Endocrinol Metab.
2014 Jun;29(2):185-194. 10.3803/EnM.2014.29.2.185.
A Novel Cytosolic Isoform of Mitochondrial Trans-2-Enoyl-CoA Reductase Enhances Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor alpha Activity
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physiology, Institute of Health Science, Medical Research Center for Neural Dysfunction, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Jinju, Korea. jaeyong@gnu.ac.kr
- 2Center for Functional Connectomics, Korea Institute of Science and Technology, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Marine Life Science, Chosun University College of Natural Sciences, Gwangju, Korea.
- KMID: 2169426
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2014.29.2.185
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
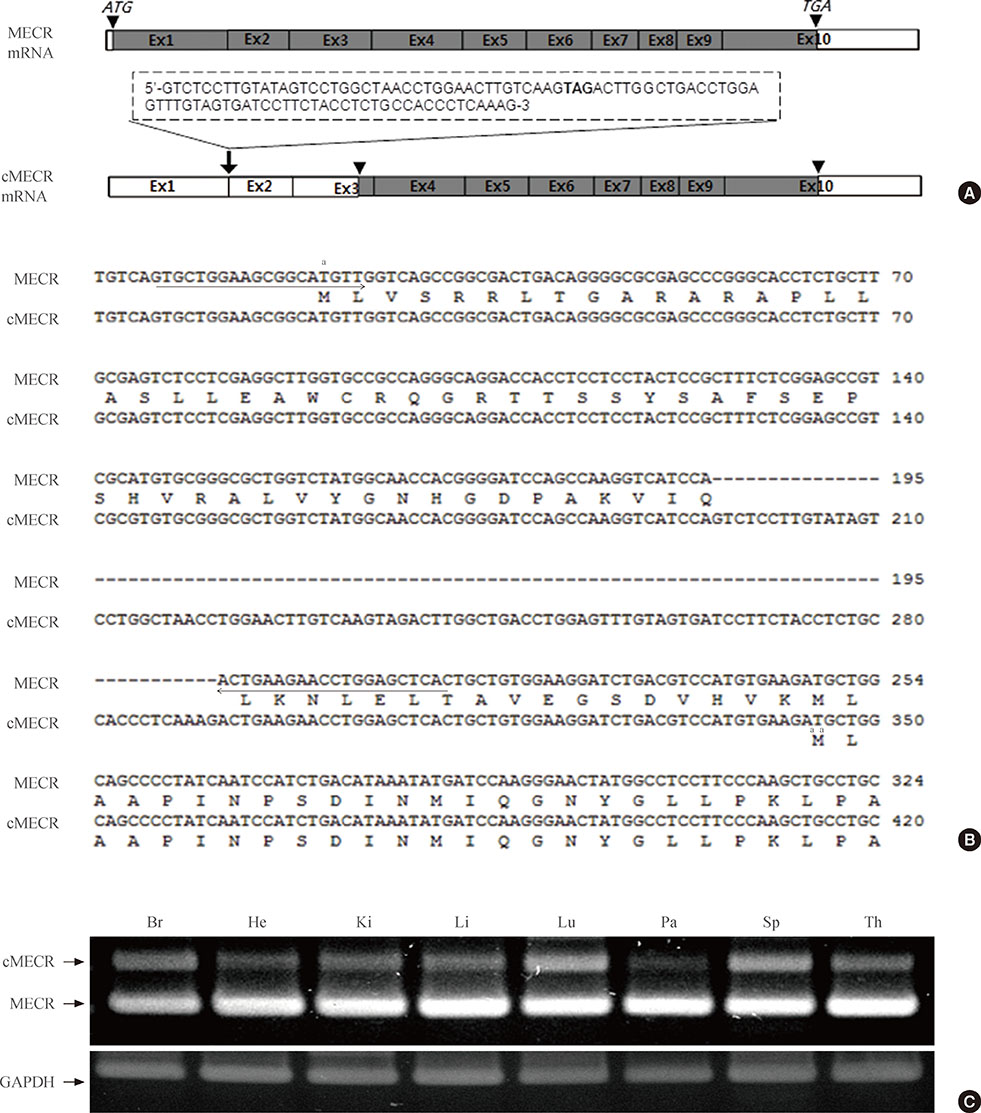
Mitochondrial trans-2-enoyl-CoA reductase (MECR) is involved in mitochondrial synthesis of fatty acids and is highly expressed in mitochondria. MECR is also known as nuclear receptor binding factor-1, which was originally reported with yeast two-hybrid screening as a binding protein of the nuclear hormone receptor peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARalpha). However, MECR and PPARalpha are localized at different compartment, mitochondria, and the nucleus, respectively. Therefore, the presence of a cytosolic or nuclear isoform of MECR is necessary for functional interaction between MECR and PPARalpha.
