Clin Orthop Surg.
2010 Mar;2(1):47-54. 10.4055/cios.2010.2.1.47.
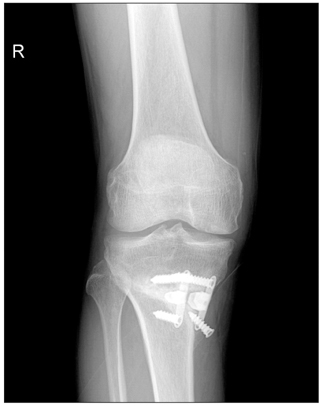
The Short-term Follow-up Results of Open Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy with Using an Aescula Open Wedge Plate and an Allogenic Bone Graft: The Minimum 1-Year Follow-up Results
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Mok-dong Himchan Hospital, Seoul, Korea. changcape@naver.com
- KMID: 1110349
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2010.2.1.47
Abstract
-
BACKGROUND: This study examined the results of open wedge high tibial osteotomy with using an Aescula open wedge plate and an allogenic bone graft as a surgical technique for the patients who suffer from osteoarthritis of the knee with a genu varum deformity.
METHODS
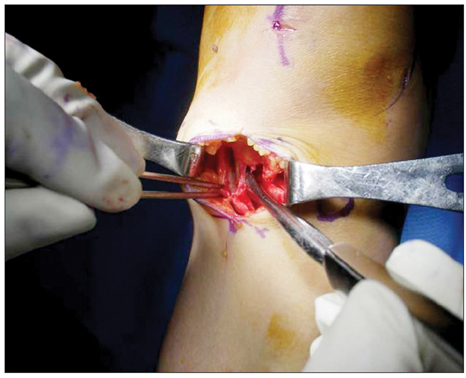
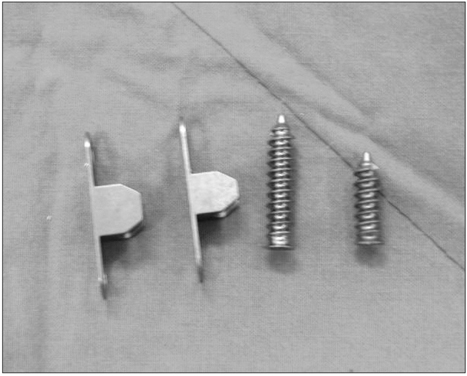
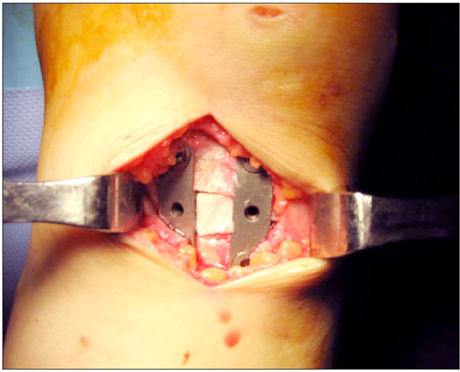
From March 2007 to August 2007, 33 patients (37 cases) with osteoarthritis of the knee and a genu varum deformity underwent a high tibial osteotomy with using an Aescula open wedge plate and an allogenic bone graft. The patients were followed up for more than 1 year. Before and after surgery, the correction angle of the genu varum was measured by the lower extremity scannogram and the posterior tibial slope, the joint space distance and the time to bone union were evaluated. The functional factors were evaluated using the Knee Society Score.
