Korean J Neurotrauma.
2013 Oct;9(2):36-40. 10.13004/kjnt.2013.9.2.36.
Post-Traumatic Ictogenesis and Epileptogenesis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Hallym University College of Medicine Kangdong Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym Institute of Epilepsy Research, Seoul, Korea. hksong@hallym.or.kr
- KMID: 2156097
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2013.9.2.36
Abstract
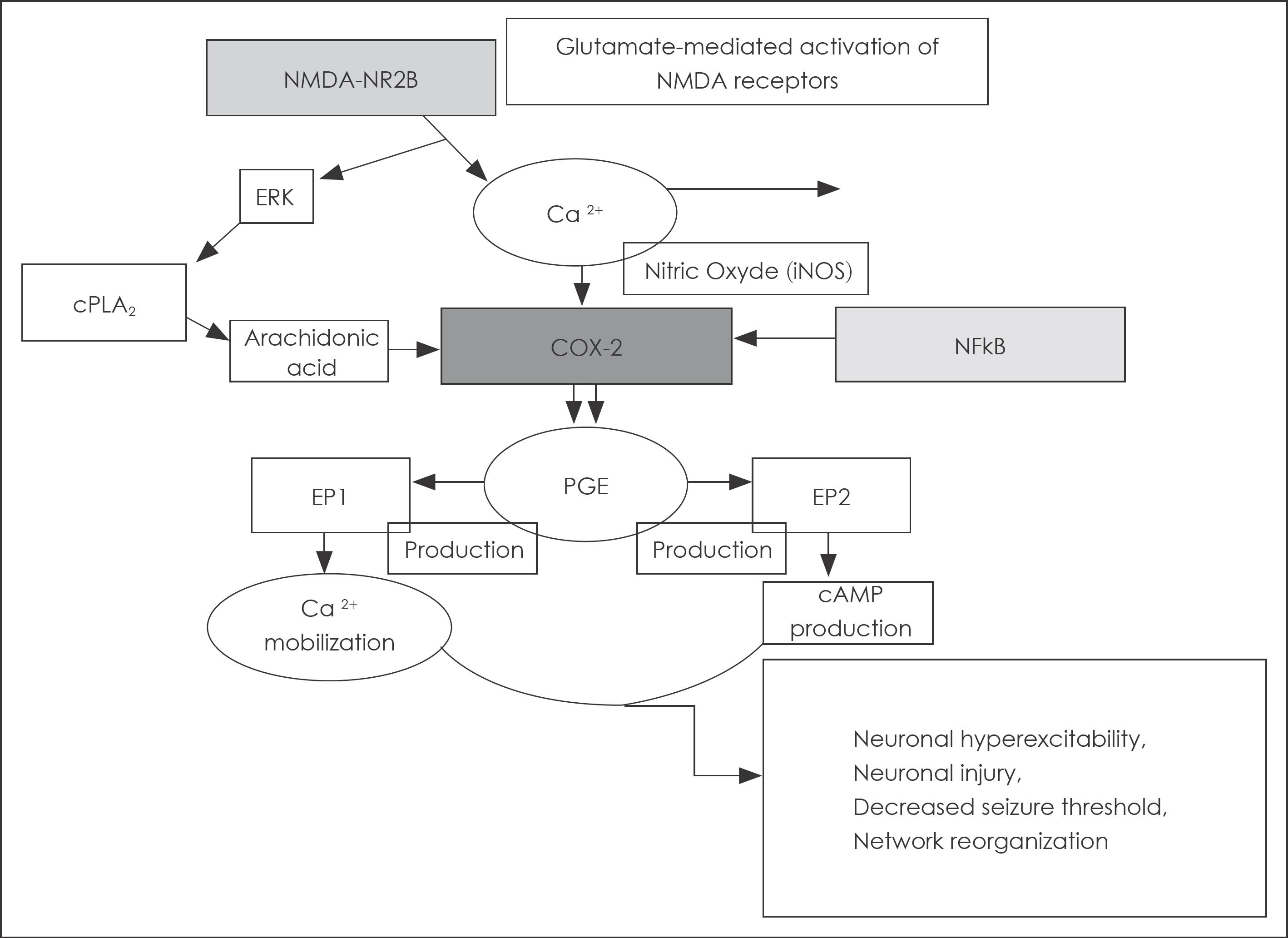
- For ictogenesis, initial step is intrinsic bursts of pacemaker neurons and, through exaggerated circuits or networks, the involved neurons become hyperexcitable state. Hypersynchrony of hyperexcitable neurons can induce paroxysmal depolarization shift for developing seizure. The mechanism underlying the development of post-traumatic epilepsy still remains to be elucidated. By traumatic brain injury, breakdown of blood-brain barrier (BBB) may lead network changes, long-lasting epileptiform activity and eventual neurodegeneration. Recently the concept of inflammation and epileptogenesis is widely accepted. In the surgically resected brain tissue from refractory partial epilepsy patients, there are hallmarks of a chronic inflammatory state and, also, via animal experiments, we can find the role of inflammation in the genesis of seizure and epilepsy. Inflammatory mediators (IL-1b, TGF-beta1 and COX-2) are associated with the epileptogenic brain. They can reduce seizure threshold, induce neurodegeneration, neurogenesis, and synaptic plasticity, and also disregulate BBB permeability. The increase in knowledge about a role of inflammation in epileptogenesis may support the use of specific anti-inflammatory drugs for developing disease-modifying treatments that can interfere epileptogenesis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Cacheaux LP, Ivens S, David Y, Lakhter AJ, Bar-Klein G, Shapira M, et al. Transcriptome profiling reveals TGF-beta signaling involvement in epileptogenesis. J Neurosci. 29:8927–8935. 