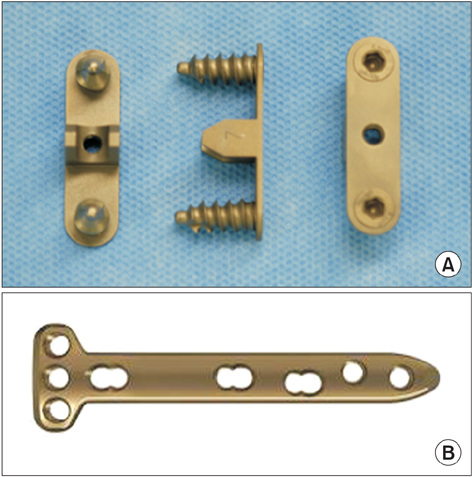
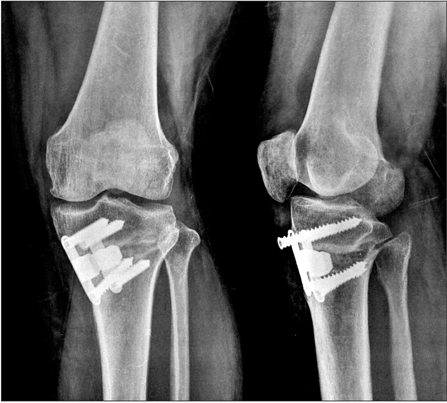
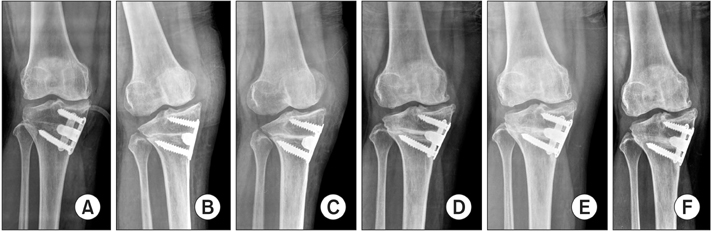
Clin Orthop Surg.
2015 Jun;7(2):185-190. 10.4055/cios.2015.7.2.185.
Biplanar Open Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy in the Medial Compartment Osteoarthritis of the Knee Joint: Comparison between the Aescula and TomoFix Plate
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. hskyung@knu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2164543
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2015.7.2.185
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
The purpose of this study was to compare the results of Aescula and TomoFix plates used for biplanar open wedge high tibial osteotomy in medial osteoarthritis of the knee joint with varus deformity.
METHODS
A consecutive series of 50 cases of biplanar open wedge high tibial osteotomy were evaluated retrospectively. Group A contained 25 cases treated by using the Aescula plate, and group T contained 25 cases treated by using the TomoFix plate. Full weight-bearing was permitted at 6 weeks after surgery in group A and at 2 weeks in group T. Clinical evaluations were performed at the final follow-up by using postoperative knee scores and functional scores. Radiographic analysis included postoperative mechanical femur-tibia angle, change in posterior tibial slope angle, and complications related to implants. The mean follow-up periods were 30 months in group A and 26 months in group T.
RESULTS
The knee and functional scores were improved at the final follow-up in both groups (p < 0.05), but no differences were observed between the two groups (p > 0.05). An acceptable correction angle was obtained in 52% of group A and in 84% of group T (p = 0.015). Change in posterior tibial slope angle was larger in group A than in group T (p < 0.001), showing better maintenance of posterior tibial slope in group T. In group A, there were 3 cases of screw loosening and 4 cases of delayed union. In addition, there were residual varus deformities in 7 cases (6 in group A and 1 in group T).
