Cancer Res Treat.
2006 Feb;38(1):48-53.
Resveratrol at High Doses Acts as an Apoptotic Inducer in Endothelial Cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Molecular Biology & the Institute of Nanosensor and Biotechnology, Dankook Univiersity, Seoul, Korea. heonyong@dankook.ac.kr
Abstract
- PURPOSE
S: Resveratrol is a phenolic compound found in grapes and other food products. In order to assess the availability of resveratrol as an angio-inhibiting drug, we examined whether resveratrol plays an important role in bovine aortic endothelial cells (BAECs) for cell apoptosis and cell migration.
METHODS
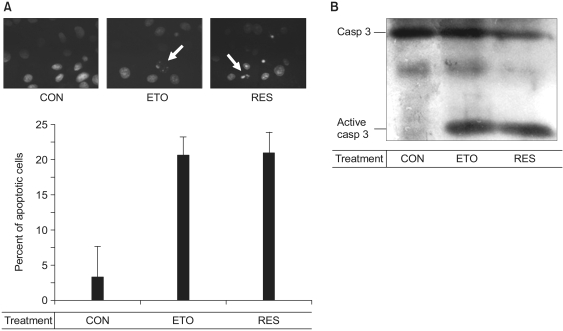
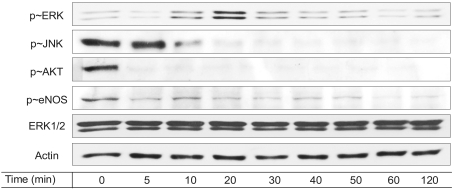
AND MATERIALS: Endothelial cell apoptosis was observed as detected by the Hoechst staining and the caspase-3 activity. Additionally, Western blotting was performed for monitoring the activities of various cell signaling molecules.
RESULTS
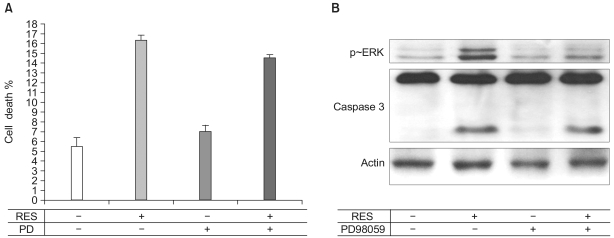
Resveratrol was shown to act as a pro-apoptotic agent. The pro-apoptotic effect of resveratrol was as great as that of etoposide, a well-known anti-cancer drug. In addition, resveratrol had an inhibitory effect on endothelial cell migration. The demonstrated efficacy of resveratrol suggests that resveratrol may be utilized as an anti-angiogenic drug. To determine the underlying mechanisms, we further investigated which signaling molecules are activated by resveratrol. Extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) was activated by the treatment with resveratrol in BAECs, whereas endothelial nitric oxide synthetase (eNOS), Akt, and Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) were inhibited. The pretreatment with PD compound, an ERK inhibitor, had no effect on the pro-apoptosis induced by resveratrol.
CONCLUSION
Resveratrol plays an important role in endothelial cell apoptosis, indicating that resveratrol can be utilized as a potent anti-angiogenic drug.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gasparini G. The rationale and future potential of angiogenesis inhibitors in neoplasia. Drugs. 1999; 58:17–38. PMID: 10439927.
Article2. Jang M, Cai L, Udeani GO, Slowing KV, Thomas CF, Beecher CW, et al. Cancer Chemopreventive activity of resveratrol, a natural product derived from grapes. Science. 1997; 275:218–220. PMID: 8985016.
Article3. Signorelli P, Ghidoni R. Resveratrol as an anticancer nutrient: molecular basis, open questions and promises. J Nutr Biochem. 2005; 16:449–466. PMID: 16043028.
Article4. Klinge CM, Blankenship KA, Resinger KE, Bhatnagar S, Noisin EL, Sumanasekera WK, et al. Resveratrol and estradiol rapidly activate MAPK signaling through estrogen receptors α and β in endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 2005; 280:7460–7468. PMID: 15615701.
