Distinct Inflammatory Profiles in Atopic and Nonatopic Patients With Chronic Rhinosinustis Accompanied by Nasal Polyps in Western China
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China.
- 2Department of Otolaryngology, People's Hospital of the Tibet Autonomous Region, Lasha, China.
- 3Department of Geriatrics, Center for Medical Stem Cell Biology, State Key Laboratory of Biotherapy, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China. bhanor@163.com
- 4Department of Otolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery, Xinhua Hospital, Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China. allergyli@163.com
- KMID: 2166682
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2015.7.4.346
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The role of systemic sensitization in the pathophysiology of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP) remains elusive. This study sought to characterize the pattern of cytokines in polyp tissues from atopic and nonatopic patients with CRSwNP.
METHODS
Atopic and nonatopic polyp and normal tissues were collected from 70 CRSwNP patients and 26 control subjects, respectively. The distribution of inflammatory cells (eosinophils, neutrophils, mast cells, etc.) were examined using immunohistochemistry, the mRNA levels of the transcription factors GATA-3, T-bet, RORc, and FOXP3 were determined using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. The levels of inflammatory mediators (IFN-gamma, IL-5, IL-17A, etc.) in tissue homogenates were measured using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Moreover, the levels of inflammatory mediators in the supernatant of anti-IgE stimulated polyp tissues were measured using ELISA.
RESULTS
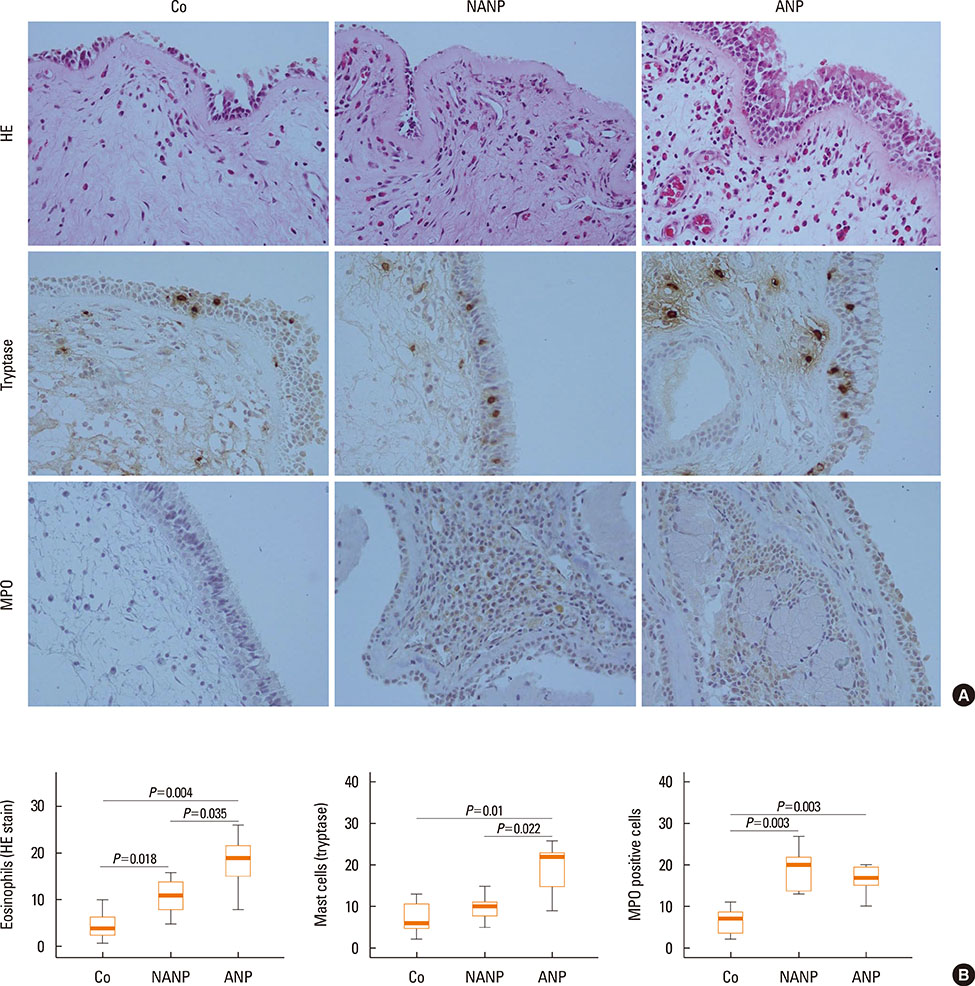
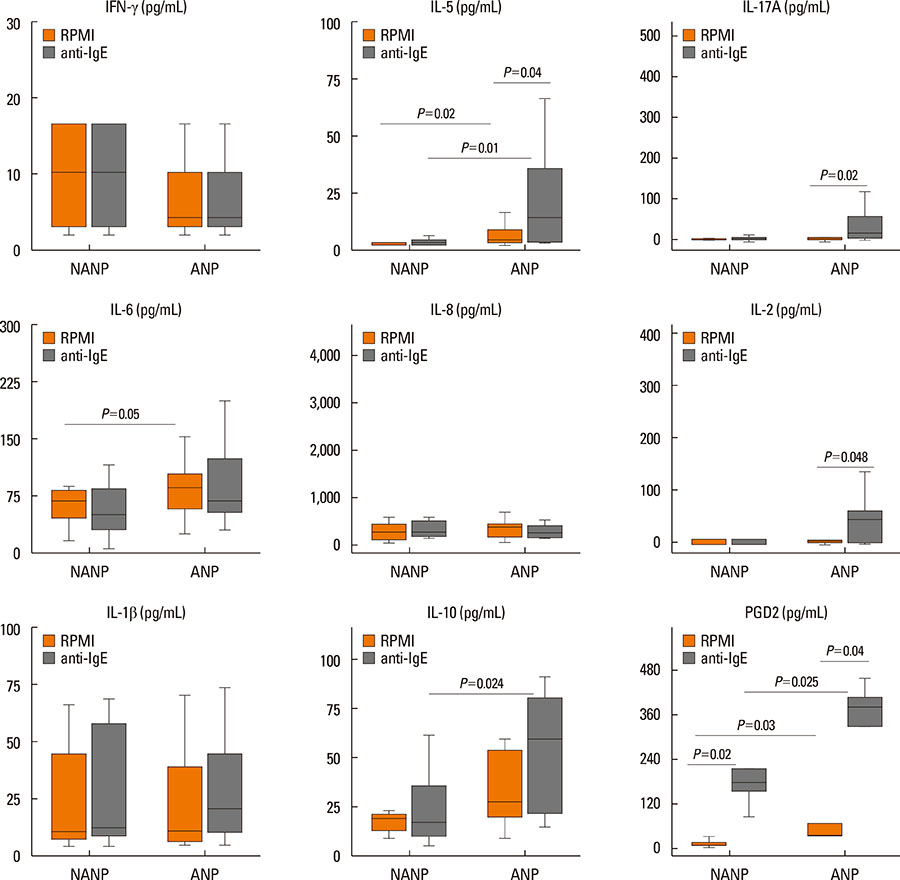