RESULTS
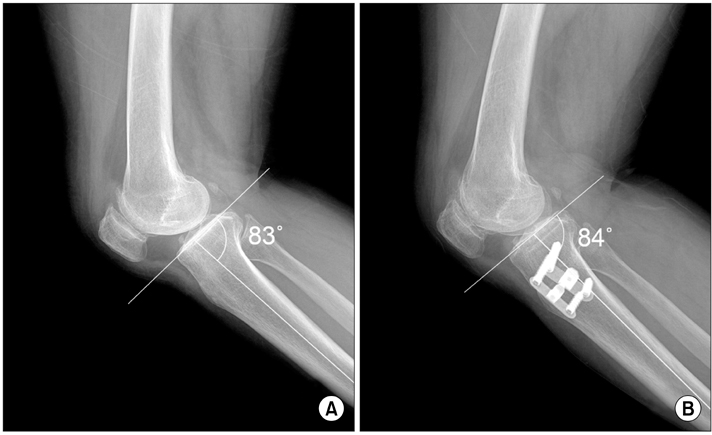
The average knee score and function score improved from 52.19 +/- 11.82 to 92.49 +/- 5.10 and 52.84 +/- 6.23 to 89.05 +/- 5.53, respectively (p < 0.001). According to the lower extremity scannogram, the mean preoperative varus angle was -1.86 +/- 2.76degrees, and the average correction angle at the last follow-up was 10.93 +/- 2.50degrees (p < 0.001). The tibial posterior slope before surgery and at the last follow-up were 8.20 +/- 1.80degrees and 8.04 +/- 1.30degrees, respectively (p = 0.437). The joint space distance increased from 4.05 +/- 1.30 mm to 4.83 +/- 1.33 mm (p < 0.001). The average time to complete bone union was 12.69 +/- 1.5 weeks.
CONCLUSIONS
An open wedge high tibial osteotomy using an Aescula open wedge plate and an allogeneic bone graft to treat osteoarthritis of the knee with a genu varum deformity showed good results for the precision of the correction angle, the time to bone union and the functional improvement.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Arthroscopy
*Bone Plates
*Bone Transplantation
Female
Humans
Joint Deformities, Acquired/diagnosis/etiology/radiography/*surgery
Knee Joint
Male
Middle Aged
Orthopedic Procedures/*methods
Osteoarthritis, Knee/complications/diagnosis/radiography/*surgery
Osteotomy/*methods
Tibia/radiography/*surgery
Transplantation, Homologous
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Pharmacologic treatment of osteoarthritis
Seung-Hoon Baek, Shin-Yoon Kim
J Korean Med Assoc. 2013;56(12):1123-1131. doi: 10.5124/jkma.2013.56.12.1123.
Reference
-
1. Coventry MB. Osteotomy about the knee for degenerative and rheumatoid arthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1973. 55(1):23–48.
Article2. Coventry MB. Upper tibial osteotomy for gonarthrosis: the evolution of the operation in the last 18 years and long term results. Orthop Clin North Am. 1979. 10(1):191–210.3. Dowd GS, Somayaji HS, Uthukuri M. High tibial osteotomy for medial compartment osteoarthritis. Knee. 2006. 13(2):87–92.
Article4. Dugdale TW, Noyes FR, Styer D. Preoperative planning for high tibial osteotomy: the effect of lateral tibiofemoral separation and tibiofemoral length. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1992. (274):248–264.5. Bauer GC, Insall J, Koshino T. Tibial osteotomy in gonarthrosis (osteo-arthritis of the knee). J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1969. 51(8):1545–1563.
Article6. Pape D, Rupp S. Preoperative planning for high tibial osteotomies. Oper Tech Orthop. 2007. 17(1):2–11.
Article7. Fujisawa Y, Masuhara K, Shiomi S. The effect of high tibial osteotomy on osteoarthritis of the knee: an arthroscopic study of 54 knee joints. Orthop Clin North Am. 1979. 10(3):585–608.8. Noyes FR, Goebel SX, West J. Opening wedge tibial osteotomy: the 3-triangle method to correct axial alignment and tibial slope. Am J Sports Med. 2005. 33(3):378–387.
Article9. Insall J, Salvati E. Patella position in the normal knee joint. Radiology. 1971. 101(1):101–104.
Article10. Kim SJ, Mahajan RH, Park KY, Kim TE, Lee DH, Choi WJ. Biplanar medial open wedge high tibial osteotomy for medial compartment osteoarthritis of the Knee: a novel technique and follow-up. Oper Tech Orthop. 2007. 17(1):29–37.
Article11. Flierl S, Sabo D, Hornig K, Perlick L. Open wedge high tibial osteotomy using fractioned drill osteotomy: a surgical modification that lowers the complication rate. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 1996. 4(3):149–153.
