Anat Cell Biol.
2010 Jun;43(2):157-164. 10.5115/acb.2010.43.2.157.
Evaluation of recombinant adenovirus-mediated gene delivery for expression of tracer genes in catecholaminergic neurons
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anatomy and Neurobiology, School of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea. ybhuh@khu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2168889
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.2010.43.2.157
Abstract
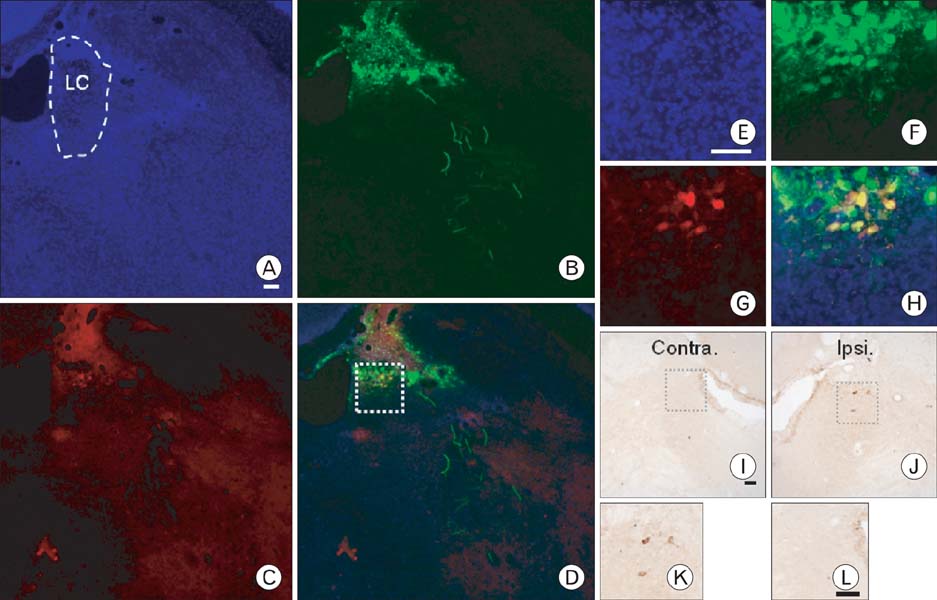
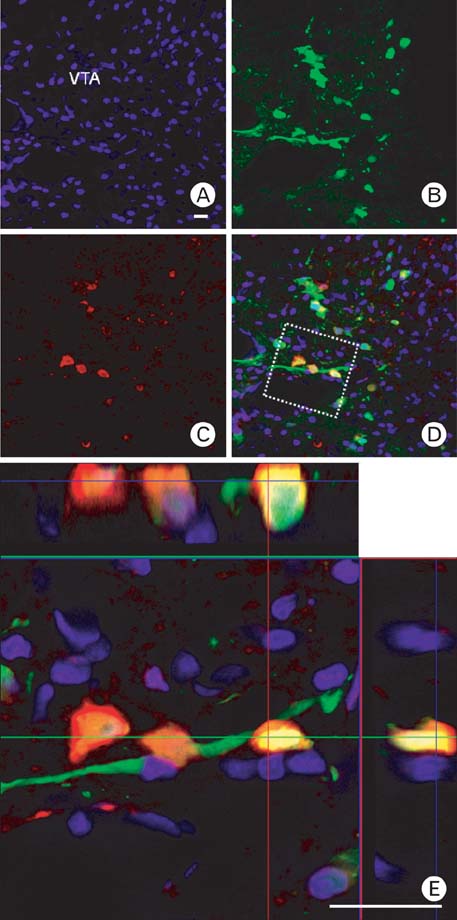
- Selective labeling of small populations of neurons of a given phenotype for conventional neuronal tracing is difficult because tracers can be taken up by all neurons at the injection site, resulting in nonspecific labeling of unrelated pathways. To overcome these problems, genetic approaches have been developed that introduce tracer proteins as transgenes under the control of cell-type-specific promoter elements for visualization of specific neuronal pathways. The aim of this study was to explore the use of tracer gene expression for neuroanatomical tracing to chart the complex interconnections of the central nervous system. Genetic tracing methods allow for expression of tracer molecules using cell-type-specific promoters to facilitate neuronal tracing. In this study, the rat tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) promoter and an adenoviral delivery system were used to express tracers specifically in dopaminergic and noradrenergic neurons. Region-specific expression of the transgenes was then analyzed. Initially, we characterized cell-type-specific expression of GFP or RFP in cultured cell lines. We then injected an adenovirus carrying the tracer transgene into several brain regions using a stereotaxic apparatus. Three days after injection, strong GFP expression was observed in the injected site of the brain. RFP and WGA were expressed in a cell-type-specific manner in the cerebellum, locus coeruleus, and ventral tegmental regions. Our results demonstrate that selective tracing of catecholaminergic neuronal circuits is possible in the rat brain using the TH promoter and adenoviral expression.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Boldogkoi Z, Sik A, Denes A, et al. Novel tracing paradigms--genetically engineered herpesviruses as tools for mapping functional circuits within the CNS: present status and future prospects. Prog Neurobiol. 2004. 72:417–445.2. Broadwell RD, Balin BJ. Endocytic and exocytic pathways of the neuronal secretory process and trans-synaptic transfer of wheat germ agglutinin-horseradish peroxidase in vivo. J Comp Neurol. 1985. 242:632–650.3. Fabian RH, Coulter JD. Transneuronal transport of lectins. Brain Res. 1985. 344:41–48.4. Gonatas NK, Harper C, Mizutani T, et al. Superior sensitivity of conjugates of horseradish peroxidase with wheat germ agglutinin for studies of retrograde axonal transport. J Histochem Cytochem. 1979. 27:728–734.5. He TC, Zhou S, da Costa LT, et al. A simplified system for generating recombinant adenoviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998. 95:2509–2514.6. Hickman-Davis JM, Davis IC. Transgenic mice. Paediatr Respir Rev. 2006. 7:49–53.7. Itaya SK. Anterograde transsynaptic transport of WGA-HRP in rat olfactory pathways. Brain Res. 1987. 