Atopic CRSwNP patients were characterized by increased eosinophil accumulation, enhanced eosinophilic inflammation (elevated IL-5, ECP, and total IgE), and significantly increased GATA-3 mRNA levels (P<0.05), whereas both atopic and non-atopic CRSwNP patients showed decreased FOXP3 mRNA expression (P<0.05). After addition of anti-IgE stimulation, atopic CRSwNP patients produced more IL-5, IL-2, IL-10, IL-17A, and PGD2 in the supernatant of stimulated polyp tissues than nonatopic CRSwNP patients did.
CONCLUSIONS
Atopic and nonatopic CRSwNP patients may possess the patterns of inflammatory response in polyp tissues.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
China*
Cytokines
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Eosinophils
Humans
Immunoglobulin E
Immunohistochemistry
Inflammation
Interleukin-10
Interleukin-17
Interleukin-2
Interleukin-5
Mast Cells
Nasal Polyps*
Neutrophils
Polyps
Prostaglandin D2
Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
RNA, Messenger
Transcription Factors
Cytokines
Immunoglobulin E
Interleukin-10
Interleukin-17
Interleukin-2
Interleukin-5
Prostaglandin D2
RNA, Messenger
Transcription Factors
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Differential Hrd1 Expression and B-Cell Accumulation in Eosinophilic and Non-eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis With Nasal Polyps
Kun Chen, Miaomiao Han, Mengyao Tang, Yadong Xie, Yuting Lai, Xianting Hu, Jia Zhang, Jun Yang, Huabin Li
Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2018;10(6):698-715. doi: 10.4168/aair.2018.10.6.698.Classification of chronic rhinosinusitis according to a nasal polyp and tissue eosinophilia: limitation of current classification system for Asian population
Sung-Woo Cho, Dae Woo Kim, Jeong-Whun Kim, Chul Hee Lee, Chae-Seo Rhee
Asia Pac Allergy. 2017;7(3):121-130. doi: 10.5415/apallergy.2017.7.3.121.Endotype of Eosinophilic Nasal Polyposis According to the Presence of Atopy
Do Hyun Kim, Boo-Young Kim, Il Hwan Lee, Sung Won Kim, Soo Whan Kim
Korean J Otorhinolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2020;63(12):579-585. doi: 10.3342/kjorl-hns.2020.00472.
