Cancer Res Treat.
2014 Apr;46(2):165-171.
Metabolic Burden Measured by 18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography Is a Prognostic Factor in Patients with Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea. leemk@pusan.ac.kr
- 2Biomedical Research Institute, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- 3Department of Nuclear Medicine, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Evidence regarding the usefulness of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography (18F-FDG PET/CT) in predicting the prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer is increasing. However, data on small cell lung cancer (SCLC) are scarce. The aim of this study was to evaluate the prognostic value of metabolic parameters measured using 18F-FDG PET/CT in patients with SCLC.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
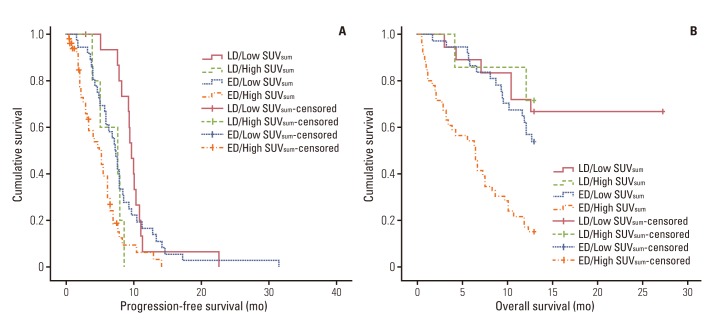
We conducted a retrospective review of 114 patients with pathologically proven SCLC (26 cases of limited disease and 88 cases of extensive disease) who underwent pretreatment 18F-FDG PET/CT. The maximal SUV (SUVmax) was used quantitatively for determination of FDG PET activity. The SUVmax of the primary tumor (primary SUVmax), the sum of SUVmax values of malignant lesions (SUVsum), and the mean SUVmax of malignant lesions were calculated.
RESULTS
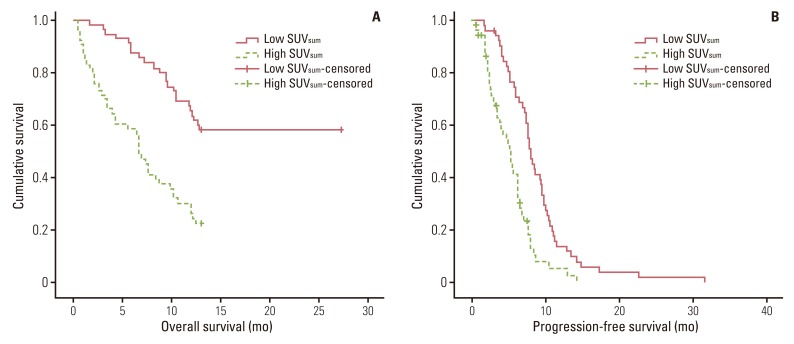
The patient population was subdivided using a median SUVsum value of 24.6. High SUVsum showed a significant association with known factors for poor prognosis, including higher neuron-specific enolase (p=0.010), CYFRA 21-1 (p=0.014), and extensive disease status (p=0.007). Patients with high SUVsum had significantly shorter median overall survival (6.6 months vs. 13.0 months, p<0.001) and progression-free survival (5.2 months vs. 8.0 months, p<0.001) than patients with low SUVsum. Results of multivariate analysis showed that SUVsum, chemotherapy cycles, and the response to first-line treatment were significant prognostic factors of survival. In contrast, mean SUVmax and primary SUVmax were not significant predictors of survival.
CONCLUSION
In this study, metabolic burden represented by SUVsum from pretreatment 18F-FDG PET/CT was an independent prognostic factor in patients with SCLC.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Carcinoma, Non-Small-Cell Lung
Disease-Free Survival
Drug Therapy
Electrons*
Fluorodeoxyglucose F18
Humans
Multivariate Analysis
Phosphopyruvate Hydratase
Positron-Emission Tomography and Computed Tomography
Prognosis
Retrospective Studies
Small Cell Lung Carcinoma*
Tumor Burden
Fluorodeoxyglucose F18
Phosphopyruvate Hydratase
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011; 61:69–90. PMID: 21296855.
Article2. Aisner J. Extensive-disease small-cell lung cancer: the thrill of victory: the agony of defeat. J Clin Oncol. 1996; 14:658–665. PMID: 8636784.
Article3. Mountain CF. Revisions in the international system for staging lung cancer. Chest. 1997; 111:1710–1717. PMID: 9187198.
Article4. Yip D, Harper PG. Predictive and prognostic factors in small cell lung cancer: current status. Lung Cancer. 2000; 28:173–185. PMID: 10812187.
Article5. Albain KS, Crowley JJ, LeBlanc M, Livingston RB. Determinants of improved outcome in small-cell lung cancer: an analysis of the 2,580-patient Southwest Oncology Group data base. J Clin Oncol. 1990; 8:1563–1574. PMID: 2167954.
Article6. Pillot G, Siegel BA, Govindan R. Prognostic value of fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography in non-small cell lung cancer: a review. J Thorac Oncol. 2006; 1:152–159. PMID: 17409845.
