Characteristics of Hospitalized Children with 2009 Pandemic Influenza A (H1N1): A Multicenter Study in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Hanyang University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. sungheeo@hanyang.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Green Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pediatrics, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Pediatrics, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Incheon, Korea.
- 5Department of Pediatrics, College of Medicine, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Department of Pediatrics, Jeju National University School of Medicine, Jeju, Korea.
- KMID: 2157902
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2012.27.4.408
Abstract
- The majority of Korean patients with pandemic influenza A (H1N1) during the 2009 epidemic were under 20 yr of age. The limited data on the clinical characteristics of these children led us to conduct a case note-based investigation of children admitted to 6 university hospitals with 2009 H1N1 influenza. A total of 804 children was enrolled. The median age was 5 yr; 63.8% were males; and 22.4% had at least one chronic underlying disease. Ninety-five of the patients (11.8%) were critically ill and they suffered more from shortness of breath, dyspnea and lymphopenia than the other patients. Among all the patients, 98.8% were treated with antivirals and 73% received treatment within 48 hr of illness onset. All the enrolled patients are alive and appear to have had good outcomes, probably due to the early intervention and antiviral treatment. This study deals with hospitalized children whose diagnoses of influenza A (H1N1) were confirmed, and therefore provides important new information about the clinical patterns of children with influenza A (H1N1) in Korea.
MeSH Terms
-
Adolescent
Antiviral Agents/therapeutic use
Child
Child, Hospitalized
Child, Preschool
Critical Illness
Dyspnea/etiology
Female
Humans
Infant
Infant, Newborn
Influenza A Virus, H1N1 Subtype/genetics/*isolation & purification
Influenza, Human/*diagnosis/drug therapy/epidemiology
Lymphopenia/etiology
Male
Oseltamivir/therapeutic use
Pandemics
Republic of Korea/epidemiology
Retrospective Studies
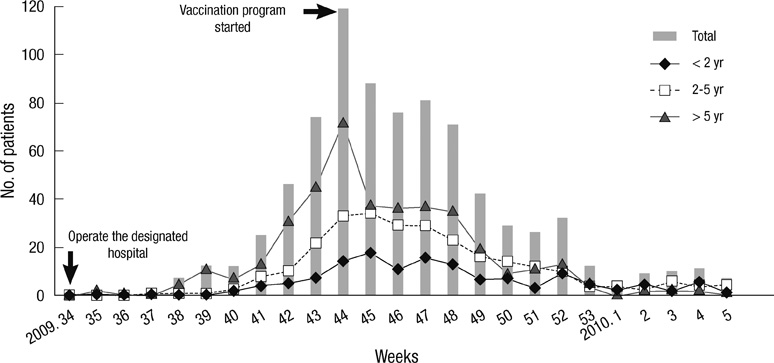
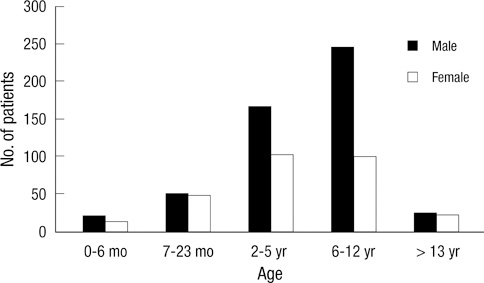
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
The Determinant of the Severity Who was Hospitalized with Asthma-like Symptoms in Influenza A (H1N1) Season
Yoon Ha Hwang, Sang Yun Choi, Sung Won Kim
Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2012;22(2):147-153. doi: 10.7581/pard.2012.22.2.147.The Comparison of Clinical Characteristics and Courses of Pediatric Patients Hospitalized with Pandemic Influenza A (H1N1) and Seasonal Influenza from 2009 to 2011
Song I Yang, Jung Hee Rho, Yong Han Sun, Kang Ho Cho, So Yeon Shim, Byung Wook Eun, Jee Eun Kim, Dong Woo Son, Hann Tchah
Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2012;22(3):292-301. doi: 10.7581/pard.2012.22.3.292.Incidence and Epidemiological Characteristics of 2009 Pandemic Influenza A (H1N1) Among School-Based Populations in Korea
Hyun Jung Kim, Byung Chul Chun, Hoo Jae Hann, Jang Wook Sohn, Sae Yoon Kee, Si Hyun Kim, Myoung Youn Jo, Kyung Young Lee, Seok Hyeon Lee, Min Ja Kim, Hyeong Sik Ahn
Infect Chemother. 2012;44(6):431-438. doi: 10.3947/ic.2012.44.6.431.