Reference
-
1. Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Mullol J, Bachert C, Alobid I, Baroody F, et al. EPOS 2012: European position paper on rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps 2012. A summary for otorhinolaryngologists. Rhinology. 2012; 50:1–12.2. Hsu J, Peters AT. Pathophysiology of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyp. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2011; 25:285–290.3. Hamilos DL. Host-microbial interactions in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013; 131:1263–1264. 1264.e1–1264.e6.4. Akdis CA, Bachert C, Cingi C, Dykewicz MS, Hellings PW, Naclerio RM, et al. Endotypes and phenotypes of chronic rhinosinusitis: a PRACTALL document of the European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology and the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013; 131:1479–1490.5. Chin D, Harvey RJ. Nasal polyposis: an inflammatory condition requiring effective anti-inflammatory treatment. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2013; 21:23–30.6. Wen W, Liu W, Zhang L, Bai J, Fan Y, Xia W, et al. Increased neutrophilia in nasal polyps reduces the response to oral corticosteroid therapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012; 129:1522–1528.e5.7. Zhang N, Van Zele T, Perez-Novo C, Van Bruaene N, Holtappels G, DeRuyck N, et al. Different types of T-effector cells orchestrate mucosal inflammation in chronic sinus disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008; 122:961–968.8. Kim JW, Hong SL, Kim YK, Lee CH, Min YG, Rhee CS. Histological and immunological features of non-eosinophilic nasal polyps. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2007; 137:925–930.9. Ishitoya J, Sakuma Y, Tsukuda M. Eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis in Japan. Allergol Int. 2010; 59:239–245.10. Cao PP, Li HB, Wang BF, Wang SB, You XJ, Cui YH, et al. Distinct immunopathologic characteristics of various types of chronic rhinosinusitis in adult Chinese. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 124:478–484. 484.e1–484.e2.11. Ba L, Zhang N, Meng J, Zhang J, Lin P, Zhou P, et al. The association between bacterial colonization and inflammatory pattern in Chinese chronic rhinosinusitis patients with nasal polyps. Allergy. 2011; 66:1296–1303.12. Luo B, Feng L, Jintao D, Yafeng L, Shixi L, Nan Z, et al. Immunopathology features of chronic rhinosinusitis in high-altitude dwelling Tibetans. Allergy Rhinol (Providence). 2013; 4:e69–e76.13. Van Zele T, Claeys S, Gevaert P, Van Maele G, Holtappels G, Van Cauwenberge P, et al. Differentiation of chronic sinus diseases by measurement of inflammatory mediators. Allergy. 2006; 61:1280–1289.14. Hamilos DL, Leung DY, Wood R, Cunningham L, Bean DK, Yasruel Z, et al. Evidence for distinct cytokine expression in allergic versus nonallergic chronic sinusitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1995; 96:537–544.15. Perić A, Vojvodić D, Vukomanović-Durdevid B. Influence of allergy on clinical, immunological and histological characteristics of nasal polyposis. B-ENT. 2012; 8:25–32.16. Scavuzzo MC, Fattori B, Ruffoli R, Rocchi V, Carpi A, Berni R, et al. Inflammatory mediators and eosinophilia in atopic and non-atopic patients with nasal polyposis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2005; 59:323–329.17. Zhang N, Holtappels G, Claeys C, Huang G, van Cauwenberge P, Bachert C. Pattern of inflammation and impact of Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxins in nasal polyps from southern China. Am J Rhinol. 2006; 20:445–450.18. Van Crombruggen K, Zhang N, Gevaert P, Tomassen P, Bachert C. Pathogenesis of chronic rhinosinusitis: inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 128:728–732.19. Kennedy JL, Borish L. Chronic sinusitis pathophysiology: the role of allergy. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2013; 27:367–371.20. Krouse JH. Allergy and chronic rhinosinusitis. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2005; 38:1257–1266. ix–x.21. Wise SK, Ahn CN, Schlosser RJ. Localized immunoglobulin E expression in allergic rhinitis and nasal polyposis. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2009; 17:216–222.22. Bachert C, Gevaert P, Holtappels G, Johansson SG, van Cauwenberge P. Total and specific IgE in nasal polyps is related to local eosinophilic inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001; 107:607–614.23. Matsuwaki Y, Uno K, Okushi T, Otori N, Moriyama H. Total and antigen- (fungi, mites and staphylococcal enterotoxins) specific IgEs in nasal polyps is related to local eosinophilic inflammation. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2013; 161:Suppl 2. 147–153.24. Baba S, Kondo K, Toma-Hirano M, Kanaya K, Suzukawa K, Ushio M, et al. Local increase in IgE and class switch recombination to IgE in nasal polyps in chronic rhinosinusitis. Clin Exp Allergy. 2014; 44:701–712.25. Cao PP, Zhang YN, Liao B, Ma J, Wang BF, Wang H, et al. Increased local IgE production induced by common aeroallergens and phenotypic alteration of mast cells in Chinese eosinophilic, but not non-eosinophilic, chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Clin Exp Allergy. 2014; 44:690–700.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Endotypes of Asian chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps: A narrative review
- Pathogenesis of Nasal Polyps
- Endotype of Eosinophilic Nasal Polyposis According to the Presence of Atopy
- Understanding the Role of Neutrophils in Refractoriness of Chronic Rhinosinusitis With Nasal Polyps
- Medical treatment according to phenotypes of chronic rhinosinusitis