Dement Neurocogn Disord.
2019 Mar;18(1):30-32. 10.12779/dnd.2019.18.1.30.
Improvement of Post Stroke Echolalia after Using Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Veterans Health Service Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. astro76@naver.com
- KMID: 2444265
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12779/dnd.2019.18.1.30
Abstract
- No abstract available.
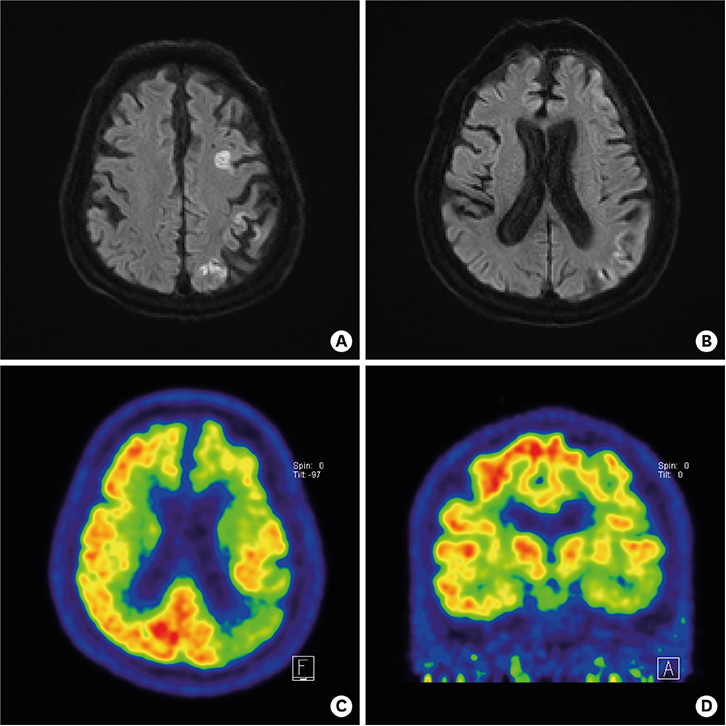
Figure
Reference
-
1. Geschwind N, Quadfasel FA, Segarra JM. Isolation of speech area. Neuropsychologia. 1968; 6:327–340.2. Choi-Kwon S, Han SW, Kwon SU, Kang DW, Choi JM, Kim JS. Fluoxetine treatment in poststroke depression, emotional incontinence, and anger proneness: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Stroke. 2006; 37:156–161.
Article3. Berthier ML, Torres-Prioris MJ, López-Barroso D. Thinking on treating echolalia in aphasia: recommendations and caveats for future research directions. Front Hum Neurosci. 2017; 11:164.
Article4. Berthier ML. Echophenomena, Automatic Speech and Prosody, in Transcortical Aphasias. East Sussex: Psychology Press;1999. p. 151–186.5. Hickok G. The role of mirror neurons in speech and language processing. Brain Lang. 2010; 112:1–2.
Article6. Posey DJ, Stigler KA, Erickson CA, McDougle CJ. Antipsychotics in the treatment of autism. J Clin Invest. 2008; 118:6–14.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Change of Serotonin Concentraions in Rat Medial Preoptic Area of Hypothalmus by Clomipramine and Various Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors
- Serotonin reuptake inhibitors and bone health: A review of clinical studies and plausible mechanisms
- Probable tramadol-induced atypical serotonin syndrome in a patient receiving selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor and stopped at 10 days before surgery: A case report
- Augmentation Strategies in Obsessive Compulsive Disorder
- Apathy syndrome in a patient previously treated with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors for depression