METHODS
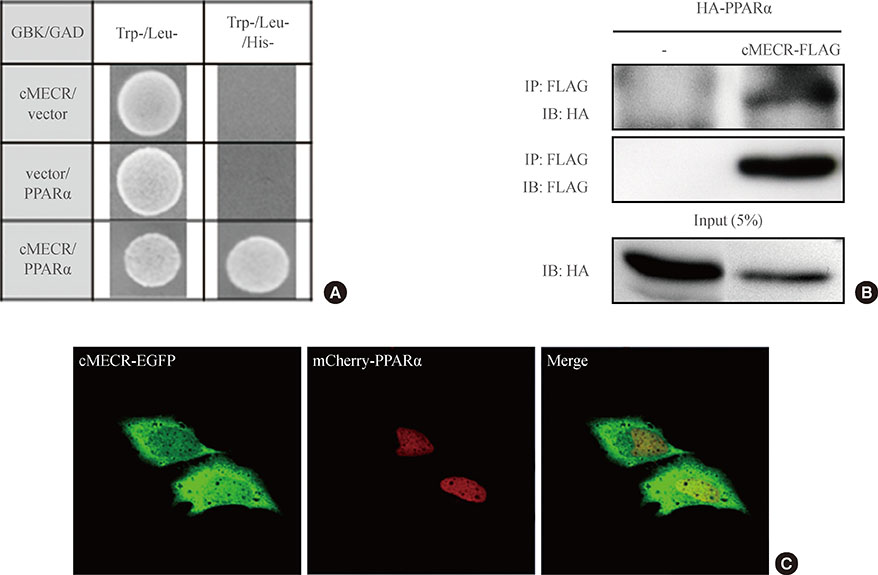
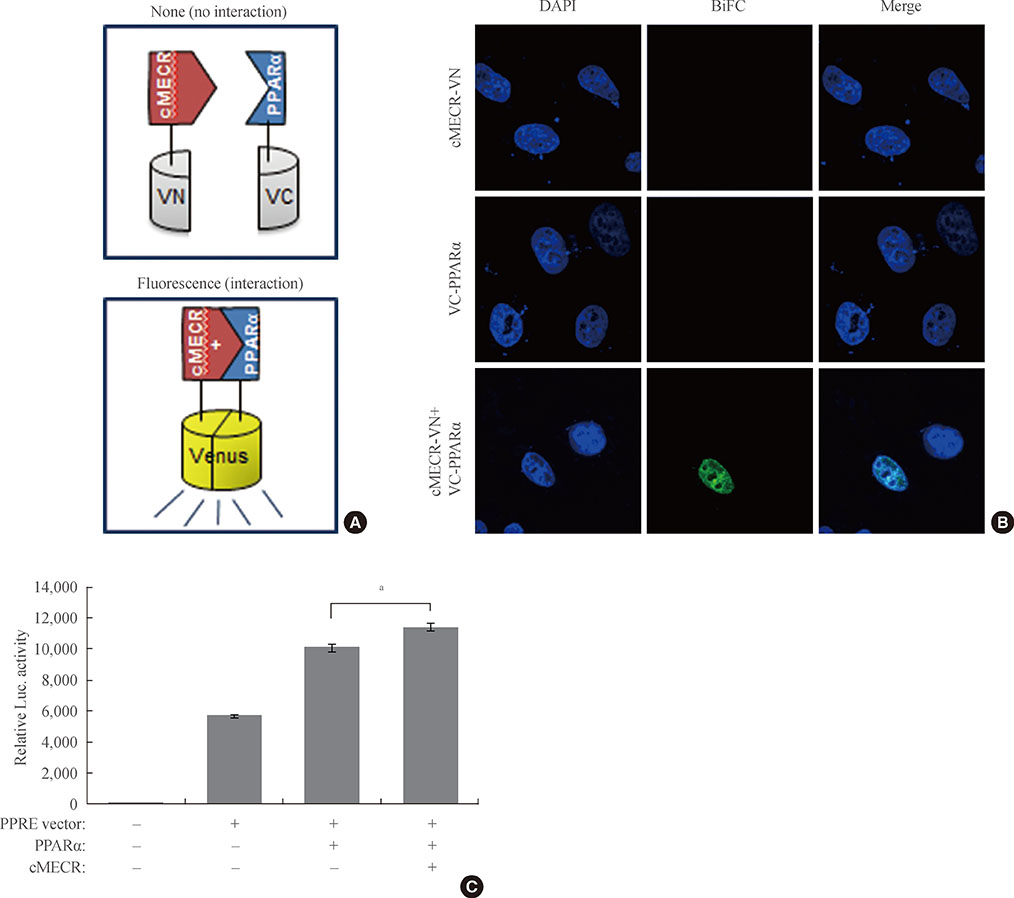
To identify the expression pattern of MECR and the cytosolic form of MECR (cMECR), we performed reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) with various tissue samples from Sprague-Dawley rats. To confirm the interaction between cMECR and PPARalpha, we performed several binding assays such as yeast two-hybrid, coimmunoprecipitation, and bimolecular fluorescence complementation. To observe subcellular localization of these proteins, immunocytochemistry was performed. A luciferase assay was used to measure PPARalpha activity.
