J Korean Med Sci.
2006 Feb;21(1):100-106. 10.3346/jkms.2006.21.1.100.
Evidence for Cyclooxygenase-2 Association with Caveolin-3 in Primary Cultured Rat Chondrocytes
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology, College of Medicine, Inha University, Incheon, Korea. shcha@inha.ac.kr
- 2Department of Biological Engineering, College of Medicine, Inha University, Incheon, Korea.
- 3National Creative Research Initiative, Center for Secretory Granule Research, College of Medicine, Inha University, Incheon, Korea.
- 4Department of Laboratory Animal, Medical Research Center, College of Medicine, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Laboratory of Molecular Neuroscience, Department of Life Science, POSTECH, Pohang, Korea.
- KMID: 2157791
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2006.21.1.100
Abstract
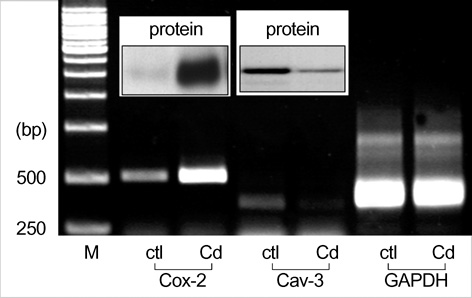
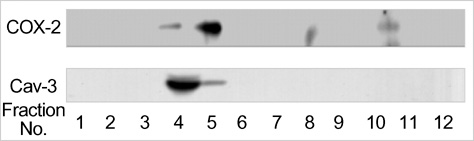
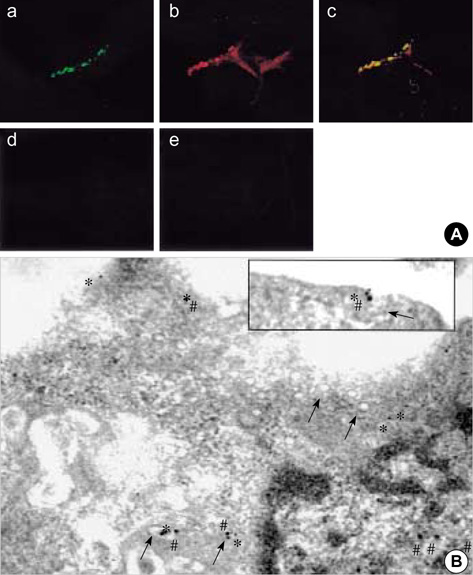
- The purpose of this study was to demonstrate the cellular localization of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and caveolin-3 (Cav-3) in primarily cultured rat chondrocytes. In normal rat chondrocytes, we observed relatively high levels of Cav-3 and a very low level of COX-2 mRNA and protein. Upon treating the chondrocytes with 5 microM of CdCl2 (Cd) for 6 hr, the expressions of COX-2 mRNA and protein were increased with the decreased Cav-3 mRNA and protein expressions. The detergent insoluble caveolae-rich membranous fractions that were isolated from the rat chondrocytes and treated with Cd contained the both proteins of both COX-2 and Cav-3 in a same fraction. The immuno-precipitation experiments showed complex formation between the COX-2 and Cav-3 in the rat chondrocytes. Purified COX-2 with glutathione S-transferase-fused COX-2 also showed complex formation with Cav-3. Confocal and electron microscopy also demonstrated the co-localization of COX-2 and Cav-3 in the plasma membrane. The results from our current study show that COX-2 and Cav-3 are co-localized in the caveolae of the plasma membrane, and they form a protein-protein complex. The co-localization of COX-2 with Cav-3 in the caveolae suggests that the caveolins might play an important role for regulating the function of COX-2.
