Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2011 Mar;4(1):33-39.
Changes of Alpha1-Antitrypsin Levels in Allergen-induced Nasal Inflammation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Allergy and Rheumatology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. hspark@ajou.ac.kr
- 3Department of Pathology, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
Alpha1-antitrypsin (AAT) is the main inhibitor of human neutrophil elastase, and plays a role in counteracting the tissue damage caused by elastase in local inflammatory conditions. The study evaluated the involvement of AAT in nasal allergic inflammation.
METHODS
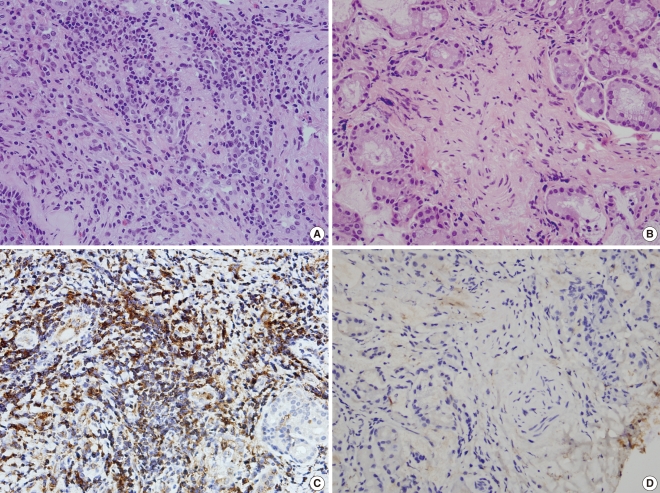
Forty subjects with mono-sensitization to Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus (Dpt) were enrolled. Twenty allergic rhinitis patients frequently complained of nasal symptoms such as rhinorrhea, stuffiness, sneezing, and showed positive responses to the nasal provocation test (NPT) with Dpt (Group I). The other 20 asymptomatic patients showed sensitization to Dpt but negative NPT (Group II). The levels of AAT, eosinophil cationic protein (ECP), and Dpt-specific IgA antibodies were measured in the nasal lavage fluids (NLFs), collected at baseline, 10 minutes, 30 minutes, 3 hours, and 6 hours after the NPT. Nasal mucosa AAT expression was evaluated with immunohistochemical staining from Group I and Group II.
RESULTS
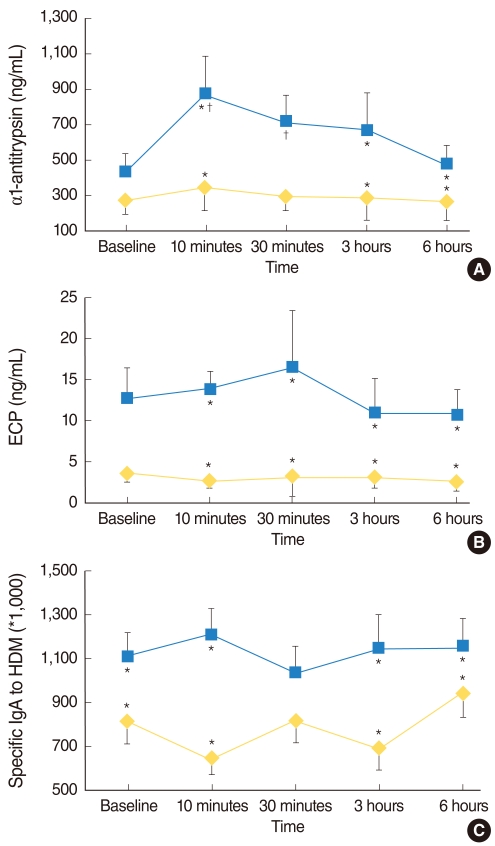
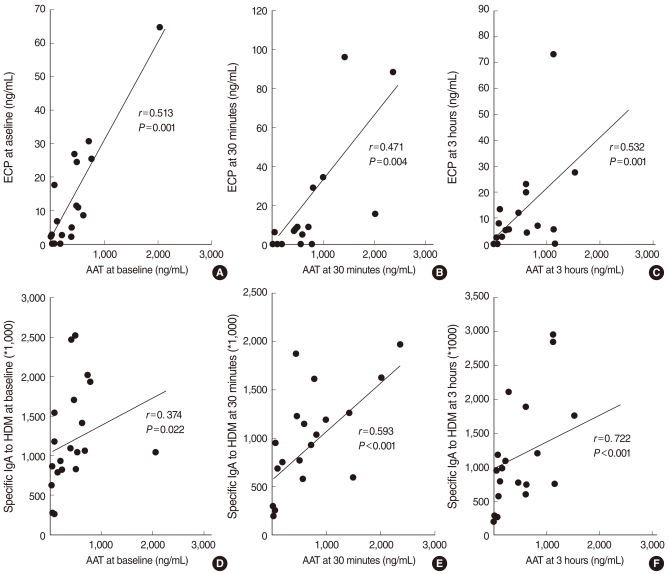
At baseline, only the Dpt-specific IgA level was significantly increased in the NLFs of Group I compared with Group II, while ECP and AAT levels were not significantly different between two groups. After Dpt provocation, AAT, ECP, and Dpt-specific IgA levels were significantly increased in the NLFs of Group I during the early and late responses. The protein expression level of AAT was mostly found in the infiltrating inflammatory cells of the nasal mucosa, which was significantly increased in Group I compared to Group II.
