J Korean Med Sci.
2012 Apr;27(4):430-436. 10.3346/jkms.2012.27.4.430.
Interaction of Morphine and Selective Serotonin Receptor Inhibitors in Rats Experiencing Inflammatory Pain
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, CHA Medical Center, CHA University, Gumi, Korea.
- 2Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jongyeon_park@amc.seoul.kr
- KMID: 2157905
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2012.27.4.430
Abstract
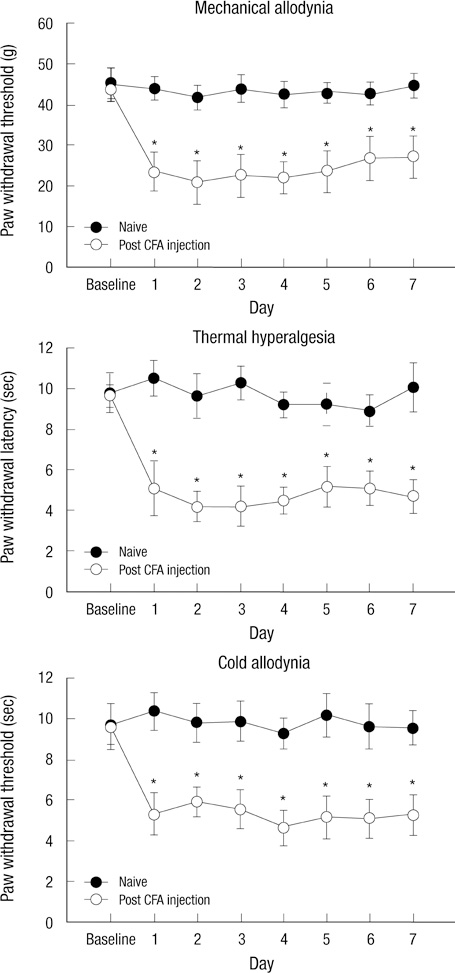
- Citalopram and paroxetine are selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and also have antinociceptive effects. We investigated the antiallodynic and antihyperalgesic effects of intrathecally administered morphine, citalopram, paroxetine, and combinations thereof, in a rat model in which peripheral inflammation was induced by complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA). Drugs were intrathecally administered via direct lumbar puncture. Mechanical allodynia was measured using a Dynamic Plantar Aesthesiometer. Thermal hyperalgesia and cold allodynia were determined by measuring latency of paw withdrawal in response to radiant heat and cold water. Behavioral tests were run before and 15, 30, 45, and 60 min after intrathecal injection. Intraplantar injection of CFA produced mechanical allodynia, thermal hyperalgesia, and cold allodynia. Intrathecally administered morphine (0.3 or 1 microg) had antiallodynic or antihyperalgesic effects (24.0%-71.9% elevation). The effects of morphine were significantly increased when a combination of citalopram (100 microg) and paroxetine (100 microg) was added (35.2%-95.1% elevation). This rise was reversed by naloxone and methysergide. The effects of citalopram and paroxetine were also reversed by naloxone and methysergide. We suggest that the mu opioid receptor and serotonin receptors play major roles in production of the antiallodynic and antihyperalgesic effects of morphine, citalopram, paroxetine, and combinations thereof, in animals experiencing inflammatory pain.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Analgesics, Opioid/administration & dosage/*pharmacology
Animals
Behavior, Animal/drug effects
Citalopram/administration & dosage/pharmacology
Disease Models, Animal
Hyperalgesia/etiology
Inflammation/*chemically induced/pathology
Injections, Spinal
Male
Morphine/administration & dosage/*pharmacology
Pain/*prevention & control
Pain Measurement
Pain Threshold/drug effects
Paroxetine/administration & dosage/pharmacology
Rats
Rats, Sprague-Dawley
Receptors, Serotonin/*chemistry/metabolism
Serotonin Uptake Inhibitors/administration & dosage/*pharmacology
Temperature
Time Factors
Figure
Reference
-
1. Wang GK, Mitchell J, Wang SY. Block of persistent late Na+ currents by antidepressant sertraline and paroxetine. J Membr Biol. 2008. 222:79–90.2. Coquoz D, Porchet C, Dayer P. Central analgesic effects of desipramine, fluvoxamine, and moclobemide after single oral dosing: a study in healthy volunteers. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1993. 54:339–344.3. Korzeniewska-Rybicka I, Płaźnik A. Analgesic effect of antidepressant drugs. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1998. 59:331–338.4. Finley PR. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors: pharmacologic profiles and potential therapeutic distinctions. Ann Pharmacother. 1994. 28:1359–1369.5. Cookson J. Side-effects of antidepressants. Br J Psychiatry Suppl. 1993. 20–24.6. Richelson E, Pfenning M. Blockade by antidepressants and related compounds of biogenic amine uptake into rat brain synaptosomes: most antidepressants selectively block norepinephrine uptake. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984. 104:277–286.7. Martin WJ, Gupta NK, Loo CM, Rohde DS, Basbaum AI. Differential effects of neurotoxic destruction of descending noradrenergic pathways on acute and persistent nociceptive processing. Pain. 1999. 80:57–65.8. Millan MJ. Descending control of pain. Prog Neurobiol. 2002. 66:355–474.9. Yoshimura M, Furue H. Mechanisms for the anti-nociceptive actions of the descending noradrenergic and serotonergic systems in the spinal cord. J Pharmacol Sci. 2006. 101:107–117.10. Beaudry H, Proteau-Gagné A, Li S, Dory Y, Chavkin C, Gendron L. Differential noxious and motor tolerance of chronic delta opioid receptor agonists in rodents. Neuroscience. 2009. 161:381–391.11. Kwon MY, Jun IG, Kim TH, Park JY. The interaction of morphine and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors on mechanical allodynia in rats with a spinal nerve ligation. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2008. 55:87–94.12. Xu JJ, Walla BC, Diaz MF, Fuller GN, Gutstein HB. Intermittent lumbar puncture in rats: a novel method for the experimental study of opioid tolerance. Anesth Analg. 2006. 103:714–720.13. Hargreaves K, Dubner R, Brown F, Flores C, Joris J. A new and sensitive method for measuring thermal nociception in cutaneous hyperalgesia. Pain. 1988. 32:77–88.14. Lynch JJ III, Wade CL, Zhong CM, Mikusa JP, Honore P. Attenuation of mechanical allodynia by clinically utilized drugs in a rat chemotherapy-induced neuropathic pain model. Pain. 2004. 110:56–63.15. Otsuka N, Kiuchi Y, Yokogawa F, Masuda Y, Oguchi K, Hosoyamada A. Antinociceptive efficacy of antidepressants: assessment of five antidepressants and four monoamine receptors in rats. J Anesth. 2001. 15:154–158.16. Pettersen VL, Zapata-Sudo G, Raimundo JM, Trachez MM, Sudo RT. The synergistic interaction between morphine and maprotiline after intrathecal injection in rats. Anesth Analg. 2009. 109:1312–1317.17. Max MB, Lynch SA, Muir J, Shoaf SE, Smoller B, Dubner R. Effects of desipramine, amitriptyline, and fluoxetine on pain in diabetic neuropathy. N Engl J Med. 1992. 326:1250–1256.18. Jackson KC 2nd. Pharmacotherapy for neuropathic pain. Pain Pract. 2006. 6:27–33.19. Bourin M, Chue P, Guillon Y. Paroxetine: a review. CNS Drug Rev. 2001. 7:25–47.20. Richelson E. Pharmacology of antidepressants. Mayo Clin Proc. 2001. 76:511–527.21. Jung AC, Staiger T, Sullivan M. The efficacy of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors for the management of chronic pain. J Gen Intern Med. 1997. 12:384–389.22. Obata H, Saito S, Koizuka S, Nishikawa K, Goto F. The monoamine-mediated antiallodynic effects of intrathecally administered milnacipran, a serotonin noradrenaline reuptake inhibitor, in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Anesth Analg. 2005. 100:1406–1410.23. Nagata K, Imai T, Yamashita T, Tsuda M, Tozaki-Saitoh H, Inoue K. Antidepressants inhibit P2X4 receptor function: a possible involvement in neuropathic pain relief. Mol Pain. 2009. 5:20.24. Sindrup SH, Gram LF, Brøsen K, Eshøj O, Mogensen EF. The selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor paroxetine is effective in the treatment of diabetic neuropathy symptoms. Pain. 1990. 42:135–144.25. Ikeda T, Ishida Y, Naono R, Takeda R, Abe H, Nakamura T, Nishimori T. Effects of intrathecal administration of newer antidepressants on mechanical allodynia in rat models of neuropathic pain. Neurosci Res. 2009. 63:42–46.26. Gray AM, Spencer PS, Sewell RD. The involvement of the opioidergic system in the antinociceptive mechanism of action of antidepressant compounds. Br J Pharmacol. 1998. 124:669–674.27. Sawynok J, Liu XJ. Adenosine in the spinal cord and periphery: release and regulation of pain. Prog Neurobiol. 2003. 69:313–340.28. Lavand'homme PM, Eisenach JC. Exogenous and endogenous adenosine enhance the spinal antiallodynic effects of morphine in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Pain. 1999. 80:31–36.29. Hwang JH, Hwang GS, Cho SK, Han SM. Morphine can enhance the antiallodynic effect of intrathecal R-PIA in rats with nerve ligation injury. Anesth Analg. 2005. 100:461–468.30. Ossipov MH, Lai J, Malan TP Jr, Porreca F. Spinal and supraspinal mechanisms of neuropathic pain. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000. 909:12–24.31. King T, Rao S, Vanderah T, Chen Q, Vardanyan A, Porreca F. Differential blockade of nerve injury-induced shift in weight bearing and thermal and tactile hypersensitivity by milnacipran. J Pain. 2006. 7:513–520.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The interaction of morphine and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors on mechanical allodynia in rats with a spinal nerve ligation
- Change of Serotonin Concentraions in Rat Medial Preoptic Area of Hypothalmus by Clomipramine and Various Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors
- Assessment for the Role of Serotonin Receptor Subtype 3 for the Analgesic Action of Morphine at the Spinal Level
- Probable tramadol-induced atypical serotonin syndrome in a patient receiving selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor and stopped at 10 days before surgery: A case report
- Improvement of Post Stroke Echolalia after Using Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors