Infect Chemother.
2011 Feb;43(1):36-41. 10.3947/ic.2011.43.1.36.
The Association of Lymphopenia with the Clinical Severity in the Korean Children Admitted to the Hospital with Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 Infection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Yonsei University, Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea. khm9120@yonsei.ac.kr
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Yonsei University, Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University, Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea.
- 4Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Yonsei University, Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea.
- KMID: 2170331
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2011.43.1.36
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Critical illness due to pandemic (H1N1) 2009 is an emerging threat to global health. In this study, lymphopenia was focused on as a major risk factor for a critical clinical course of pandemic (H1N1) 2009 infection. We investigated the association of lymphopenia at the time of admission with the clinical severity of the admitted children with pandemic (H1N1) 2009 infection. Material and Methods: We performed a retrospective study on the patients who were younger than 15 years of age and who were admitted to Wonju Christian Hospital due to pandemic (H1N1) 2009 infection between August 20, 2009 and February 20, 2010. Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 infection was confirmed by reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) in all patients. We divided the study period into two periods as August 20 - November 30 2009 (pre-vaccination period) and December 1 2009 - February 20 2010 (post-vaccination period). The clinical differences between two periods were analyzed. To define the role of lymphopenia, we examined the differences of clinical manifestations between the H1N1 patients with lymphopenia and those without lymphopenia.
RESULTS
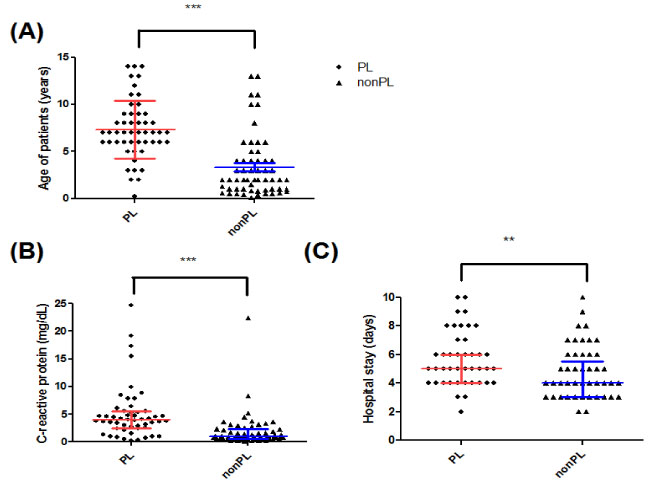
Among the 2,399 children who had H1N1 infection, 149 patients (6.2%) were admitted under the following diagnoses: pneumonia (67.1%), bronchiolitis/asthma (18.8%), croup (6%) and febrile convulsion (8.7%). The median age of the patients was significantly different between during the pre-vaccination period and the post-vaccination period (6 years of age [range: 0.25-14] vs. 3 years of age, [range: 0.1-14], P<0.05). The proportion of patients who had lymphopenia was significantly different between two periods (39.5% vs. 20%, P<0.05). When we compared the clinical severity between the patients with lymphopenia and those without lymphopenia, age (P<0.0001), the length of hospital stay (P<0.0001) and the serum levels of C-reactive protein (P<0.01) were significantly different.
CONCLUSION
Our data support that lymphopenia may be a major determining factor that could cause a critical clinical course during pandemic period among children in the Republic of Korea.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
The Influence of Atopic Findings on Severity of Pneumonia in Children with 2009 Pandemic Influenza A (H1N1) Infection
Jong Hee Kim, Hyun Jeong Kim, Im Ju Kang
Korean J Pediatr Infect Dis. 2011;18(2):182-192. doi: 10.14776/kjpid.2011.18.2.182.
Reference
-
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Update: infections with a swine-origin influenza A (H1N1) virus--United States and other countries, April 28, 2009. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2009. 58:431–433.2. Flahault A, Vergu E, Boëlle PY. Potential for a global dynamic of Influenza A (H1N1). BMC Infect Dis. 2009. 9:129.
Article3. Miller E, Hoschler K, Hardelid P, Stanford E, Andrews N, Zambon M. Incidence of 2009 pandemic influenza A H1N1 infection in England: a cross-sectional serological study. Lancet. 2010. 375:1100–1108.
Article4. Choi WS, Kim WJ, Cheong HJ. The evaluation of policies on 2009 influenza pandemic in Korea. J Prev Med Public Health. 2010. 43:105–108.
Article5. Oh CE, Lee J, Kang JH, Hong YJ, Kim YK, Cheong HJ, Ahn YJ, Kim SH, Lee HJ. Safety and immunogenicity of an inactivated split-virus influenza A/H1N1 vaccine in healthy children from 6 months to <18 years of age: a prospective, open-label, multicenter trial. Vaccine. 2010. 28:5857–5863.