2009.2. Ivens S, Kaufer D, Flores LP, Bechmann I, Zumsteg D, Tomkins O, et al. TGF-beta receptormediated albumin uptake into astrocytes is involved in neocortical epileptogenesis. Brain 130 (Pt 2): 535–547. 2007.3. Jones SW. Overview of voltage-dependent calcium channels. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 30:299–312. 1998.4. Kim JE, Choi HC, Song HK, Jo SM, Kim DS, Choi SY, et al. Levetiracetam inhibits interleukin-1 beta inflammatory responses in the hippocampus and piriform cortex of epileptic rats. Neurosci Lett. 471:94–99. 2010.5. Kim YI, Kwon OY, Kang TC. Cellular aspects of epileptogenesis in Korean Epilepsy Socieity (ed): Clinical epilepileptology, revised ed. Reston: E-public, pp29–41;2013.6. Malenka RC. Synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus: LTP and LTD. Cell. 78:535–538. 1994.
Article7. Santhakumar V, Aradi I, Soltesz I. Role of mossy fiber sprouting and mossy cell loss in hyperexcitability: a network model of the dentate gyrus incorporating cell types and axonal topography. J Neurophysiol. 93:437–453. 2005.
Article8. Schweitzer JS, Patrylo PR, Dudek FE. Prolonged field bursts in the dentate gyrus: dependence on low calcium, high potassium, and nonsynaptic mechanisms. J Neurophysiol. 68:2016–2025. 1992.
Article9. Tomkins O, Shelef I, Kaizerman I, Eliushin A, Afawi Z, Misk A, et al. Blood-brain barrier disruption in posttraumatic epilepsy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 79:774–777. 2008.
Article10. Vezzani A, Friedman A, Dingledine RJ. The role of inflammation in epileptogenesis. Neuropharmacology. 69:16–24. 2013.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Use of antiseizure medications after traumatic brain injury
- The Moderating Effect of Calling in the Relationship between Post-Traumatic Stress and Turnover Intention of Nurses Who Cared for COVID-19 Patients
- Post-Traumatic stress disorder
- Post-Traumatic Cerebral Infarction
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder, Depression and Anxiety among North Korean Refugees: A Meta-Analysis