CONCLUSIONS
This study shows that firm fixation using a TomoFix plate for open wedge high tibial osteotomy produces better radiologic results and a low complication rate than those of the Aescula spacer plate.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hofmann AA, Kane KR. Total knee arthroplasty after high tibial osteotomy. Orthopedics. 1994; 17(9):887–890.2. Keene JS, Dyreby JR Jr. High tibial osteotomy in the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee: the role of preoperative arthroscopy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1983; 65(1):36–42.3. Pape D, Kohn D, van Giffen N, Hoffmann A, Seil R, Lorbach O. Differences in fixation stability between spacer plate and plate fixator following high tibial osteotomy. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013; 21(1):82–89.4. Brinkman JM, Lobenhoffer P, Agneskirchner JD, Staubli AE, Wymenga AB, van Heerwaarden RJ. Osteotomies around the knee: patient selection, stability of fixation and bone healing in high tibial osteotomies. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008; 90(12):1548–1557.5. van den Bekerom MP, Patt TW, Kleinhout MY, van der Vis HM, Albers GH. Early complications after high tibial osteotomy: a comparison of two techniques. J Knee Surg. 2008; 21(1):68–74.6. Lobenhoffer P, Agneskirchner JD. Improvements in surgical technique of valgus high tibial osteotomy. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2003; 11(3):132–138.7. Schroter S, Gonser CE, Konstantinidis L, Helwig P, Albrecht D. High complication rate after biplanar open wedge high tibial osteotomy stabilized with a new spacer plate (Position HTO plate) without bone substitute. Arthroscopy. 2011; 27(5):644–652.8. Spahn G. Complications in high tibial (medial opening wedge) osteotomy. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2004; 124(10):649–653.9. Asada S, Akagi M, Mori S, Matsushita T, Hashimoto K, Hamanishi C. Increase in posterior tibial slope would result in correction loss in frontal plane after medial open-wedge high tibial osteotomy. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012; 20(3):571–578.10. Brinkman JM, Luites JW, Wymenga AB, van Heerwaarden RJ. Early full weight bearing is safe in open-wedge high tibial osteotomy. Acta Orthop. 2010; 81(2):193–198.11. Niemeyer P, Schmal H, Hauschild O, von Heyden J, Sudkamp NP, Kostler W. Open-wedge osteotomy using an internal plate fixator in patients with medial-compartment gonarthritis and varus malalignment: 3-year results with regard to preoperative arthroscopic and radiographic findings. Arthroscopy. 2010; 26(12):1607–1616.12. Takeuchi R, Ishikawa H, Aratake M, et al. Medial opening wedge high tibial osteotomy with early full weight bearing. Arthroscopy. 2009; 25(1):46–53.13. Fujisawa Y, Masuhara K, Shiomi S. The effect of high tibial osteotomy on osteoarthritis of the knee: an arthroscopic study of 54 knee joints. Orthop Clin North Am. 1979; 10(3):585–608.14. Noyes FR, Barber SD, Simon R. High tibial osteotomy and ligament reconstruction in varus angulated, anterior cruciate ligament-deficient knees: a two- to seven-year follow-up study. Am J Sports Med. 1993; 21(1):2–12.15. Hernigou P, Medevielle D, Debeyre J, Goutallier D. Proximal tibial osteotomy for osteoarthritis with varus deformity: a ten to thirteen-year follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1987; 69(3):332–354.16. Matsuda S, Miura H, Nagamine R, et al. Posterior tibial slope in the normal and varus knee. Am J Knee Surg. 1999; 12(3):165–168.17. Yoshioka Y, Siu DW, Scudamore RA, Cooke TD. Tibial anatomy and functional axes. J Orthop Res. 1989; 7(1):132–137.18. Staubli AE, Jacob HA. Evolution of open-wedge high-tibial osteotomy: experience with a special angular stable device for internal fixation without interposition material. Int Orthop. 2010; 34(2):167–172.19. Zaki SH, Rae PJ. High tibial valgus osteotomy using the Tomofix plate: medium-term results in young patients. Acta Orthop Belg. 2009; 75(3):360–367.20. Staubli AE, De Simoni C, Babst R, Lobenhoffer P. TomoFix: a new LCP-concept for open wedge osteotomy of the medial proximal tibia: early results in 92 cases. Injury. 2003; 34:Suppl 2. B55–B62.21. Dejour H, Walch G, Neyret P, Adeleine P. Dysplasia of the femoral trochlea. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 1990; 76(1):45–54.22. Giffin JR, Vogrin TM, Zantop T, Woo SL, Harner CD. Effects of increasing tibial slope on the biomechanics of the knee. Am J Sports Med. 2004; 32(2):376–382.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Results after Medial Opening Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy in Medial Compartment Osteoarthritis of the Knee: TomoFix(R) versus Aescula(R) Plates
- Open Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy with Aescula(R) Plate
- The Short-term Follow-up Results of Open Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy with Using an Aescula Open Wedge Plate and an Allogenic Bone Graft: The Minimum 1-Year Follow-up Results
- Severe Genu Recurvatum after a Closing-wedge High Tibial Osteotomy: A Case Report
- Opening Wedge High Tibia Osteotomy