Article12. Noda T, Yasuda S, Nagano K, Takahara Y, Namba Y, Inoue H. Clinico-radiological study of total knee arthroplasty after high tibial osteotomy. J Orthop Sci. 2000. 5(1):25–36.
Article13. Amendola A, Panarella L. High tibial osteotomy for the treatment of unicompartmental arthritis of the knee. Orthop Clin North Am. 2005. 36(4):497–504.
Article14. Koshino T, Murase T, Saito T. Medial opening-wedge high tibial osteotomy with use of porous hydroxyapatite to treat medial compartment osteoarthritis of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003. 85(1):78–85.
Article15. Koshino T, Morii T, Wada J, Saito H, Ozawa N, Noyori K. High tibial osteotomy with fixation by a blade plate for medial compartment osteoarthritis of the knee. Orthop Clin North Am. 1989. 20(2):227–243.16. Aglietti P, Rinonapoli E, Stringa G, Taviani A. Tibial osteotomy for the varus osteoarthritic knee. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1983. (176):239–251.
Article17. Aoki Y, Yasuda K, Mikami S, Ohmoto H, Majima T, Minami A. Inverted V-shaped high tibial osteotomy compared with closing-wedge high tibial osteotomy for osteoarthritis of the knee: ten-year follow-up result. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006. 88(10):1336–1340.18. Coventry MB, Ilstrup DM, Wallrichs SL. Proximal tibial osteotomy: a critical long-term study of eighty-seven cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1993. 75(2):196–201.
Article19. Rudan JF, Simurda MA. High tibial osteotomy: a prospective clinical and roentgenographic review. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990. (255):251–256.20. Gunes T, Sen C, Erdem M. Tibial slope and high tibial osteotomy using the circular external fixator. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2007. 15(2):192–198.
Article21. Rodner CM, Adams DJ, Diaz-Doran V, et al. Medial opening wedge tibial osteotomy and the sagittal plane: the effect of increasing tibial slope on tibiofemoral contact pressure. Am J Sports Med. 2006. 34(9):1431–1441.
Article22. Hoell S, Suttmoeller J, Stoll V, Fuchs S, Gosheger G. The high tibial osteotomy, open versus closed wedge, a comparison of methods in 108 patients. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2005. 125(9):638–643.
Article23. Dejour H, Bonnin M. Tibial translation after anterior cruciate ligament rupture: two radiological tests compared. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1994. 76(5):745–749.
Article24. Insall JN, Joseph DM, Msika C. High tibial osteotomy for varus gonarthrosis: a long-term follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1984. 66(7):1040–1048.
Article25. Coventry MB, Bowman PW. Long-term results of upper tibial osteotomy for degenerative arthritis of the knee. Acta Orthop Belg. 1982. 48(1):139–156.26. Agneskirchner JD, Hurschler C, Wrann CD, Lobenhoffer P. The effects of valgus medial opening wedge high tibial osteotomy on articular cartilage pressure of the knee: a biomechanical study. Arthroscopy. 2007. 23(8):852–861.
Article27. Wright JM, Heavrin B, Begg M, Sakyrd G, Sterett W. Observations on patellar height following opening wedge proximal tibial osteotomy. Am J Knee Surg. 2001. 14(3):163–173.28. Noyes FR, Mayfield W, Barber-Westin SD, Albright JC, Heckmann TP. Opening wedge high tibial osteotomy: an operative technique and rehabilitation program to decrease complications and promote early union and function. Am J Sports Med. 2006. 34(8):1262–1273.29. Bae DK, Jeon IH, Park BJ, Yang HS. The relation between clinical results and correction angle in proximal tibial osteotomy. J Korean Knee Soc. 1999. 11(1):82–89.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Open Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy with Aescula(R) Plate
- Biplanar Open Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy in the Medial Compartment Osteoarthritis of the Knee Joint: Comparison between the Aescula and TomoFix Plate
- A Short Term Follow-up of Open Wedge High Tibial Osteotomyusing Locking Compression Plate(R)
- Severe Genu Recurvatum after a Closing-wedge High Tibial Osteotomy: A Case Report
- Open-Wedge and Closed-Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy: Current Concept and Long-Term Results