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Animals, Newborn
Blotting, Western
Cadmium Chloride/pharmacology
Caveolae/drug effects/metabolism/ultrastructure
Caveolin 3/*genetics/metabolism
Cell Membrane/drug effects/metabolism
Cells, Cultured
Chondrocytes/cytology/drug effects/*metabolism
Cyclooxygenase 2/*genetics/metabolism
Gene Expression
Immunoprecipitation
Microscopy, Confocal
Microscopy, Electron
RNA, Messenger/genetics/metabolism
Rats
Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction
Figure
Reference
-
1. Nasrallah R, Hebert RL. Prostacyclin signaling in the kidney: implications for health and disease. Am J Physiol. 2005. 289:235–246.
Article2. Smith WL, Garavito RM, DeWitt DL. Prostaglandin endoperoxide H synthases (cyclooxygenase)-1 and -2. J Biol Chem. 1996. 271:33157–33160.3. Rodrigues S, Bruyneel E, Rodrigue CM, Shahin E, Gespach C. Cyclooxygenase 2 and carcinogenesis. Bull Cancer. 2004. 91:S61–S76.4. Park MK, Hwang SY, Kim JO, Kwack MH, Kim JC, Kim MK, Sung YK. NS398 inhibits the growth of Hep3B human hepatocellular carcinoma cells via caspase-independent apoptosis. Mol Cells. 2004. 17:45–50.5. O'Neill GP, Ford-Hutchinson AW. Expression of mRNA for cyclooxygenase-2 and cyclooxygenase-2 in human tissues. FEBS Lett. 1993. 330:156–160.6. Wu KK. Cyclooxygenase 2 induction: molecular mechanism and pathophysiologic roles. J Lab Clin Med. 1996. 128:242–245.
Article7. Williams TM, Lisanti MP. The caveolin genes: from cell biology to medicine. Ann Med. 2004. 36:584–595.
Article8. Liu P, Rudick M, Anderson RG. Multiple functions of caveolin-1. J Biol Chem. 2002. 277:41295–41298.
Article9. Liou JY, Deng WG, Gilroy DW, Shyue SK, Wu KK. Colocalization and interaction of cyclooxygenase-2 with caveolin-1 in human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 2001. 276:34975–34982.
Article10. Cha SH, Jung NH, Kim BR, Kim HW, Kwak JO. Evidence for cyclooxygenase-1 association with caveolin-1 and -2 in cultured human embryonic kidney (HEK 293) cells. IUBMB Life. 2004. 56:221–227.11. Ikezu T, Ueda H, Trapp BD, Nishiyama K, Sha JF, Volonte D, Galbiati F, Byrd AL, Bassell G, Serizawa H, Lane WS, Lisanti MP, Okamoto T. Affinity-purification and characterization of caveolins from the brain: differential expression of caveolin-1, -2, and -3 in brain endothelial and astroglial cell types. Brain Res. 1998. 804:177–192.
Article12. Schwab W, Galbiati F, Volonte D, Hempel U, Wenzel KW, Funk RH, Lisanti MP, Kasper M. Characterisation of caveolins from cartilage: expression of caveolin-1, -2 and -3 in chondrocytes and in alginate cell culture of the rat tibia. Histochem Cell Biol. 1999. 112:41–49.
Article13. Kiepe D, Andress DL, Mohan S, Standker L, Ulinski T, Himmele R, Mehls O, Tonshoff B. Intact IGF-binding protein-4 and -5 and their respective fragments isolated from chronic renal failure serum differentially modulate IGF-1 actions in cultured growth plate chondrocytes. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2001. 12:2400–2410.14. Ferretti A, Knijn A, Raggi C, Sargiacomo M. High-resolution proton NMR measures mobile lipids associated with triton-resistant membrane domains in haematopoietic K562 cells lacking or expression caveolin-1. Eur Biophys J. 2003. 32:83–95.15. Spector DL, Fu XD, Maniatis T. Associations between distinct premRNA splicing components and the cell nucleus. EMBO J. 1991. 10:3467–3481.