Article5. Jo H, Sipos K, Go YM, Law R, Rong J, McDonald JM. Differential effect of shear stress on extracellular signal-regulated kinase and N-terminal Jun kinase in endothelial cells. Gi2- and Gbeta/gamma-dependent signaling pathways. J Biol Chem. 1997; 272:1395–1401. PMID: 8995450.6. Park H, Go YM, St John PL, Maland MC, Lisanti MP, Abrahamson DR, et al. Plasma membrane cholesterol is a key molecule in shear stress-dependent activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase. J Biol Chem. 1998; 273:32304–32311. PMID: 9822710.
Article7. Park SG, Kang YS, Ahn YH, Lee SH, Kim KR, Kim KW, et al. Dose-dependent biphasic activity of tRNA synthetase-associating factor, p43, in angiogenesis. J Biol Chem. 2002; 277:45243–45248. PMID: 12237313.
Article8. Ou HC, Chou FP, Sheen HM, Lin TM, Yang CH, Huey-Herng Sheu W. Resveratrol, a polyphenolic compound in red wine, protects against oxidized LDL-induced cytotoxicity in endothelial cells. Clin Chim Acta. 2006; 364:196–204. PMID: 16095586.
Article9. Rodriguez-Lopez AM, Xenaki D, Eden TO, Hickman JA, Chresta CM. MDM2 mediated nuclear exclusion of p53 attenuates ectoposide-induced apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells. Mol Pharmacol. 2001; 59:135–143. PMID: 11125034.10. Li J, Zhang YP, Kirsner RS. Angiogenesis in wound repair: angiogenic growth factors and the extracellular matrix. Microsc Res Tech. 2003; 60:107–114. PMID: 12500267.
Article11. Oak MH, Bedoui J, Schini-Kerth VB. Antiangiogenic properties of natural polyphenols from red wine and green tea. J Nutr Biochem. 2005; 16:1–8. PMID: 15629234.
Article12. Karin M. The regulation of AP-1 activity by mitogen-activated protein kinases. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1996; 351:127–134. PMID: 8650258.
Article13. Zuckerbraun BS, McCloskey CA, Mahidhara RS, Kim PK, Taylor BS, Tzeng E. Overexpression of mutated IkappaBalpha inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and intimal hyperplasia formation. J Vasc Surg. 2003; 38:812–819. PMID: 14560235.14. Park H, Park SG, Kim J, Ko YG, Kim S. Signaling pathways for TNF production induced by human aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase-associating factor, p43. Cytokine. 2002; 20:148–153. PMID: 12543078.
Article15. She QB, Huang C, Zhang Y, Dong Z. Involvment of c-jun NH(2)-terminal kinase in resveratrol-induced activation of p53 and apoptosis. Mol Carcinog. 2002; 33:244–250. PMID: 11933078.16. Sanna B, Debidda M, Pintus G, Tandolini B, Posadino AM, Bennardini F, et al. The anti-metastatic agent imidazolium trans-imidazoledimethylsulfoxide-tetrachlororuthenate induces endothelial cell apoptosis by inhibiting the mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling pathway. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2002; 403:209–218. PMID: 12139970.
Article17. Ranieri G, Gasparini G. Angiogenesis and angiogenesis inhibitors: a new potential anticancer therapeutic strategy. Curr Drug Targets Immune Endocr Metabol Disord. 2001; 1:241–253. PMID: 12477290.18. Iyer S, Chaplin DJ, Rosenthal DS, Boulares AH, Li Ly, Smulson ME. Induction of apoptosis in proliferating human endothelial cells by the tumor-specific antiangiogenesis agent combretastatin A-4. Cancer Res. 1998; 58:4510–4514. PMID: 9788591.19. Lenz HJ. Antiangiogenic agents in cancer therapy. Oncology. 2005; 19(4):Suppl 3. 17–25. PMID: 15934499.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Dose-dependent effect of resveratrol on proliferation and apoptosis in endothelial and tumor cell cultures
- Effect of Resveratrol on Cell Differentiation and Mineralization in Cultured Odontoblasts
- Resveratrol blunts tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced monocyte adhesion and transmigration
- Antichemosensitizing effect of resveratrol in cotreatment with oxaliplatin in HCT116 colon cancer cell
- Neuroprotective effects of resveratrol on 6-hydroxydopamine-induced damage of SH-SY5Y cell line