RESULTS
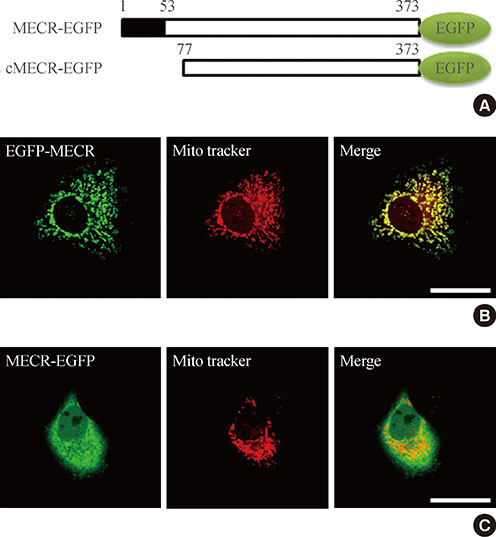
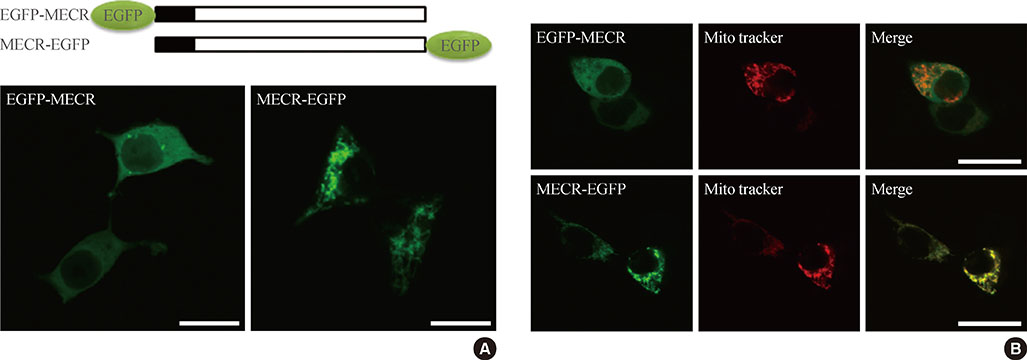
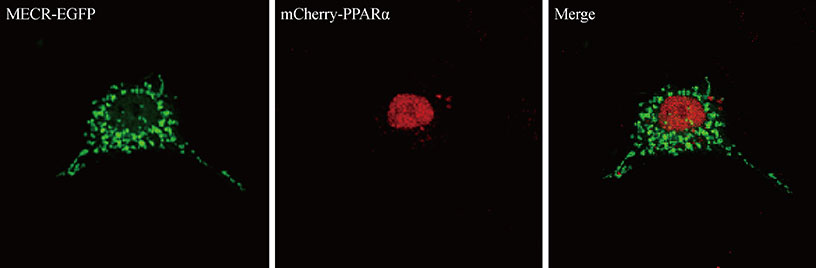
We provide evidence of an alternatively spliced variant of the rat MECR gene that yields cMECR. The cMECR lacks the N-terminal 76 amino acids of MECR and shows uniform distribution in the cytoplasm and nucleus of HeLa cells. cMECR directly bound PPARalpha in the nucleus and increased PPARalpha-dependent luciferase activity in HeLa cells.