CONCLUSION
The increment of AAT showed a close relationship with the activation of eosinophils induced by allergen-specific IgA in the NLFs of patients with allergic rhinitis after allergen stimulation. These findings implicate AAT in allergen-induced nasal inflammation.
MeSH Terms
-
Antibodies
Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus
Eosinophil Cationic Protein
Eosinophils
Humans
Immunoglobulin A
Inflammation
Leukocyte Elastase
Nasal Lavage Fluid
Nasal Mucosa
Nasal Provocation Tests
Pancreatic Elastase
Rhinitis
Rhinitis, Allergic, Perennial
Sneezing
Antibodies
Eosinophil Cationic Protein
Immunoglobulin A
Leukocyte Elastase
Pancreatic Elastase
Figure
Reference
-
1. Naclerio RM, Proud D, Peters SP, Silber G, Kagey-Sobotka A, Adkinson NF Jr, et al. Inflammatory mediators in nasal secretions during induced rhinitis. Clin Allergy. 1986; 3. 16(2):101–110. PMID: 3708789.
Article2. Borregaard N, Cowland JB. Granules of the human neutrophilic polymorphonuclear leukocyte. Blood. 1997; 5. 15. 89(10):3503–3521. PMID: 9160655.
Article3. Travis J, Salvesen GS. Human plasma proteinase inhibitors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983; 52:655–709. PMID: 6193754.
Article4. Hubbard R, Crystal RG. Crystal RG, West JB, editors. Antiproteases. The lung. 1991. New York: Raven Press;p. 1775–1788.5. Cichy J, Potempa J, Travis J. Biosynthesis of alpha1-proteinase inhibitor by human lung-derived epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1997; 3. 28. 272(13):8250–8255. PMID: 9079644.6. Bergman D, Kadner SS, Cruz MR, Esterman AL, Tahery MM, Young BK, et al. Synthesis of alpha 1-antichymotrypsin and alpha 1-antitrypsin by human trophoblast. Pediatr Res. 1993; 9. 34(3):312–317. PMID: 8134173.7. Paakko P, Kirby M, du Bois RM, Gillissen A, Ferrans VJ, Crystal RG. Activated neutrophils secrete stored alpha 1-antitrypsin. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1996; 12. 154(6 Pt 1):1829–1833. PMID: 8970377.