Article6. Cunha BA, Pherez FM, Schoch P. Diagnostic importance of relative lymphopenia as a marker of swine influenza (H1N1) in adults. Clin Infect Dis. 2009. 49:1454–1456.
Article7. Perez-Padilla R, de la Rosa-Zamboni D, Ponce de Leon S, Hernandez M, Quiñones-Falconi F, Bautista E, Ramirez-Venegas A, Rojas-Serrano J, Ormsby CE, Corrales A, Higuera A, Mondragon E, Cordova-Villalobos JA. INER Working Group on Influenza. Pneumonia and respiratory failure from swine-origin influenza A (H1N1) in Mexico. N Engl J Med. 2009. 361:680–689.
Article8. Coskun O, Avci IY, Sener K, Yaman H, Ogur R, Bodur H, Eyigün CP. Relative lymphopenia and monocytosis may be considered as a surrogate marker of pandemic influenza a (H1N1). J Clin Virol. 2010. 47:388–389.
Article9. Cui W, Zhao H, Lu X, Wen Y, Zhou Y, Deng B, Wang Y, Wang W, Kang J, Liu P. Factors associated with death in hospitalized pneumonia patients with 2009 H1N1 influenza in Shenyang, China. BMC Infect Dis. 2010. 10:145.
Article10. Cunha BA, Syed U, Mickail N, Strollo S. Rapid clinical diagnosis in fatal swine influenza (H1N1) pneumonia in an adult with negative rapid influenza diagnostic tests (RIDTs): diagnostic swine influenza triad. Heart Lung. 2010. 39:78–86.
Article11. Sun K, Metzger DW. Inhibition of pulmonary antibacterial defense by interferon-gamma during recovery from influenza infection. Nat Med. 2008. 14:558–564.
Article12. Lee DH, Shin SS, Jun BY, Lee JK. National level response to pandemic (H1N1) 2009. J Prev Med Public Health. 2010. 43:99–104.
Article13. Kim YK, Kim HY, Uh Y, Chun JK. Detection rate of rapid antigen test for Pandemic Influenza A (H1N1 2009). Infect Chemother. 2010. 42:95–98.
Article14. Sectish TC, Prober CG. Kliegman RM, Behrman RE, Jenson HB, Stanton BF, editors. Pneumonia. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 2007. 18th ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders;1795–1799.15. Choi WJ, Kim WY, Kim SH, Oh BJ, Kim W, Lim KS, Hong SB, Lim CM, Koh Y. Clinical characteristics of pneumonia in hospitalized patients with novel influenza A (H1N1) in Korea. Scand J Infect Dis. 2010. 42:311–314.
Article16. Cunha BA. Swine Influenza (H1N1) pneumonia: clinical considerations. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2010. 24:203–228.
Article17. Castillo A, Sola A, Baquero H, Neira F, Alvis R, Deulofeut R, Critz A. Pulse oxygen saturation levels and arterial oxygen tension values in newborns receiving oxygen therapy in the neonatal intensive care unit: is 85% to 93% an acceptable range? Pediatrics. 2008. 121:882–889.
Article18. Chien YS, Su CP, Tsai HT, Huang AS, Lien CE, Hung MN, Chuang JH, Kuo HS, Chang SC. Predictors and outcomes of respiratory failure among hospitalized pneumonia patients with 2009 H1N1 influenza in Taiwan. J Infect. 2010. 60:168–174.
Article19. Refaeli Y, Van Parijs L, Alexander SI, Abbas AK. Interferon gamma is required for activation-induced death of T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 2002. 196:999–1005.20. Zhang Y, Wang Y, Gilmore X, Xu K, Chen M, Tebebi P, Mbawuike IN. Apoptosis and reduced influenza A virus specific CD8+ T cells in aging mice. Cell Death Differ. 2002. 9:651–660.
Article21. Okada H, Kobune F, Sato TA, Kohama T, Takeuchi Y, Abe T, Takayama N, Tsuchiya T, Tashiro M. Extensive lymphopenia due to apoptosis of uninfected lymphocytes in acute measles patients. Arch Virol. 2000. 145:905–920.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Influence of Atopic Findings on Severity of Pneumonia in Children with 2009 Pandemic Influenza A (H1N1) Infection
- Clinical and Laboratory Characteristics of Pandemic Influenza A/H1N1 2009 Infection among Patients with Malignancy in Korea
- Epidemiology, clinical manifestations, and management of pandemic novel Influenza A (H1N1)
- Characteristics of Hospitalized Children with 2009 Pandemic Influenza A (H1N1): A Multicenter Study in Korea
- Clinical Characteristic of Respiratory Tract Infections in Children during Pandemic Influenza (H1N1 2009) in Korea