CONCLUSION
We found the cytosolic form of MECR (cMECR) was expressed in the cytosolic and/or nuclear region, directly binds with PPARalpha, and enhances PPARalpha activity.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Alternative Splicing
Amino Acids
Animals
Carrier Proteins
Complement System Proteins
Cytoplasm
Cytosol*
Fatty Acids
Fluorescence
HeLa Cells
Humans
Immunohistochemistry
Luciferases
Mass Screening
Mitochondria
Oxidoreductases*
Polymerase Chain Reaction
PPAR alpha*
Rats
Rats, Sprague-Dawley
Reverse Transcription
Yeasts
Amino Acids
Carrier Proteins
Complement System Proteins
Fatty Acids
Luciferases
Oxidoreductases
PPAR alpha
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chen Z, Leskinen H, Liimatta E, Sormunen RT, Miinalainen IJ, Hassinen IE, Hiltunen JK. Myocardial overexpression of Mecr, a gene of mitochondrial FAS II leads to cardiac dysfunction in mouse. PLoS One. 2009; 4:e5589.2. White SW, Zheng J, Zhang YM, Rock . The structural biology of type II fatty acid biosynthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 2005; 74:791–831.3. Torkko JM, Koivuranta KT, Miinalainen IJ, Yagi AI, Schmitz W, Kastaniotis AJ, Airenne TT, Gurvitz A, Hiltunen KJ. Candida tropicalis Etr1p and Saccharomyces cerevisiae Ybr026p (Mrf1'p), 2-enoyl thioester reductases essential for mitochondrial respiratory competence. Mol Cell Biol. 2001; 21:6243–6253.4. Chen ZJ, Pudas R, Sharma S, Smart OS, Juffer AH, Hiltunen JK, Wierenga RK, Haapalainen AM. Structural enzymological studies of 2-enoyl thioester reductase of the human mitochondrial FAS II pathway: new insights into its substrate recognition properties. J Mol Biol. 2008; 379:830–844.5. Hoffmeister M, Piotrowski M, Nowitzki U, Martin W. Mitochondrial trans-2-enoyl-CoA reductase of wax ester fermentation from Euglena gracilis defines a new family of enzymes involved in lipid synthesis. J Biol Chem. 2005; 280:4329–4338.6. Pfanner N. Protein sorting: recognizing mitochondrial presequences. Curr Biol. 2000; 10:R412–R415.7. Emanuelsson O, Nielsen H, Brunak S, von Heijne G. Predicting subcellular localization of proteins based on their N-terminal amino acid sequence. J Mol Biol. 2000; 300:1005–1016.8. Claros MG, Vincens P. Computational method to predict mitochondrially imported proteins and their targeting sequences. Eur J Biochem. 1996; 241:779–786.9. Chen JQ, Delannoy M, Cooke C, Yager JD. Mitochondrial localization of ERalpha and ERbeta in human MCF7 cells. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2004; 286:E1011–E1022.10. Masuda N, Yasumo H, Furusawa T, Tsukamoto T, Sadano H, Osumi T. Nuclear receptor binding factor-1 (NRBF-1), a protein interacting with a wide spectrum of nuclear hormone receptors. Gene. 1998; 221:225–233.11. Desvergne B, Wahli W. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors: nuclear control of metabolism. Endocr Rev. 1999; 20:649–688.12. Kersten S, Desvergne B, Wahli W. Roles of PPARs in health and disease. Nature. 2000; 405:421–424.13. Evans RM, Barish GD, Wang YX. PPARs and the complex journey to obesity. Nat Med. 2004; 10:355–361.14. Park JY, Hwang EM, Yarishkin O, Seo JH, Kim E, Yoo J, Yi GS, Kim DG, Park N, Ha CM, La JH, Kang D, Han J, Oh U, Hong SG. TRPM4b channel suppresses store-operated Ca2+ entry by a novel protein-protein interaction with the TRPC3 channel. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008; 368:677–683.15. Hu CD, Chinenov Y, Kerppola TK. Visualization of interactions among bZIP and Rel family proteins in living cells using bimolecular fluorescence complementation. Mol Cell. 2002; 9:789–798.16. Shyu YJ, Liu H, Deng X, Hu CD. Identification of new fluorescent protein fragments for bimolecular fluorescence complementation analysis under physiological conditions. Biotechniques. 2006; 40:61–66.17. Kallenberger BC, Love JD, Chatterjee VK, Schwabe JW. A dynamic mechanism of nuclear receptor activation and its perturbation in a human disease. Nat Struct Biol. 2003; 10:136–140.18. McKenna NJ, Lanz RB, O'Malley BW. Nuclear receptor coregulators: cellular and molecular biology. Endocr Rev. 1999; 20:321–344.19. Plutzky J. The PPAR-RXR transcriptional complex in the vasculature: energy in the balance. Circ Res. 2011; 108:1002–1016.20. Ziouzenkova O, Plutzky J. Lipolytic PPAR activation: new insights into the intersection of triglycerides and inflammation? Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2004; 7:369–375.21. Han SH, Quon MJ, Koh KK. Beneficial vascular and metabolic effects of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha activators. Hypertension. 2005; 46:1086–1092.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Safety and Efficacy of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-alpha Agonist for Treating Cardiovascular Disease
- Refocusing Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptor-alpha: A New Insight for Therapeutic Roles in Diabetes
- Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptor-delta (PPAR-delta)
- Peroxisome Proliferator-activated Receptors (PPARs) in Diabetic Nephropathy
- Fibrates Revisited: Potential Role in Cardiovascular Risk Reduction