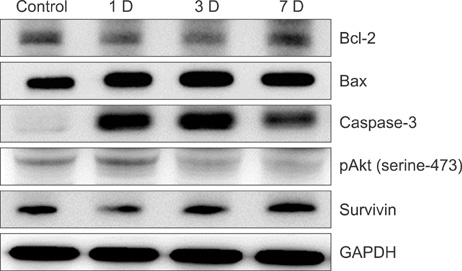
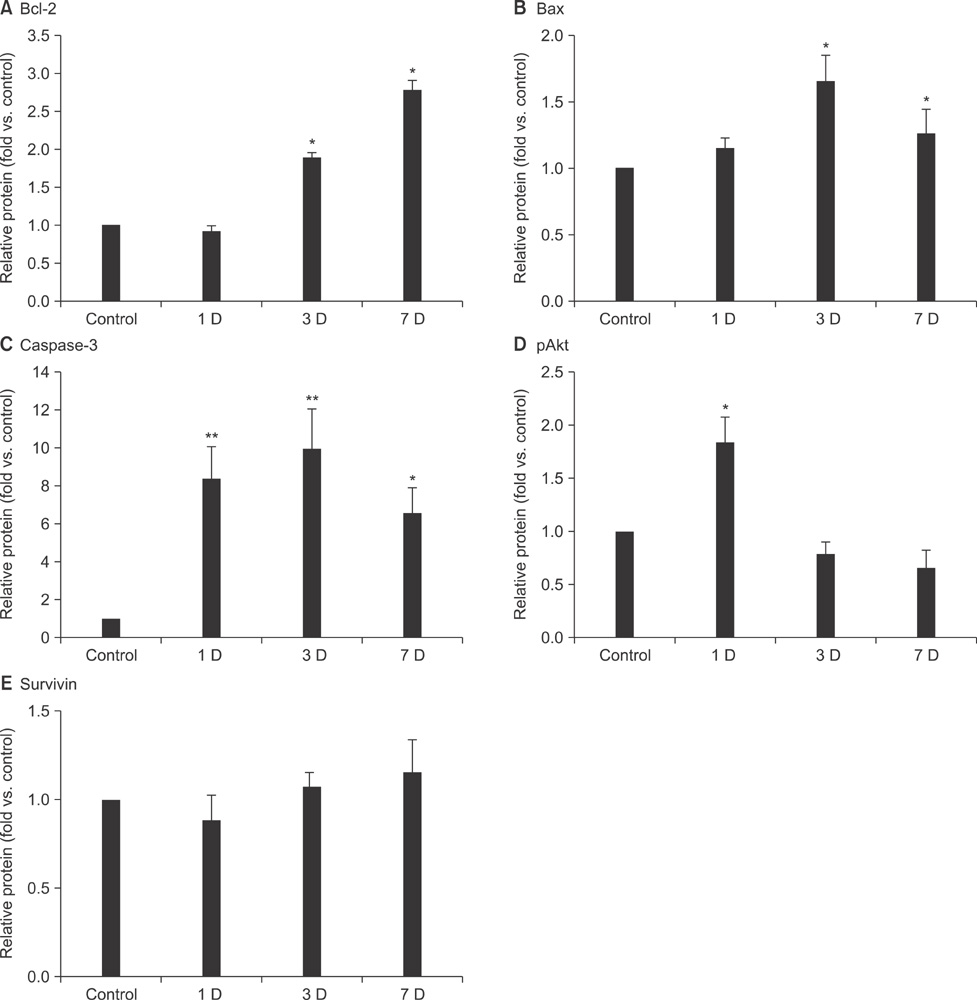
- Apoptosis after global or focal cerebral ischemia plays a crucial role in mediating cell death. In this study, we observed the time point expression of physiologic events involving apoptosis regulatory proteins after photochemically-induced focal cerebral ischemia in Sprague-Dawley rats. Protein expression was evaluated at days 1, 3, and 7 by Western blot. Bcl-2, Bax, caspase-3, and phosphorylated Akt (pAkt) activity markedly increased in the ischemic hemisphere in a time-dependent manner, not affected. The expression of Bcl-2, Bax, and caspase-3 was dramatically changed around day 3, whereas changes in pAkt expression occurred at day 1. Differential elevation of these apoptosis regulatory proteins at various time points indicates that different modes of cell death occur in photochemically-induced focal cerebral ischemia in a rat brain.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
An Experimental Infarct Targeting the Internal Capsule: Histopathological and Ultrastructural Changes
Chang-Woo Han, Kyung-Hwa Lee, Myung Giun Noh, Jin-Myung Kim, Hyung-Seok Kim, Hyung-Sun Kim, Ra Gyung Kim, Jongwook Cho, Hyoung-Ihl Kim, Min-Cheol Lee
J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(3):292-305. doi: 10.4132/jptm.2017.02.17.