Article7. Berghmans T, Dusart M, Paesmans M, Hossein-Foucher C, Buvat I, Castaigne C, et al. Primary tumor standardized uptake value (SUVmax) measured on fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) is of prognostic value for survival in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): a systematic review and meta-analysis (MA) by the European Lung Cancer Working Party for the IASLC Lung Cancer Staging Project. J Thorac Oncol. 2008; 3:6–12. PMID: 18166834.
Article8. Ikenaga N, Otomo N, Toyofuku A, Ueda Y, Toyoda K, Hayashi T, et al. Standardized uptake values for breast carcinomas assessed by fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography correlate with prognostic factors. Am Surg. 2007; 73:1151–1157. PMID: 18092653.
Article9. Allal AS, Slosman DO, Kebdani T, Allaoua M, Lehmann W, Dulguerov P. Prediction of outcome in head-and-neck cancer patients using the standardized uptake value of 2-[18F]fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004; 59:1295–1300. PMID: 15275712.
Article10. Lee YJ, Cho A, Cho BC, Yun M, Kim SK, Chang J, et al. High tumor metabolic activity as measured by fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography is associated with poor prognosis in limited and extensive stage small-cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2009; 15:2426–2432. PMID: 19318478.
Article11. Zhu D, Ma T, Niu Z, Zheng J, Han A, Zhao S, et al. Prognostic significance of metabolic parameters measured by (18)F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography in patients with small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2011; 73:332–337. PMID: 21292341.
Article12. Fletcher JW, Djulbegovic B, Soares HP, Siegel BA, Lowe VJ, Lyman GH, et al. Recommendations on the use of 18F-FDG PET in oncology. J Nucl Med. 2008; 49:480–508. PMID: 18287273.
Article13. Um SW, Kim H, Koh WJ, Suh GY, Chung MP, Kwon OJ, et al. Prognostic value of 18F-FDG uptake on positron emission tomography in patients with pathologic stage I non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2009; 4:1331–1336. PMID: 19701106.
Article14. Elias AD. Small cell lung cancer: state-of-the-art therapy in 1996. Chest. 1997; 112(4 Suppl):251S–258S. PMID: 9337299.15. Park S, Moon SH, Park LC, Hwang DW, Ji JH, Maeng CH, et al. The impact of baseline and interim PET/CT parameters on clinical outcome in patients with diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Am J Hematol. 2012; 87:937–940. PMID: 22730093.
Article16. Kumar V, Abbas AK, Fausto N, Aster JC. Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders;2009.17. Bruzzi P, Del Mastro L, Sormani MP, Bastholt L, Danova M, Focan C, et al. Objective response to chemotherapy as a potential surrogate end point of survival in metastatic breast cancer patients. J Clin Oncol. 2005; 23:5117–5125. PMID: 15955906.
Article18. Hotta K, Matsuo K, Ueoka H, Kiura K, Tabata M, Harita S, et al. Continued gefitinib treatment after disease stabilisation prolongs survival of Japanese patients with non-small-cell lung cancer: Okayama Lung Cancer Study Group experience. Ann Oncol. 2005; 16:1817–1823. PMID: 16157622.
Article19. Hotta K, Kiura K, Fujiwara Y, Takigawa N, Oze I, Ochi N, et al. Association between incremental gains in the objective response rate and survival improvement in phase III trials of first-line chemotherapy for extensive disease small-cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol. 2009; 20:829–834. PMID: 19221150.
Article20. Hotta K, Fujiwara Y, Matsuo K, Kiura K, Takigawa N, Tabata M, et al. Time to progression as a surrogate marker for overall survival in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2009; 4:311–317. PMID: 19190515.
Article21. Kubota K, Nishiwaki Y, Sugiura T, Noda K, Mori K, Kawahara M, et al. Pilot study of concurrent etoposide and cisplatin plus accelerated hyperfractionated thoracic radiotherapy followed by irinotecan and cisplatin for limited-stage small cell lung cancer: Japan Clinical Oncology Group 9903. Clin Cancer Res. 2005; 11:5534–5538. PMID: 16061870.
Article22. Simon GR, Turrisi A. American College of Chest Physicians. Management of small cell lung cancer: ACCP evidence-based clinical practice guidelines (2nd edition). Chest. 2007; 132(3 Suppl):324S–339S. PMID: 17873178.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Adult granulosa cell tumor presenting with massive ascites, elevated CA-125 level, and low 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose uptake on positron emission tomography/computed tomography
- Prognostic Significance of Volume-Based PET Parameters in Cancer Patients
- 18F-2-Deoxy-2-Fluoro-D-Glucose Positron Emission Tomography: Computed Tomography for Preoperative Staging in Gastric Cancer Patients
- Preoperative Nodal ¹â¸F-FDG Avidity Rather than Primary Tumor Avidity Determines the Prognosis of Patients with Advanced Gastric Cancer
- Metastases to Skeletal Muscles from Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Demonstrated by 18F-FDG PET/CT