Reference
-
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Hospitalized patients with novel influenza A (H1N1) virus infection: California, April-May, 2009. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2009. 58:536–541.2. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Analysis of reported pandemic influenza (A/H1N1 2009) virus infections in Korea: From April, 2009 through August, 2010. Public Health Wkly Rep. 2010. 3:638–642.3. Bettinger JA, Sauvé LJ, Scheifele DW, Moore D, Vaudry W, Tran D, Halperin SA, Pelletier L. Pandemic influenza in Canadian children: a summary of hospitalized pediatric cases. Vaccine. 2010. 28:3180–3184.4. Calitri C, Gabiano C, Garazzino S, Pinon M, Zoppo M, Cuozzo M, Scolfaro C, Tovo PA. Clinical features of hospitalised children with 2009 H1N1 influenza virus infection. Eur J Pediatr. 2010. 169:1511–1515.5. O'Riordan S, Barton M, Yau Y, Read SE, Allen U, Tran D. Risk factors and outcomes among children admitted to hospital with pandemic H1N1 influenza. CMAJ. 2009. 182:39–44.6. Stein M, Tasher D, Glikman D, Shachor-Meyouhas Y, Barkai G, Yochai AB, Leibovitz E, Hausman-Kedem M, Hess A, Megged O, Kassis I, Gresario G, Somekh E. Hospitalization of children with influenza A (H1N1) virus in Israel during the 2009 outbreak in Israel: a multicenter survey. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2010. 164:1015–1022.7. Parakh A, Kumar A, Kumar V, Dutta AK, Khare S. Pediatric hospitalizations associated with 2009 pandemic influenza A (H1N1): an experience from a tertiary care center in north India. Indian J Pediatr. 2010. 77:981–985.8. Louie JK, Gavali S, Acosta M, Samuel MC, Winter K, Jean C, Glaser CA, Matyas BT, Schechter R. California Pandemic (H1N1) Working Group. Children hospitalized with 2009 novel influenza A (H1N1) in California. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2010. 164:1023–1031.9. Miroballi Y, Baird JS, Zackai S, Cannon JM, Messina M, Ravindranath T, Green R, Della-Latta P, Jenkins S, Greenwald BM, Fyruya EY, Graham PL 3rd, Sonnett FM, Platt S, Delamora P, Saiman L. Novel influenza A (H1N1) in a pediatric health care facility in New York City during the first wave of the 2009 pandemic. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2010. 164:24–30.10. Libster R, Bugna J, Coviello S, Hijano DR, Dunaiewsky M, Reynoso N, Cavalieri ML, Guglielmo MC, Areso MS, Gilligan T, Santucho F, Cabral G, Gregorio GL, Moreno R, Lutz MI, Panigasi AL, Saligari L, Caballero MT, Egues Almeida RM, Gutierrez Meyer ME, Neder MD, Davenport MC, Del Valle MP, Santidrian VS, Mosca G, Garcia Dominguez M, Alvarez L, Landa P, Pota A, Bolonati N, Dalamon R, Sanchez Mercol VI, Espinoza M, Peuchot JC, Karolinski A, Bruno M, Borsa A, Ferrero F, Bonina A, Ramonet M, Albano LC, Luedicke N, Alterman E, Savy V, Baumeister E, Chappell JD, Edwards KM, Melendi GA, Polack FP. Pediatric hospitalizations associated with 2009 pandemic influenza A (H1N1) in Argentina. N Engl J Med. 2009. 362:45–55.11. Updated CDC Estimates of 2009 H1N1 Cases and Related Hospitalizations and Deaths from April 2009 - April 10, 2010. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. accessed on 25 October 2011. Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/h1n1flu/estimates_2009_h1n1.htm.12. Noh JY, Yim SY, Heo JY, Choi WS, Song JY, Cheong HJ, Kim WJ. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of pandemic influenza (H1N1 2009). Infect Chemother. 2010. 42:69–75.13. Park SI, Kim MJ, Hwang HY, Oh CE, Lee JH, Park JS. Clinical characteristics of children with 2009 pandemic influenza A (H1N1) admitted in a single institution. Korean J Pediatr. 2010. 53:886–891.14. Chun JK, Cha BH, Uh Y, Kim HY, Kim YK, Kwon WC, Kim HM. The association of lymphopenia with the clinical severity in the Korean children admitted to the hospital with pandemic (H1N1) 2009 infection. Infect Chemother. 2011. 