409:205–214.8. Kinoshita N, Mizuno T, Yoshihara Y. Adenovirus-mediated WGA gene delivery for transsynaptic labeling of mouse olfactory pathways. Chem Senses. 2002. 27:215–223.9. Kissa K, Mordelet E, Soudais C, et al. In vivo neuronal tracing with GFP-TTC gene delivery. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2002. 20:627–637.10. Köbbert C, Apps R, Bechmann I, et al. Current concepts in neuroanatomical tracing. Prog Neurobiol. 2000. 62:327–351.11. Kügler S, Meyn L, Holzmuller H, et al. Neuron-specific expression of therapeutic proteins: evaluation of different cellular promoters in recombinant adenoviral vectors. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2001. 17:78–96.12. Liu BH, Wang X, Ma YX, et al. CMV enhancer/human PDGF-beta promoter for neuron-specific transgene expression. Gene Ther. 2004. 11:52–60.13. Liu J, Merlie JP, Todd RD, et al. Identification of cell type-specific promoter elements associated with the rat tyrosine hydroxylase gene using transgenic founder analysis. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1997. 50:33–42.14. Livet J, Weissman TA, Kang H, et al. Transgenic strategies for combinatorial expression of fluorescent proteins in the nervous system. Nature. 2007. 450:56–62.15. Maskos U, Kissa K, St Cloment C, et al. Retrograde trans-synaptic transfer of green fluorescent protein allows the genetic mapping of neuronal circuits in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. 99:10120–10125.16. Navarro V, Millecamps S, Geoffroy MC, et al. Efficient gene transfer and long-term expression in neurons using a recombinant adenovirus with a neuron-specific promoter. Gene Ther. 1999. 6:1884–1892.17. Niwa H, Yamamura K, Miyazaki J. Efficient selection for high-expression transfectants with a novel eukaryotic vector. Gene. 1991. 108:193–199.18. Oh MS, Hong SJ, Huh Y, et al. Expression of transgenes in midbrain dopamine neurons using the tyrosine hydroxylase promoter. Gene Ther. 2009. 16:437–440.19. Pilpel N, Landeck N, Klugmann M, et al. Rapid, reproducible transduction of select forebrain regions by targeted recombinant virus injection into the neonatal mouse brain. J Neurosci Methods. 2009. 182:55–63.20. Prakash N, Wurst W. Development of dopaminergic neurons in the mammalian brain. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2006. 63:187–206.21. Wickersham IR, Finke S, Conzelmann KK, et al. Retrograde neuronal tracing with a deletion-mutant rabies virus. Nat Methods. 2007a. 4:47–49.22. Wickersham IR, Lyon DC, Barnard RJ, et al. Monosynaptic restriction of transsynaptic tracing from single, genetically targeted neurons. Neuron. 2007b. 53:639–647.23. Yoshihara Y. Visualizing selective neural pathways with WGA transgene: combination of neuroanatomy with gene technology. Neurosci Res. 2002. 44:133–140.24. Yoshihara Y, Mizuno T, Nakahira M, et al. A genetic approach to visualization of multisynaptic neural pathways using plant lectin transgene. Neuron. 1999. 22:33–41.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Stromelysin Gene Expression in Rat Eye Mediated by the Adenovirus Vector
- Adenovirus Vector-mediated Gene Transfer into Human Trabecular Cell
- Development of Tetracycline-regulated Adenovirus Expression Vector System
- Gene Therapy of Brain Tumors:Effects of Adenovirus-mediated Wild Type p53 Gene Transfer in Human Glioma Cells
- Effects of Integrin avB5 and av B53 on the Adenovirus - Mediated Gene Transduction