Article16. Harris ED Jr. Rheumatoid arthritis. Pathophysiology and implications for therapy. N Engl J Med. 1990. 322:1277–1289.17. Hardy MM, Seibert K, Manning PT, Currie MG, Woerner BM, Edwards D, Koki A, Tripp CS. Cyclooxygenase 2-dependent prostaglandin E2 modulates cartilage proteoglycan degradation in human osteoarthritis explants. Arthritis Rheum. 2002. 46:1789–1803.
Article18. Blanco FJ, Guitian R, Moreno J, de Toro FJ, Galdo F. Effect of anti-inflammatory drugs on COX-1 and COX-2 activity in human articular chondrocytes. J Rheumatol. 1999. 26:1366–1373.19. Choi YA, Lee DJ, Lim HK, Jeong JH, Sonn JK, Kang SS, Baek SH. Interleukin-1β stimulates matrix metalloproteinase-2 expression via a prostaglandin E2-dependent mechanism in human chondrocytes. Exp Mol Med. 2004. 36:226–232.20. Gilroy DW, Colville-Nash PR, Willis D, Chivers J, Paul-Clark MJ, Willoughby DA. Inducible cyclooxygenase may have anti-inflammatory properties. Nat Med. 1999. 5:698–701.
Article21. Fahmi H, Pelletier JP, Martel-Pelletier J. PPARgamma ligands as modulators of inflammatory and catabolic responses in arthritis. An overview. J Rheumatol. 2002. 29:3–14.22. Sandell LJ, Adler P. Developmental patterns of cartilage. Front Biosci. 1999. 4:731–742.
Article23. DeLise AM, Fischer L, Tuan RS. Cellular interactions and signaling in cartilage development. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2000. 8:309–334.
Article24. Li XA, Everson WV, Smart EJ. Caveolae, lipid rafts, and vascular disease. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2005. 15:92–96.
Article25. Couet J, Li S, Okamoto T, Ikezu T, Lisanti MP. Identification of peptide and protein ligands for the caveolin-scaffolding domain. Implications for the interaction of caveolin with caveolae-associated proteins. J Biol Chem. 1997. 272:6525–6533.26. Parton RG. Caveolae and caveolins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1996. 8:542–548.
Article27. Okamoto T, Schlegel A, Scherer PE, Lisanti MP. Caveolins, a family of scaffolding proteins for organizing "preassembled signaling complexes" at the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1998. 273:5419–5422.
Article28. Scherer PE, Lewis RY, Volonte D, Engelman JA, Galbiati F, Couet J, Kohtz DS, Donselaar E, Perters P, Lisanti MP. Cell-type and tissue-specific expression of caveolin-2: Caveolins 1 and 2 co-localize and form a stable hetero-oligomeric complex in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1997. 272:29337–29346.29. Li S, Galbiati F, Volonte D, Sargiacomo M, Engelman JA, Das K, Scherer PE, Lisanti MP. Mutational analysis of caveolin-induced vesicle formation. Expression of caveolin-1 recruits caveolin-2 to caveolae membranes. FEBS Lett. 1998. 434:127–134.30. Song KS, Scherer PE, Tang Z, Okamoto T, Li S, Chafel M, Chu C, Kohtz DS, Lisanti MP. Expression of Caveolin-3 in Skeletal, Cardiac, and Smooth Muscle Cells. Caveolin-3 is a component of the sarcolemma and co-fractionates with dystrophin and dystrophin-associated glycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1996. 271:15160–15165.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ectopic Expression of Caveolin-1 Induces COX-2 Expression in Rabbit Articular Chondrocytes via MAP Kinase Pathway
- Src Kinase Regulates Nitric Oxide-induced Dedifferentiation and Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression in Articular Chondrocytes via p38 Kinase-dependent Pathway
- p38 Kinase Regulates Nitric Oxide-induced Dedifferentiation and Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression of Articular Chondrocytes
- Expression of Caveolin-3 in the Myelin Sheath of Peripheral Nerve
- Immunohistochemical study of caveolin-1 and -2 in the rat retina