43:36–41.15. Moon JS, Lee SY, Nam CM, Choi JM, Choe BK, Seo JW, Oh K, Jang MJ, Hwang SS, Yoo MH, Kim YT, Lee CG. 2007 Korean National Growth Charts: review of developmental process and an outlook. Korean J Pediatr. 2008. 51:1–25.16. Stanley FL. Kliegman RM, Stanton BF, St. Geme JW, Schor NF, Behrman RE, editors. Reference intervals for laboratory tests and children. Nelson textbook of pediatrics. 2011. 19th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders;2466.17. Donaldson LJ, Rutter PD, Ellis BM, Greaves FE, Mytton OT, Pebody RG, Yardley IE. Mortality from pandemic A/H1N1 2009 influenza in England: Public Health Surveillance Study. BMJ. 2009. 339:b5213.18. Sugaya N, Shinjoh M, Mitamura K, Takahashi T. Very low pandemic influenza A (H1N1) 2009 mortality associated with early neuraminidase inhibitor treatment in Japan: Analysis of 1000 hospitalized children. J Infect. 2011. 63:288–294.19. Lee DH, Shin SS, Jun BY, Lee JK. National level response to pandemic (H1N1) 2009. J Prev Med Public Health. 2010. 43:99–104.20. Kim HS, Kim JH, Shin SY, Kang YA, Lee HG, Kim JS, Lee JK, Cho B. Fatal cases of 2009 pandemic influenza A (H1N1) in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2011. 26:22–27.21. Yoo SJ, Moon SJ, Kuak EY, Yoo HM, Kim CK, Chey MJ, Shin BM. Frequent detection of pandemic (H1N1) 2009 virus in stools of hospitalized patients. J Clin Microbiol. 2010. 48:2314–2315.22. To KK, Chan KH, Li IW, Tsang TY, Tse H, Chan JF, Hung IF, Lai ST, Leung CW, Kwan YW, Lau YL, Ng TK, Cheng VC, Peiris JS, Yuen KY. Viral load in patients infected with pandemic H1N1 2009 influenza A virus. J Med Virol. 2010. 82:1–7.23. Bagdure D, Curtis DJ, Dobyns E, Glodé MP, Dominguez SR. Hospitalized children with 2009 pandemic influenza A (H1N1): comparison to seasonal influenza and risk factors for admission to the ICU. PLoS One. 2010. 5:e15173.24. Jain S, Kamimoto L, Bramley AM, Schmitz AM, Benoit SR, Louie J, Sugerman DE, Druckenmiller JK, Ritger KA, Chugh R, Jasuja S, Deutscher M, Chen S, Walker JD, Duchin JS, Lett S, Soliva S, Wells EV, Swerdlow D, Uyeki TM, Fiore AE, Olsen SJ, Fry AM, Bridges CB, Finelli L. Hospitalized patients with 2009 H1N1 influenza in the United States, April-June 2009. N Engl J Med. 2009. 361:1935–1944.25. Nichols JE, Niles JA, Roberts NJ Jr. Human lymphocyte apoptosis after exposure to influenza A virus. J Virol. 2001. 75:5921–5929.26. Zhang Y, Wang Y, Gilmore X, Xu K, Chen M, Tebebi P, Mbawuike IN. Apoptosis and reduced influenza A virus specific CD8+ T cells in aging mice. Cell Death Differ. 2002. 9:651–660.27. Libster R, Coviello S, Cavalieri ML, Morosi A, Alabart N, Alvarez L, Ferrero F, Edwards KM, Polack FP. Pediatric hospitalizations due to influenza in 2010 in Argentina. N Engl J Med. 2010. 363:2472–2473.28. Giesecke J. Experiences of giving oseltamivir to school children during the 2009 influenza A (H1N1) pandemic. Euro Surveill. 2010. 15:19570.29. Strong M, Burrows J, Stedman E, Redgrave P. Adverse drug effects following oseltamivir mass treatment and prophylaxis in a school outbreak of 2009 pandemic influenza A (H1N1) in June 2009, Sheffield, United Kingdom. Euro Surveill. 2010. 15:19565.30. Wallensten A, Oliver I, Lewis D, Harrison S. Compliance and side effects of prophylactic oseltamivir treatment in a school in South West England. Euro Surveill. 2009. 14:19285.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Epidemiology, clinical manifestations, and management of pandemic novel Influenza A (H1N1)
- Clinical Characteristic of Respiratory Tract Infections in Children during Pandemic Influenza (H1N1 2009) in Korea
- Clinical and Laboratory Characteristics of Pandemic Influenza A/H1N1 2009 Infection among Patients with Malignancy in Korea
- The 2009 H1N1 Pandemic Influenza in Korea
- Clinical characteristics and outcomes among pediatric patients hospitalized with pandemic influenza A/H1N1 2009 infection