Reference
-
1. Ferrer I. Apoptosis: future targets for neuroprotective strategies. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2006. 21:Suppl 2. 9–20.
Article2. Belayev L, Alonso OF, Busto R, Zhao W, Ginsberg MD. Middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat by intraluminal suture. Neurological and pathological evaluation of an improved model. Stroke. 1996. 27:1616–1622.
Article3. Watson BD, Dietrich WD, Busto R, Wachtel MS, Ginsberg MD. Induction of reproducible brain infarction by photochemically initiated thrombosis. Ann Neurol. 1985. 17:497–504.
Article4. Feng R, Li S, Li F. Toll-like receptor 4 is involved in ischemic tolerance of postconditioning in hippocampus of tree shrews to thrombotic cerebral ischemia. Brain Res. 2011. 1384:118–127.
Article5. Nakka VP, Gusain A, Mehta SL, Raghubir R. Molecular mechanisms of apoptosis in cerebral ischemia: multiple neuroprotective opportunities. Mol Neurobiol. 2008. 37:7–38.
Article6. Traystman RJ. Animal models of focal and global cerebral ischemia. ILAR J. 2003. 44:85–95.
Article7. Ginsberg MD. Adventures in the pathophysiology of brain ischemia: penumbra, gene expression, neuroprotection: the 2002 Thomas Willis Lecture. Stroke. 2003. 34:214–223.
Article8. Ferrer I, Friguls B, Dalfó E, Justicia C, Planas AM. Caspase-dependent and caspase-independent signalling of apoptosis in the penumbra following middle cerebral artery occlusion in the adult rat. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2003. 29:472–481.
Article9. Hakim AM. Ischemic penumbra: the therapeutic window. Neurology. 1998. 51:3 Suppl 3. S44–S46.
Article10. Wei Y, Yemisci M, Kim HH, Yung LM, Shin HK, Hwang SK, et al. Fingolimod provides long-term protection in rodent models of cerebral ischemia. Ann Neurol. 2011. 69:119–129.
Article11. Wang Q, Li X, Chen Y, Wang F, Yang Q, Chen S, et al. Activation of epsilon protein kinase C-mediated anti-apoptosis is involved in rapid tolerance induced by electroacupuncture pretreatment through cannabinoid receptor type 1. Stroke. 2011. 42:389–396.
Article12. Okazaki T, Magaki T, Takeda M, Kajiwara Y, Hanaya R, Sugiyama K, et al. Intravenous administration of bone marrow stromal cells increases survivin and Bcl-2 protein expression and improves sensorimotor function following ischemia in rats. Neurosci Lett. 2008. 430:109–114.
Article13. Hu X, Wester P, Brännström T, Watson BD, Gu W. Progressive and reproducible focal cortical ischemia with or without late spontaneous reperfusion generated by a ring-shaped, laser-driven photothrombotic lesion in rats. Brain Res Brain Res Protoc. 2001. 7:76–85.
Article14. Eichenbaum JW, Pevsner PH, Pivawer G, Kleinman GM, Chiriboga L, Stern A, et al. A murine photochemical stroke model with histologic correlates of apoptotic and nonapoptotic mechanisms. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 2002. 47:67–71.
Article15. Isenmann S, Stoll G, Schroeter M, Krajewski S, Reed JC, Bähr M. Differential regulation of Bax, Bcl-2, and Bcl-X proteins in focal cortical ischemia in the rat. Brain Pathol. 1998. 8:49–62.