Article8. Johansson B, Malm J, Persson T, Janciauskiene S, Andersson P, Carlson J, et al. Alpha-1-antitrypsin is present in the specific granules of human eosinophilic granulocytes. Clin Exp Allergy. 2001; 3. 31(3):379–386. PMID: 11260148.
Article9. Westin U, Lundberg E, Wihl JA, Ohlsson K. The effect of immediate-hypersensitivity reactions on the level of SLPI, granulocyte elastase, alpha1-antitrypsin, and albumin in nasal secretions, by the method of unilateral antigen challenge. Allergy. 1999; 8. 54(8):857–864. PMID: 10485390.10. Ghafouri B, Irander K, Lindbom J, Tagesson C, Lindahl M. Comparative proteomics of nasal fluid in seasonal allergic rhinitis. J Proteome Res. 2006; 2. 5(2):330–338. PMID: 16457599.
Article11. Oh JH, Hur GY, Ye YM, Kim JE, Park K, Park HS. Correlation between specific IgA and eosinophil numbers in the lavage fluid of patients with perennial allergic rhinitis. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2008; Mar–Apr. 29(2):152–160. PMID: 18430312.
Article12. Choi GS, Park HJ, Hur GY, Choi SJ, Shin SY, Ye YM, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor in allergen-induced nasal inflammation. Clin Exp Allergy. 2009; 5. 39(5):655–661. PMID: 19236408.
Article13. Nikasinovic L, Just J, Sahraoui F, Seta N, Grimfeld A, Momas I. Nasal inflammation and personal exposure to fine particles PM2.5 in asthmatic children. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006; 6. 117(6):1382–1388. PMID: 16751001.
Article14. Nouri-Aria KT, O'Brien F, Noble W, Jabcobson MR, Rajakulasingam K, Durham SR. Cytokine expression during allergen-induced late nasal responses: IL-4 and IL-5 mRNA is expressed early (at 6 h) predominantly by eosinophils. Clin Exp Allergy. 2000; 12. 30(12):1709–1716. PMID: 11122208.15. Gelfand EW. Inflammatory mediators in allergic rhinitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004; 11. 114(5 Suppl):S135–S138. PMID: 15536444.
Article16. Benson M, Reinholdt J, Cardell LO. Allergen-reactive antibodies are found in nasal fluids from patients with birch pollen-induced intermittent allergic rhinitis, but not in healthy controls. Allergy. 2003; 5. 58(5):386–392. PMID: 12752324.
Article17. Carlson J, Eriksson S. Alpha 1-antitrypsin and other acute phase reactants in liver disease. Acta Med Scand. 1980; 207(1-2):79–83. PMID: 6966119.18. Owen S, Pearson D, Suarez-Mendez V, O'Driscoll R, Woodcock A. Evidence of free-radical activity in asthma. N Engl J Med. 1991; 8. 22. 325(8):586–587. PMID: 1857396.
Article19. Foreman RC, Mercer PF, Kroegel C, Warner JA. Role of the eosinophil in protein oxidation in asthma: possible effects on proteinase/antiproteinase balance. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1999; Feb–Apr. 118(2-4):183–186. PMID: 10224372.
Article20. Nagai K, Betsuyaku T, Konno S, Ito Y, Nasuhara Y, Hizawa N, et al. Diversity of protein carbonylation in allergic airway inflammation. Free Radic Res. 2008; 11. 42(11-12):921–929. PMID: 19031315.
Article21. Kalsheker NA, Deam S, Chambers L, Sreedharan S, Brocklehurst K, Lomas DA. The house dust mite allergen Der p1 catalytically inactivates alpha 1-antitrypsin by specific reactive centre loop cleavage: a mechanism that promotes airway inflammation and asthma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1996; 4. 05. 221(1):59–61. PMID: 8660343.22. Banda MJ, Rice AG, Griffin GL, Senior RM. The inhibitory complex of human alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor and human leukocyte elastase is a neutrophil chemoattractant. J Exp Med. 1988; 5. 01. 167(5):1608–1615. PMID: 3259253.
Article