Article16. Nishioka T, Nakase H, Nakamura M, Konishi N, Sakaki T. Sequential and spatial profiles of apoptosis in ischemic penumbra after two-vein occlusion in rats. J Neurosurg. 2006. 104:938–944.
Article17. Lee JK, Kwak HJ, Piao MS, Jang JW, Kim SH, Kim HS. Quercetin reduces the elevated matrix metalloproteinases-9 level and improves functional outcome after cerebral focal ischemia in rats. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2011. 153:1321–1329.
Article18. Broughton BR, Reutens DC, Sobey CG. Apoptotic mechanisms after cerebral ischemia. Stroke. 2009. 40:e331–e339.
Article19. Pevsner PH, Eichenbaum JW, Miller DC, Pivawer G, Eichenbaum KD, Stern A, et al. A photothrombotic model of small early ischemic infarcts in the rat brain with histologic and MRI correlation. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 2001. 45:227–233.
Article20. Xing B, Chen H, Zhang M, Zhao D, Jiang R, Liu X, et al. Ischemic postconditioning inhibits apoptosis after focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in the rat. Stroke. 2008. 39:2362–2369.
Article21. Okuno S, Saito A, Hayashi T, Chan PH. The c-Jun N-terminal protein kinase signaling pathway mediates Bax activation and subsequent neuronal apoptosis through interaction with Bim after transient focal cerebral ischemia. J Neurosci. 2004. 24:7879–7887.
Article22. Wu C, Fujihara H, Yao J, Qi S, Li H, Shimoji K, et al. Different expression patterns of Bcl-2, Bcl-xl, and Bax proteins after sublethal forebrain ischemia in C57Black/Crj6 mouse striatum. Stroke. 2003. 34:1803–1808.
Article23. Panayiotidis MI, Bortner CD, Cidlowski JA. On the mechanism of ionic regulation of apoptosis: would the Na+/K+-ATPase please stand up? Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2006. 187:205–215.
Article24. Chaitanya GV, Babu PP. Activation of calpain, cathepsin-b and caspase-3 during transient focal cerebral ischemia in rat model. Neurochem Res. 2008. 33:2178–2186.
Article25. Le DA, Wu Y, Huang Z, Matsushita K, Plesnila N, Augustinack JC, et al. Caspase activation and neuroprotection in caspase-3-deficient mice after in vivo cerebral ischemia and in vitro oxygen glucose deprivation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. 99:15188–15193.
Article26. Noshita N, Lewén A, Sugawara T, Chan PH. Akt phosphorylation and neuronal survival after traumatic brain injury in mice. Neurobiol Dis. 2002. 9:294–304.
Article27. Dietrich WD, Busto R, Watson BD, Scheinberg P, Ginsberg MD. Photochemically induced cerebral infarction. II. Edema and blood-brain barrier disruption. Acta Neuropathol. 1987. 72:326–334.28. Lee MC, Jin CY, Kim HS, Kim JH, Kim MK, Kim HI, et al. Stem cell dynamics in an experimental model of stroke. Chonnam Med J. 2011. 47:90–98.
Article29. Conway EM, Zwerts F, Van Eygen V, DeVriese A, Nagai N, Luo W, et al. urvivin-dependent angiogenesis in ischemic brain: molecular mechanisms of hypoxia-induced up-regulation. Am J Pathol. 2003. 163:935–946.30. Zhang Y, Park TS, Gidday JM. Hypoxic preconditioning protects human brain endothelium from ischemic apoptosis by Akt-dependent survivin activation. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007. 292:H2573–H2581.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Changes in Gene Expression in the Rat Hippocampus after Focal Cerebral Ischemia
- Ischemic postconditioning may not influence early brain injury induced by focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion in rats
- Upregulation of miR-20b Protects Against Cerebral Ischemic Stroke by Targeting Thioredoxin Interacting Protein (TXNIP)
- The effects of gabapentin pretreatment on brain injury induced by focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion in the rat
- Changes in Expression of BCL-2, BAX and ICE mRNA After Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion in Rat